The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 19th April 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download

India’s Nuanced approach in the South China Sea
Why in News?
India's Ministry of External Affairs recently expressed firm support for the Philippines in defending its national sovereignty amidst tensions with China over the South China Sea.
What is the Dispute in the South China Sea Region?
- The territorial disputes in the South China Sea involve multiple countries claiming various islands and maritime territories.
- These disputes are primarily centered around competing territorial claims, fishing rights, and potential natural resources such as oil and gas reserves.
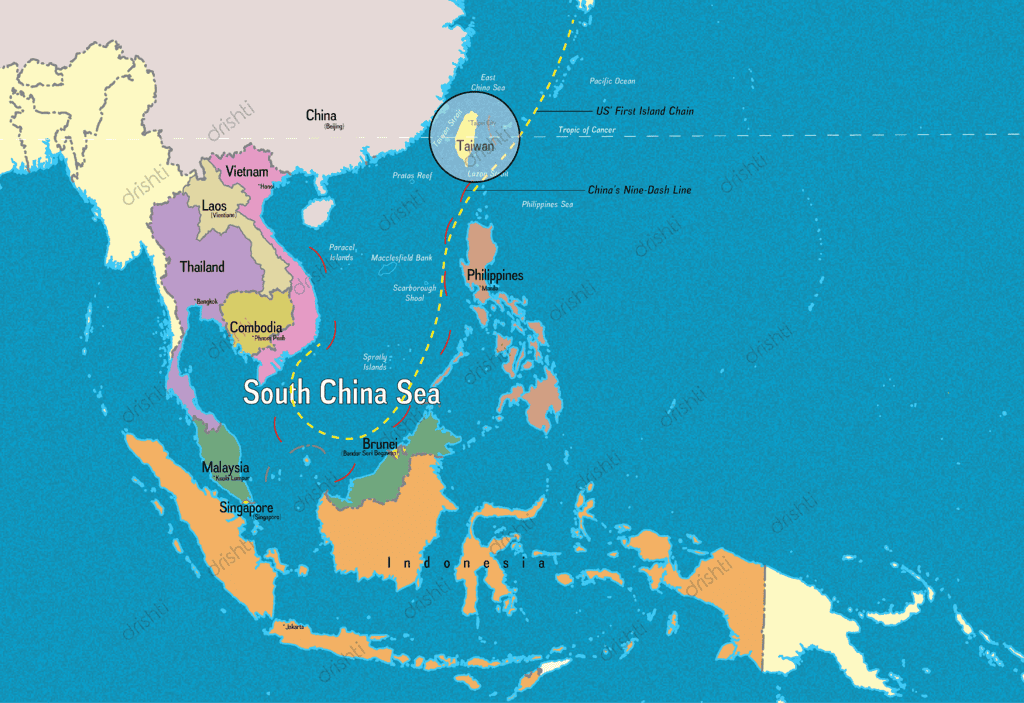
- China's expansive territorial claims in the region, as represented by the Nine-dash line, have been particularly contentious.
- The region has seen increased militarization, with countries like China constructing artificial islands to assert control over strategic areas.
- The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) is a key legal framework governing maritime disputes in the region, but not all countries involved are parties to this agreement.
- Tensions in the South China Sea have implications for regional security and international trade, as it is a crucial maritime thoroughfare through which a significant amount of global trade passes.
Significance of South China Sea:
Strategic Location:
The South China Sea holds a crucial strategic position, bordered by China and Taiwan to the north, the Indo-Chinese peninsula to the west, Indonesia and Brunei to the south, and the Philippines to the east, known as the West Philippine Sea.It is linked to the East China Sea via the Taiwan Strait and to the Philippine Sea through the Luzon Strait.
This location facilitates significant maritime activities and trade routes.
Trade Importance:
Approximately one-third of global shipping transits through the South China Sea, with over 64% of China's maritime trade passing through this region.Moreover, more than 55% of India's trade relies on the South China Sea and the Malacca Strait.
These waters play a vital role in international trade and commerce.
Fishing Ground:
Apart from its strategic value, the South China Sea is a significant fishing area, supporting millions of livelihoods and ensuring food security for the region.The sea hosts diverse marine life, sustaining fisheries that contribute substantially to the economies and food supplies of nearby countries.
Dispute:
The central issue in the South China Sea revolves around conflicting claims over land formations such as islands and reefs, along with the adjacent waters.Involved parties in these disputes include China, Brunei, Taiwan, the Philippines, Vietnam, and Malaysia.
China's expansive 'nine-dash line' claim covers a vast portion of the sea, leading to heightened tensions.
Key areas of contention include the Spratly Islands, Paracel Islands, Pratas, Natuna Islands, and Scarborough Shoal.
- Strategic Location: The South China Sea is positioned strategically, bordered by significant regions: China and Taiwan to the north, the Indo-Chinese peninsula (comprising Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, and Singapore) to the west, Indonesia and Brunei to the south, and the Philippines to the east (known as the West Philippine Sea).
- Trade Importance: About one-third of all global shipping occurs through the South China Sea. Moreover, over 64% of China's maritime trade navigates this sea, with over 55% of India's trade passing through both the South China Sea and the Malacca Strait.
- Fishing Ground: Beyond its geopolitical and trade significance, the South China Sea serves as a vital fishing zone. This area sustains a diverse marine ecosystem, supporting fisheries that are crucial for the livelihoods and food security of millions in the region. The fishing activities contribute significantly to the economies and food supplies of the surrounding nations.
 What is Salami Slicing Technique in Maritime Disputes?
What is Salami Slicing Technique in Maritime Disputes?
- Salami Slicing is a strategy used in territorial disputes where small, incremental actions are taken to avoid large-scale retaliation or detection.
- This technique involves making a series of small moves that individually may seem insignificant, but when combined, they have a significant impact on altering the status quo.
- By gradually advancing their position or control, a party employing this method aims to achieve their goals without eliciting a strong response from other involved parties or the international community.
- An example of the Salami Slicing technique is when a country slowly builds structures on disputed islands or reefs, gradually strengthening its presence without triggering a full-blown conflict.
- About: It involves countries incrementally asserting control over maritime areas through small, gradual actions over time. It avoids direct confrontation, exploits legal ambiguities, and aims to assert influence and create irreversible situations in disputed waters.
- It avoids direct confrontation, exploits legal ambiguities, and aims to assert influence and create irreversible situations in disputed waters.
- Example: China has been accused of employing the salami slicing technique in the South China Sea through actions like building artificial islands, conducting resource exploration, and imposing fishing bans to assert control and limit access for other countries. For instance, recently Chinese coast guard ships blocked Philippine vessels at Second Thomas Shoal, resulting in escalated tensions in the region.
- For instance, recently Chinese coast guard ships blocked Philippine vessels at Second Thomas Shoal, resulting in escalated tensions in the region.
What are the Areas of Cooperation Between India and the Philippines?
- Trade and Economic Relations:
- Both countries have strong economic ties, with trade agreements benefiting industries in both nations.
- Examples include the exchange of goods and services, promoting investments, and fostering economic growth.
- Defense and Security Cooperation:
- India and the Philippines collaborate on defense strategies and security measures to address common threats and challenges.
- Joint military exercises and information sharing enhance the security capabilities of both nations.
- Cultural Exchange and People-to-People Ties:
- Both countries engage in cultural exchanges to promote understanding and strengthen diplomatic relations.
- Student exchanges, cultural events, and tourism initiatives contribute to building a strong bond between the peoples of India and the Philippines.
- Environmental Collaboration:
- India and the Philippines work together on environmental protection and sustainable development projects.
- Initiatives focus on conservation efforts, renewable energy promotion, and combating climate change impacts.
India-Philippines Diplomatic Relations Overview
- About: India and the Philippines formally established diplomatic relations on November 26, 1949. This relationship has evolved significantly with the initiation of the Act East Policy in 2014, expanding into various domains including political security, trade, industry, and people-to-people connections.
Act East Policy
- The Act East Policy, launched in 2014, has played a pivotal role in diversifying the India-Philippines relationship. It has fostered deeper engagements in areas such as political security, trade, industry, and interpersonal interactions.
Bilateral Trade Dynamics
- Bilateral Trade: The official trade statistics from the Department of Commerce, Government of India, reveal that bilateral trade between India and the Philippines surpassed the USD 3 billion mark during 2022-23. India's exports to the Philippines consist of engineering goods, automobile parts, petroleum products, pharmaceuticals, bovine meat, oilseeds, tobacco, and groundnuts. On the other hand, imports from the Philippines to India encompass electrical machinery, semiconductors, ores, copper, plastics, pearls, waste from the food industry, and animal fodder.
Health and Medicine Collaborations
- The Philippines made history by being the first ASEAN member to grant Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for Bharat Biotech's Covaxin. Currently, the Philippines accounts for approximately 20% of India's pharmaceutical exports to ASEAN, with India serving as its primary pharmaceutical supplier.
Science and Technology Cooperation
- A Bilateral Programme of Cooperation (POC) in Science and Technology was inked in October 2019, encompassing diverse fields such as agricultural biotechnology, material science, and ocean science. Notably, a significant agreement was reached in January 2022 for India to deliver a shore-based anti-ship variant of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile to the Philippines, highlighting the global demand for India's advanced defense capabilities.
Trade Relations between India and the Philippines
- India exports a variety of goods to the Philippines, including engineering goods, automobile parts, petroleum products, pharmaceuticals, bovine meat, oilseeds, tobacco, and groundnuts.
- Imports from the Philippines to India consist of electrical machinery, semiconductors, ores, copper, plastics, pearls, waste from the food industry, and animal fodder.
Health and Medicine
- The Philippines holds the distinction of being the first ASEAN member to provide Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for Bharat Biotech's Covaxin.
- About 20% of India's pharmaceutical exports to ASEAN are directed towards the Philippines, making India the primary pharmaceutical supplier to the country.
Science and Technology
- A Bilateral Programme of Cooperation (POC) in Science and Technology was established in October 2019, focusing on areas such as agricultural biotechnology, material science, and ocean science.
- In January 2022, India and the Philippines inked a deal for the supply of a shore-based anti-ship variant of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile, showcasing the global demand for India's advanced defense technologies.
|
63 videos|5408 docs|1146 tests
|





















