Electricity and Circuits Chapter Notes | Physics for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Charge flows in Circuits |

|
| Circuit Diagrams |

|
| Current in series circuits |

|
Introduction
- Electricity is a form of energy that powers many devices we use daily. Electric circuits are paths through which electric current flows.
- Components of circuits include batteries, wires, switches, and light bulbs.
- Understanding circuits helps us control and use electricity safely.
- Electricity is crucial for technology, industry, and modern life.
Charge flows in Circuits
Charge flow in circuits can be explained in points:
- Electric current is the flow of electric charge.
- Electric charge is carried by tiny particles called electrons.
- In a circuit, electrons flow from the negative terminal of the battery through the wires to the positive terminal.
- This flow of electrons completes the circuit and powers the devices connected to it.
- Components like resistors, switches, and light bulbs control the flow of electrons in the circuit.
- Understanding charge flow helps us design and use circuits effectively.
Modelling Electric Current
Electric current can be understood using the rope loop model:
- The rope loop represents an electrical circuit.
- The teacher pulling the rope represents the cell or battery supplying energy.
- The flow of the rope represents electric current, which is the flow of electric charge in a circuit.
- Current is measured in units of charge per second.
- If students tighten their grip on the rope, it represents resistance in the circuit.
- Resistance makes it harder for current to flow, requiring more energy to maintain the flow.
- In a lamp, the filament offers resistance and converts electrical energy to heat and light.
- The energy lost as heat in the filament makes the lamp light up.
Conductors and Insulators
Conductors are materials with electrons that can move freely through the material, making it easy for electric current to flow.
- Examples of conductors include metals like copper, aluminum, and gold.
- Insulators are materials that do not conduct electricity well because the electrons cannot move as freely through the material.
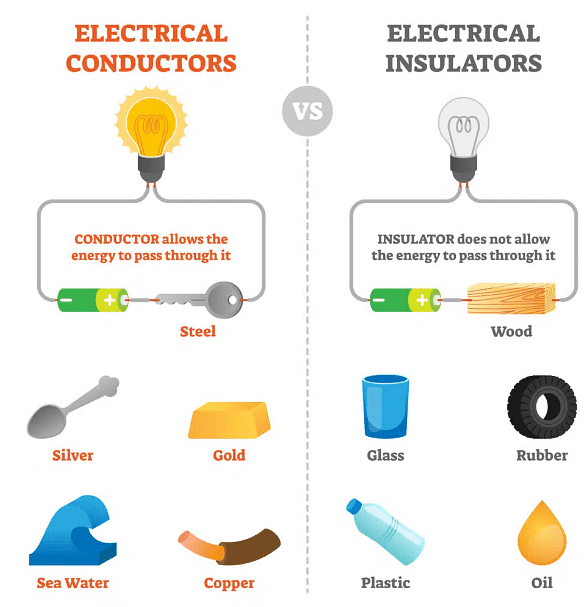
- Examples of insulators include rubber, plastic, glass, and wood.
- Conductors are used for making wires and electrical connections, while insulators are used to coat wires and protect against electric shocks.
Circuit Diagrams
Circuit diagrams are used to represent electrical circuits:
- They use standardized symbols for components like cells, lamps, wires, switches, and buzzers.
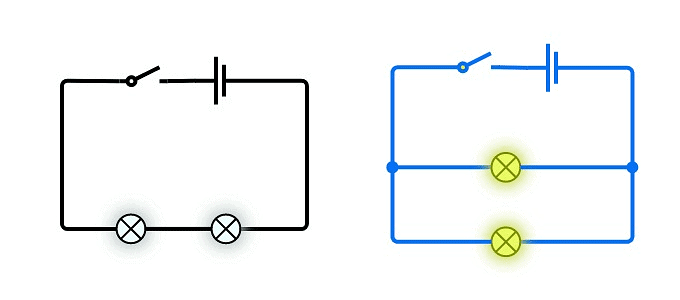
- In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end in a single path for current to flow.
- Predictions based on scientific knowledge can be compared with experimental results to verify their accuracy.
- Observations during experiments help in understanding circuit behavior.
Circuit Symbols
When drawing circuits, symbols are used to represent components:
- Components are represented by symbols to make it easier to draw and understand circuit diagrams.
- A series circuit has only one loop, while a parallel circuit has more than one loop.
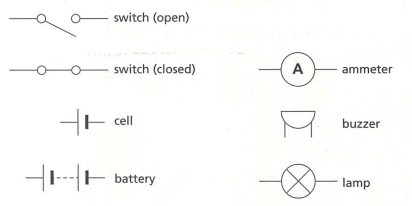
- A switch interrupts the flow of electricity in a circuit. When open, the circuit is incomplete; when closed, electricity can flow.
- A cell or battery provides energy to the circuit.
- An ammeter measures the current flowing through a circuit.
Comparing Circuits
When comparing circuits, changes in the number of lamps and cells affect brightness: The brightness of lamps increases with higher current.
The rope loop model can predict outcomes in different circuits:
- If more people pull the rope, more energy is transferred, making the lamp brighter in a circuit.
- If more people grip the rope tightly, it becomes harder to move, reducing the current flow in the circuit.
Current in series circuits
Current flows in a series circuit when there is a cell providing energy and a complete loop:
- Scientific knowledge predicts current flows with a cell and complete loop.
- Circuit components are represented by symbols for clarity.
- In an investigation, variables include cells/lamps (independent), lamp brightness (dependent), and wire type (control).
- The rope loop model predicts and explains current in a series circuit:
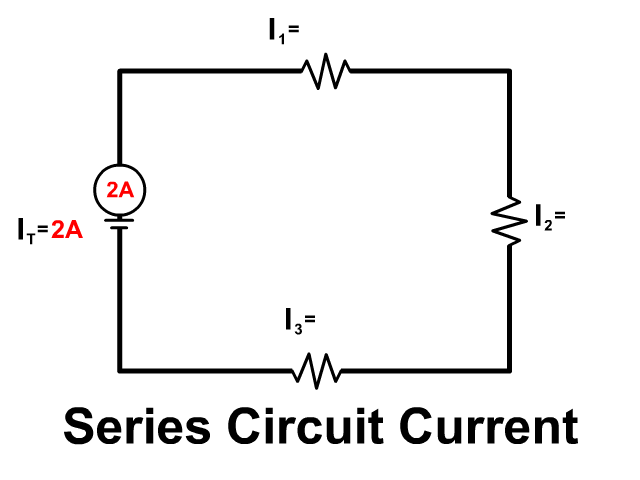 Current flows through each component.
Current flows through each component.- Opening a switch stops current.
- Lamp brightness varies with cells/lamps, affecting current.
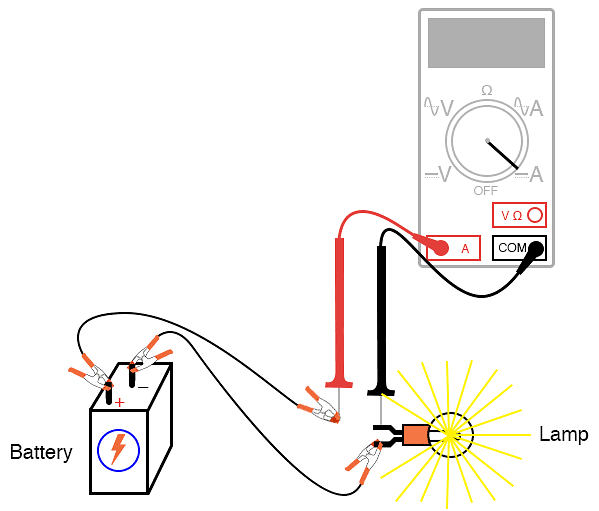
Measuring Current
Electric current is the flow of charge around a circuit. Current is measured in amperes (amps) using a device called an ammeter. Ammeters can have an analogue or digital scale, and they have a positive and negative terminal indicating the direction of current flow.
Comparing Models
In the rope loop model, current is represented by the amount of rope passing a fixed point per second.
- In an electric circuit, current is measured by the amount of charge passing a fixed point per second. The number of charges passing any point in a circuit per second is a measure of electric current.
- When more energy is applied to the rope loop model by pulling the rope harder, the rope moves faster. In an electrical circuit, adding another cell increases the amount of charges flowing, but their speed remains the same regardless of current size.
Comparing Current in Circuits
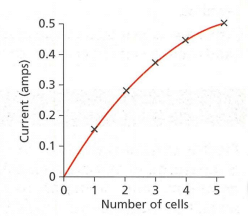
Changing components in a circuit affects the current. Adding more cells increases energy supply, causing more current to flow.
The graph illustrates how current increases with more cells. The line is not straight because as the lamp heats up, additional cells have less effect.
|
215 videos|402 docs|221 tests
|














