NCERT Summary: Peninsular Plateau | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Peninsular Plateau of India
- The Peninsular Plateau of India, also termed the Indian Peninsular Plateau, denotes the expansive flat tableland situated in the southern region of India, enclosed by oceans on three sides. This plateau represents one of India's five physiographic divisions, recognized for being the oldest landmass in the country and also for being the most extensive physiographic division.
- It is characterized by its geographical features, including a flat table-like terrain and being bounded by water bodies on three sides, contributing to its unique topography and defining its boundaries.
- The Peninsular Plateau stands out as a prominent landform in the Indian subcontinent, showcasing a rich diversity of landscapes, flora, and fauna. This region plays a crucial role in shaping India's physical geography and influencing climatic patterns.
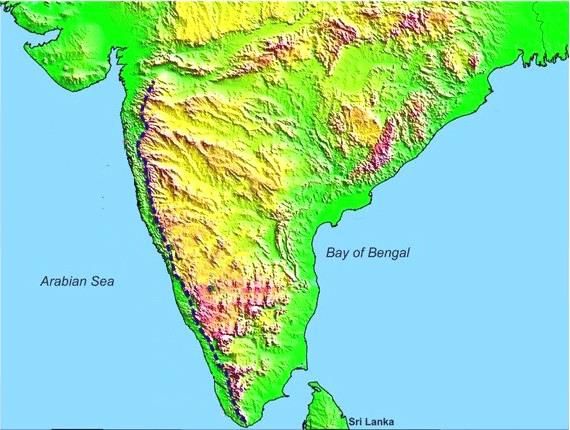
- Shape: The Peninsular Plateau of India has a roughly triangular shape. Its wide base rests at the southern boundary of the Indo-Gangetic Plains and gradually narrows down towards Kanyakumari.
- Extent: The northern boundary of the plateau follows an irregular line from Kutch along the western side of the Aravalis, extending towards regions near Delhi. This boundary then runs approximately parallel to the Yamuna and the Ganga rivers up to the Rajmahal Hills and the Ganga Delta.
- Boundaries: The plateau is encircled by mountain ranges on all three sides. To the north, it is bordered by the Aravali Range, the Vindhya Range, the Satpura Range, the Bharmer Range, and the Rajmahal Hills. In the west, it is flanked by the Western Ghats, while the Eastern Ghats form its eastern boundary.
- Area: Covering an extensive area of 16 lakh sq. km, the Peninsular Plateau constitutes the largest physiographic unit in India, occupying nearly half of the country's landmass.
- Composition: Comprising ancient tabular blocks of schists and Archaean genesis, this plateau is considered a stable shield that has undergone minimal structural changes since its formation.
- Slope: The Peninsular block predominantly slopes from west to east, influencing the directional flow of major rivers towards the Bay of Bengal, with exceptions like the Narmada and Tapi rivers.
- Elevation: The average elevation of the Peninsular Plateau of India ranges between 600 to 900 meters above mean sea level
Geomorphology of Peninsular Plateau of India
- The Peninsular Plateau of India comprises various smaller plateaus, hill ranges, river basins, and valleys.
- To understand the geomorphology of Peninsular India, one must delve into the major plateaus and hill ranges in the region.
Major Plateaus of Peninsular India
- The Indian Peninsular Plateau is characterized by multiple smaller plateaus.
- Some of the noteworthy smaller plateaus in Peninsular India include:
- The Marwar Upland
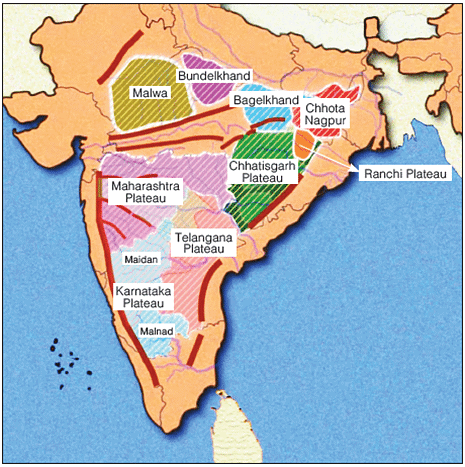
The Marwar Upland
- The Marwar Upland is a significant plateau in Peninsular India.
- It is known for its unique geographical features and plays a crucial role in the region's topography.
- This upland serves as a watershed area for several rivers, influencing the hydrology of the region.
- The Marwar Upland's elevation and terrain contribute to its distinct climate patterns, affecting local flora and fauna distribution.
In this region to the east of the Aravali Range lies the Upland of Eastern Rajasthan, characterized by an average elevation of 250-500 meters sloping eastwards. The region's composition consists of Sandstone, Shales, and Limestones from the Vindhyan period. River Banas, originating from the Vindhyan Range, is a prominent river flowing through this area. The topography showcases a rolling plateau with rounded hills and forests, sculpted by the erosional activity of River Banas and its tributaries.
The Central Highlands (Madhya Bharat Pathar)
- Location: Situated east of the Marwar Upland, the Central Highlands predominantly lie within the Chambal River Basin.
- Composition: Comprising ancient rock formations interspersed with sandstone hills, this region forms a part of India's Peninsular Plateau.
- Rivers: The Chambal River meanders through a rift valley in this area, adding to the geographical diversity.
- Topography: Characterized by expansive rolling plateaus, the Central Highlands also feature distinct landforms like the intricate Ravines or Badlands of the Chambal River.
The Bundelkhand Upland
- Location: The Bundelkhand Upland is geographically situated with the Yamuna River to the north, Madhya Bharat Pathar to the west, Vindhyan Scarplands to the east and southeast, and Malwa Plateau to the south.
- Spread: This upland region extends across the border of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, encompassing the surrounding areas in both states.
- Elevation & Slope: The average elevation of the Bundelkhand Upland ranges from 300 to 600 meters above sea level, sloping downward from the Vindhyan Scarp towards the Yamuna River.
- Composition: The Bundelkhand Upland is primarily composed of ancient 'Bundelkhand Gneiss', which consists of Granite and Gneiss rock formations.
- Rivers: Significant rivers flowing through this area include the Betwa, Dhasan, and Ken rivers.
- Topography: The topography of the Bundelkhand Upland is characterized by senile features, resulting from extensive erosion by the region's rivers. This has led to an undulating landscape unsuitable for cultivation. Moreover, the area is distinguished by a series of hillocks comprising Granite and Sandstone formations.
The Malwa Plateau
- Location: It is a triangular-shapedplateau.
- Its base lies on the Vindhyan Hills in the north and is bounded by the Aravali Range in the west and Bundelkhand in the east.
- The plateau constitutes an extension of the Deccan Traps.
- Elevation: The general height of the plateau is 600 m in the south which steeps down to 500 m in the north.
- Composition: It has been formed by basaltic lava flow, and hence is covered with black soils.
- Rivers: It is drained by two drainage systems:
- The first one, flowing towards the Arabian Sea includes – The Narmada, the Tapi, and the Mahi.
- The other one, flowing towards the Bay of Bengal includes – Chambal, Sindh, Betwa, and Ken.
- Topography: The region of the Peninsular Plateau of India comprises rolling surfaces with flat-topped hillsdissected by rivers.
- The plateau is marked by the Chambal ravines in the north.
The Baghelkhand
- Location: Situated east of the Maikal Range, it borders the Son River to the north. The area consists of anticlinal highlands and synclinal valleys made up of sandstones and limestones in the southern part.
- Elevation: The general elevation of the region ranges from 150 meters to 1200 meters.
- Composition: The western part comprises limestone and sandstones, while the eastern part is primarily composed of granite.
- Rivers: Serving as a water divide, the central part of the plateau separates the drainage systems of the Son River to the north and the Mahanadi River to the south.
- Topography: The Peninsular Plateau of India exhibits uneven relief, featuring Vindhyan sandstone scarps positioned between the Ganga Plain and the Narmada-Son Trough. The general horizontality of the region indicates minimal geological disturbances over time.
The Chotanagpur Plateau
- The Chotanagpur Plateau is a region characterized by its unique geological features.
- It is an area known for its mineral-rich resources and diverse topography.
- The plateau has played a crucial role in the industrial development of India.
- It is home to important cities like Ranchi and Jamshedpur, known for their industrial significance.
The Meghalaya Plateau
- The Meghalaya Plateau is geographically located between the Brahmaputra Valley in the north and the Surma and Meghna Valleys in the south.
Formation of the Plateau
- The plateau has a rectangular shape and was formed by the extension of the Peninsular Plateau of India towards the northeast, beyond the Rajmahal hills.
- During the Himalayan orogeny, a significant fault called the Malda Gap or Garo-Rajmahal Gap was created due to the north-eastward movement of the Indo-Australian Plate. This gap separated the Meghalaya Plateau from the Indian Peninsula, which was later filled by sedimentation from nearby rivers.
Composition of the Plateau
- The plateau predominantly consists of Archaean or Dharwarian quartzites, shales, and schists.
Topography
- The Meghalaya Plateau exhibits a diverse topography, featuring rolling grasslands, hills, and river valleys.
Major Geographical Features
- The region is characterized by several prominent geographical elements, including the Garo Hills.
The Deccan Plateau
- Location: The Deccan Plateau is a triangular-shaped plateau bordered by the Satpura and Vindhya ranges in the northwest, the Mahadev and Maikal ranges in the north, the Western Ghats in the west, and the Eastern Ghats in the east.
- Area: Covering about 5 lakh sq. km, the Deccan Plateau constitutes the largest unit of the Indian Peninsular Plateau.
- Elevation & Slope: The Deccan Plateau has an average elevation of 600 meters. It slopes from west to east, as seen from the flow of major rivers like the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Cauvery.
- Sub Plateaus: The Deccan Plateau is composed of various smaller plateaus, formed through the erosion of rivers, including the Maharashtra Plateau.
The Maharashtra Plateau
- The Maharashtra Plateau is situated in Maharashtra and comprises the northern part of the Deccan Plateau.
- The terrain of this plateau appears as a rolling plain due to extensive weathering activities.
- Presence of horizontal lava sheets has given rise to the unique Deccan Trap topography in this region.
- The entire area of this section of the Peninsular Plateau of India is characterized by black cotton soil, also referred to as Regur.
The Karnataka Plateau (Mysore Plateau)
- The Karnataka Plateau is located to the south of the Maharashtra Plateau, forming the southern part of the Deccan Plateau.
- Key rivers such as the Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri (Cauvery), Tungabhadra, Sharavati, and Bhima drain this region.
- The topography of the area resembles a rolling country landscape.
- Rivers originating from the Western Ghats divide this plateau into two distinct regions:
Malnad
- Malnad is a term used to describe hilly regions in the Kannada language.
- It comprises deep valleys adorned with dense forests, creating a picturesque landscape.
Maida
- Maida refers to a sprawling plain dotted with low granite hills.
Telangana Plateau
- The Telangana Plateau encompasses the geographical area of Telangana.
- It is drained by three primary river systems: the Godavari, the Krishna, and the Penneru.
- This region of the Peninsular Plateau of India is characterized by the presence of two main physiographic divisions, namely the Ghats and the Peneplains.
The Chhattisgarh Plain
- The Chhattisgarh Plain is a distinctive geographical feature.
- Geographical Features of Mahanadi Basin:
- Saucer-shaped Depression: The basin is shaped like a saucer and is drained by the upper stretch of the River Mahanadi.
- Location: Situated between the Hills of Odisha and the Maikala Range.
- Geological Composition: The basin consists of nearly horizontal beds of limestone and shales.
- Major Hill Ranges of Peninsular India:
- The Aravali Range:
- Location: The range runs northeast-to-southwest between Delhi and Palanpur in Gujarat, with its northeastern end marked by the Delhi Ridge.
- Formation: The Aravali Range is a remnant of one of the oldest fold mountains globally.
- Elevation: Typically ranges between 400 to 600 meters.
- Prominent Peaks: Includes Mount Abu (1158 m) and Guru Shikhar (1722 m), the highest peak of the Aravalis.
- The Aravali Range:
Aravali Range
- Its northeastern end is indicated by the Delhi Ridge.
- Origin: The Aravalis represent the remains of one of the most ancient folded mountain ranges globally.
- Elevation: Typically, this mountain range maintains a moderate elevation ranging from 400 to 600 meters.
- Prominent Peaks: Notable peaks include Mount Abu (1158 m) and Guru Shikhar (1722 m, the highest summit in the Aravalis).
The Vindhyan Range
- Location: It lies to the south of the Malwa Plateau and runs parallel to the Narmada Valleyin the east-west direction
- It stretches for a distance of over 1200 km from Jobat in Gujarat to Sasaram in Bihar.
- This range, lying in the region of the Peninsular Plateau of India, forms the northern border of the Deccan and serves as the watershed between the Ganga and South Indian River systems.
- Formation: They are considered a Block Mountain as they have been formed through cracks in the Earth’s crust.
- Elevation: The general elevation of this range is 300-650 m.
- Composition: It comprises horizontally bedded ancient sedimentary rocks with its western part covered with lava.
- Rivers: The area is drained by several rivers, including the Betwa, Ken, and Chambal.
- Ranges: These mountains continue eastward into two branches:
The Kaimur Range
- It is the northern branch that runs north of the Son River upto western Bihar.
The Bharner Hills
- It is the southern branch, running between the upper reaches of the Son and Narmada rivers to meet the Satpura Range.
The Satpura Range
- About: It is a series of seven Block Mountains, thus justifying its name Satpura
- In Sanskrit, ‘Sat’ means seven, and ‘Pura’ means mountains).
- Location: It lies in the region of the Peninsular Plateau of India and is located to the south of the Vindhyan Range and stretches in an east-west direction between the Narmada and the Tapi.
- It starts from the Rajpipla Hills in the west and continues for a distance of around 900 km through the Mahadev Hills to the Maikala Range.
- Rivers: The Satpura Range is drained by many rivers, including the Narmada, Wainganga, Wardha and Tapi.
- Important Peaks: Dhupgarh (1350 m) near Pachmarhi on Mahadev hills is the highest peak.
- The other peaks are Astamba Dongar (1325 m) and Amarkantak (1127 m).
Western Ghats
- Location: The Western Ghats are situated to the south of the Malwa Plateau and run parallel to the Narmada Valley in an east-west direction. Spanning over 1200 km from Jobat in Gujarat to Sasaram in Bihar, this range forms the northern boundary of the Deccan Plateau and acts as the watershed between the Ganga and South Indian river systems.
- Formation: These mountains are classified as Block Mountains, originating from fractures in the Earth's crust.
- Elevation: Generally, the elevation of the Western Ghats ranges from 300 to 650 meters above sea level.
- Composition: Comprised of horizontally layered ancient sedimentary rocks, with the western section covered by lava deposits.
- Rivers: The region is drained by various rivers such as the Betwa, Ken, and Chambal.
- Ranges: The Western Ghats extend eastward into two distinct branches.
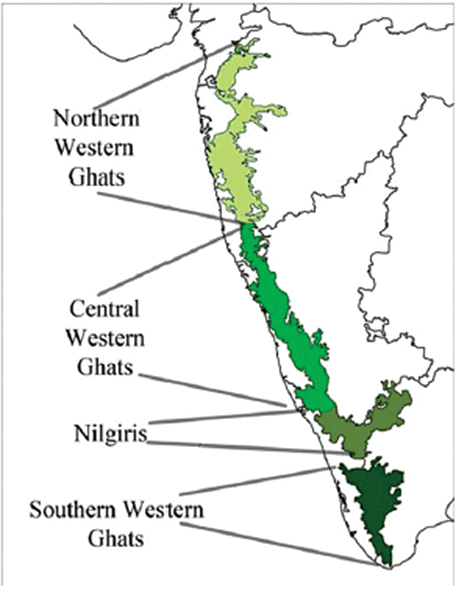
The Northern Western Ghats (The Northern Sahyadri)
- Location: The Western Ghats stretch from the Tapi Valley to a little north of Goa. They are characterized by horizontal layers of Deccan lavas, creating a prominent barrier along the western coastal plains.
- Composition: The region is primarily composed of horizontal sheets of Deccan lavas, which form a striking wall along the western coast.
- Important Peaks: Notable peaks in this region include Kalsubai (1646 m), Salher (1567 m), Mahabaleshwar (1438 m), and Harishchandragarh (1424 m).
- Important Passes: Thalghat and Bhorghat serve as crucial passages connecting the Western Coastal Plain with the Deccan Plateau.
The Central Western Ghats (The Central Sahyadri)
- Location: This part spans from 16°N latitude up to the Nilgiri Hills, exhibiting a diverse landscape.
- Composition: Comprising granites and gneisses, this section showcases a different geological makeup compared to other parts of the Western Ghats.
- Important Peaks: Noteworthy peaks in this area include Doddabetta (2637 m), Makurti (2554 m), Vavul Mala (2339 m), Kudremukh (1892 m), and Pushpagiri (1714 m).
The Southern Western Ghats (The Southern Sahyadris)
- Location: This section forms the southernmost division of the Western Ghats.
- The southern part of the Western Ghats is separated from the main Sahyadri Range by a mountain pass called the Palghat Gap.
- Important Peaks: Anai Mudi (2,695 m) is the highest peak in the peninsular plateau region as well as the whole of southern India.
The Eastern Ghats
- About: The Eastern Ghats are a sequence of fragmented mountain ranges running along the eastern edge of the Indian Peninsular Plateau. They closely align with the east coast of India.
- Location: To the west of the Eastern Ghats lies the Deccan Plateau, while to the east lies the Coastal Plains and the Bay of Bengal.
- North-South Extent: These hills stretch from the Mahanadi River in Odisha to the Vagai River in Tamil Nadu.
- Topography: Unlike the Western Ghats, the Eastern Ghats are not a continuous range but instead comprise a series of rugged and detached hills.
- Divisions: The Eastern Ghats can be categorized into two distinct sections.
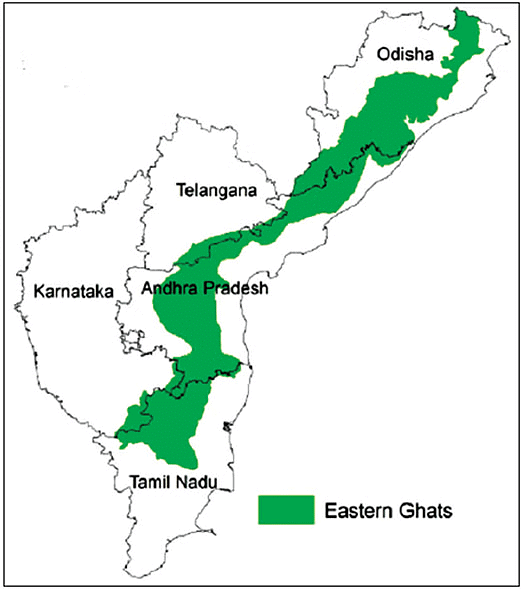
Eastern Ghats Ranges
- Location: This region of the Eastern Ghats is situated between the Mahanadi and the Godavari Valley.
- Important Hills:Some significant hill ranges in this area are:
- Maliya Range: The tallest peak in this range is Mahendra Giri standing at 1501 meters.
- Madugula Range: This range includes important peaks like Arma Konda (1680 m), Gali Konda (1643 m), Sinkram Gutta (1620 m), and others.
The Palkonda Range
- Javadi Hills These hills are situated in northern Tamil Nadu.
Shevroy-Kalrayan Hills
- Shevroy-Kalrayan Hills These hills are also located in Tamil Nadu.
Biligiri Rangan Hills
- Biligiri Rangan Hills These hills are positioned at the border of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
Significance of the Peninsular Plateau of India
As the oldest and most stable landmass of the Indian subcontinent, the Peninsular Plateau of India holds immense importance:
- Mineral resources: The plateau is rich in various minerals such as Iron, Copper, Manganese, Bauxite, Chromium, Mica, and Gold.
- Coal deposits: This region hosts 98% of the Gondwana coal deposits in the country.
- Agriculture: The presence of black soil supports the cultivation of crops like cotton, tea, coffee, rubber, and millet.
- Forest produce: Abundant forests in the area provide resources like timber.
- Rivers: The rivers in the region offer opportunities for hydroelectric power generation and irrigation for crops.
- Tourism: The Peninsular Plateau boasts scenic destinations like Ooty, Pachmarhi, Kodaikanal, Mahabaleshwar, and Mount Abu.
Going beyond its geographical features, the Peninsular Plateau serves as a crucial resource hub. However, it faces challenges like deforestation, soil erosion, and biodiversity loss. Preserving this unique landform is essential for ecological balance and sustainable development.
|
175 videos|624 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Peninsular Plateau - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the major geographical features of the Peninsular Plateau of India? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Aravali Range in the Peninsular Plateau of India? |  |
| 3. How do the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats contribute to the Peninsular Plateau's geography? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between the Deccan Plateau and the Chhattisgarh Plain in the Peninsular Plateau of India? |  |
| 5. How does the Peninsular Plateau's geomorphology impact the region's biodiversity and ecosystems? |  |
















