Textbook Solution: Structure and Properties of Material | IGCSE Cambridge Science for Year 6 - Class 6 PDF Download
Physical and chemical properties
Q1. Name five physical properties.
Ans: Color, density, volume, mass, and boiling point.
Q2. Describe the process a scientist used to find the melting point of naphthalene.
Ans: The scientist put some solid naphthalene into a test tube and heated it until it melted. Then, they placed the test tube into a beaker of ice to cool the naphthalene.
Q3(a). Name two physical properties of sodium.
Ans: Sodium is a light grey metal and is soft.
Q3(b). Name one chemical property of sodium.
Ans: Sodium reacts easily with oxygen and water.
Q4. How could a scientist use the chemical properties of hydrogen to test his hypothesis that a collected gas is hydrogen?
Ans: The scientist could expose the gas to a flame; if it is hydrogen, it will burn with a pop sound, which is a distinctive reaction of hydrogen due to its flammability.
Acidity and indicators
Q1. Why is it important for some chemicals to have hazard symbols on them?
Ans: It is important for some chemicals to have hazard symbols to quickly communicate the specific dangers and precautions required when handling them, ensuring safety and preventing accidents.
Q2. Why do scientists use symbols instead of writing words?
Ans: Scientists use symbols instead of words because symbols are universally recognized, transcending language barriers, and can convey important safety information more quickly and effectively.
Q3. A chemical could cause burns to the skin and eyes if not used safely. What hazard symbol would you put on this chemical?
Ans: The appropriate hazard symbol for a chemical that could cause burns to the skin and eyes is the corrosion symbol, which typically depicts a substance eating away at a hand and a surface.
Q4. A chemical could cause the skin to become red and itchy if it is in contact with the skin. What hazard symbol would you use for this chemical?
Ans: For a chemical that causes the skin to become red and itchy, the irritant symbol should be used. This symbol may show an exclamation mark.
Q5. Copy and complete the following table on litmus paper indicator colours in acids and alkalis.
| Colour of red litmus paper | Colour of blue litmus paper | |
|---|---|---|
| In acidic solution | Red | Red |
| In neutral solution | Red | Blue |
| In alkaline solution | Blue | Blue |
Q6. What colour would blue litmus paper turn in hydrochloric acid?
Ans: Blue litmus paper would turn red in hydrochloric acid.
Q7. What colour would red litmus paper turn in sodium hydroxide?
Ans: Red litmus paper would turn blue in sodium hydroxide.
Q8. Acids and alkalis can have a range of pH values depending on whether they are strong or weak. What range of pH does a strongly acidic solution have? What range of pH does a weakly alkaline solution have?
Ans: A strongly acidic solution has a pH range of 0-3. A weakly alkaline solution has a pH range of 8-10.
Q9. State whether the following are strongly acidic, weakly acidic, neutral, weakly alkaline or strongly alkaline:
- a) A substance with a pH of 3. - Ans: Strongly acidic
- b) A liquid with a pH of 8. - Ans: Weakly alkaline
- c) A substance which turns Universal Indicator yellow. - Ans: Weakly acidic
- d) A chemical with a pH of 7. - Ans: Neutral
- e) A substance with a pH of 14. - Ans: Strongly alkaline
- f) A liquid which turns Universal Indicator blue. - Ans: Weakly alkaline
Q10. For the following statements, say whether they are true or false. If they are false, write the correct answer:
- a) A strongly acidic solution has a pH range of 4-6. - Ans: False, 0-3
- b) A weakly alkaline solution has a pH range of 8-10. - Ans: True
- c) A neutral substance turns Universal Indicator green. - Ans: True
Q11. Using figure 4.12, give an example of a strong acid, weak acid, strong alkali, and a weak alkali.
Ans: A strong acid example is hydrochloric acid, a weak acid example is acetic acid, a strong alkali example is sodium hydroxide, and a weak alkali example is ammonia.
Q12. Draw and colour in your own pH scale and label each pH value with an example. If you can find some other examples which are not given on figure 4.12, add these.
Ans: [An example of a pH scale is drawn and labeled from pH 0 to pH 14 with substances like lemon juice at pH 2, vinegar at pH 3, pure water at pH 7, baking soda at pH 9, and drain cleaner at pH 14.]
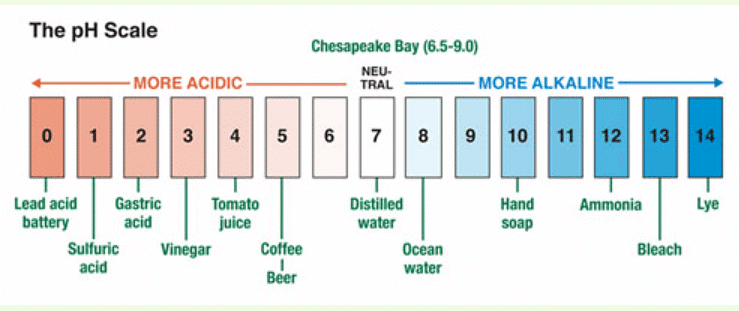
(These are sample answers. Students are advised to write the answers based on their own preferences.)
Q13. Using books or the internet, find the names of at least two other indicators that scientists use.
Ans: Two other indicators commonly used by scientists are phenolphthalein and methyl orange.
Q14. Why is Universal Indicator more useful than other indicators?
Ans: Universal Indicator is more useful than other indicators because it can provide a broad range of pH readings through colour changes, allowing for more precise determination of pH compared to single change indicators like litmus.
Q15. What is a disadvantage of using litmus indicator?
Ans: A disadvantage of using litmus indicator is that it only shows whether a solution is acidic or alkaline and cannot provide the exact pH value of the solution
The particle model
Q1. What state of matter is being described?
Ans: a) The particles are far apart.
Q2. Use the particle model to explain why you can compress a gas, but you cannot compress a solid or a liquid.
Ans: In gases, the particles are widely spaced apart and move freely, which allows them to be compressed as there is a lot of empty space between them. In solids and liquids, the particles are much closer together and do not have much space between them, making them much less compressible.
Q3. A diamond is hard and cannot be scratched easily. Use the particle model to suggest why.
Ans: Diamonds are formed by carbon atoms arranged in a crystal lattice that is extremely strong and tightly bonded, which makes the structure very hard and difficult to scratch.
Q4. Describe what happens to the particles when a liquid is heated to form a gas.
Ans: When a liquid is heated, the particles gain energy and start moving faster. As they move faster, they overcome the forces holding them together in the liquid state, spread out more, and transition into a gaseous state
Elements and the Periodic Table
Q1. Use the Periodic Table to name the element number 14.
Ans: Silicon
Q2. Which of these statements are true?
a) Aluminium only contains one type of atom.
Ans: False, Aluminium does contain only one type of atom, but this statement is poorly worded as it might imply it only has one atom in total.
b) The symbol for sodium is So.
Ans: False, the symbol for sodium is Na.
c) Oxygen contains two types of atom.
Ans: False, oxygen as an element is made of only one type of atom, but it can have different isotopes.
d) The symbol for potassium is K.
Ans: True
Elements, compounds and mixtures
Q1. Describe the difference between an element and a compound.
Ans: An element is a pure substance consisting of only one type of atom, characterized by its unique number of protons. A compound, on the other hand, is a substance formed from two or more different elements that are chemically bonded in fixed proportions.
Q2. How many carbon and oxygen atoms are in one particle of carbon dioxide (CO2)?
Ans: In one molecule of carbon dioxide (CO2), there is one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
Q3. A particle of glucose has the formula C6H12O6.
a) What elements make up glucose?
Ans: The elements that make up glucose are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O).
b) How many of each atom are in one particle of glucose?
Ans: In one molecule of glucose, there are 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms, and 6 oxygen atoms.
Q4. The compound lithium oxide has the formula Li2O. Which statement is correct?
a) There is the same number of lithium atoms as oxygen atoms.
b) There is double the number of lithium atoms as oxygen atoms.
c) There is half the number of lithium atoms as oxygen atoms.
Ans: b) There is double the number of lithium atoms as oxygen atoms.
Q5. The formula of magnesium chloride is MgCl2. A piece of magnesium chloride contains 400 chlorine particles. How many magnesium particles are there?
Ans: There are 200 magnesium particles, as the ratio of magnesium to chlorine in magnesium chloride (MgCl2) is 1:2.
Q6. Describe the difference between a compound and a mixture.
Ans: A compound is a chemical combination of two or more elements bonded together in fixed proportions and cannot be separated by physical means. A mixture consists of two or more substances physically combined, where the components can be separated by physical means and are not in fixed proportions.
Q7. Air contains the gases nitrogen, oxygen, water vapour and carbon dioxide.
For each of these substances, write down whether it is an element, a compound or a mixture:
a) Air
Ans: Mixture
b) Oxygen
Ans: Element
c) Nitrogen
Ans: Element
d) Carbon dioxide
Ans: Compound
e) Water
Ans: Compound
Q8. Mo is making concrete. He mixes sand, small stones and cement powder. He then adds water. Before he adds the water, it is a mixture. After he adds the water it is not. Explain why.
Ans: Before adding water, the sand, small stones, and cement powder are just mixed physically without any chemical bonding, forming a mixture. When water is added, it reacts chemically with the cement to form a new substance through hydration, thus creating a chemical compound rather than a simple physical mixture.
 |
Download the notes
Textbook Solution: Structure and Properties of Material
|
Download as PDF |
Properties of metals, non-metals and alloys
Q1. Metals and non-metals are in different places on the Periodic Table.
For each of these element symbols, name the element and say if it is a metal or non-metal:
a) Be
Ans: Beryllium, Metal
b) Cl
Ans: Chlorine, Non-metal
c) Al
Ans: Aluminum, Metal
d) Ar
Ans: Argon, Non-metal
Q2. List the symbols and names of three other metals shown in figure 4.35.
Ans: Fe - Iron, Cu - Copper, Zn - Zinc
Q3. Draw a table to compare the properties of metals and non-metals.
Ans: Metals are generally hard, shiny, good conductors of heat and electricity, and malleable. Non-metals are generally not shiny, poor conductors of heat and electricity, and brittle.
Q4. Use the evidence to say if each material listed below, A–C, is a metal or a non-metal. For each, give reasons for your answer.
A: A hard and shiny solid. Good conductor of heat and electricity.
Ans: Metal, as it displays properties typical of metals like conductivity and luster.
B: A shiny liquid. When put into a gap in an electrical circuit, it makes a connected loop.
Ans: Metal, specifically mercury, as it is a liquid at room temperature and conducts electricity.
C: A shiny solid. Used as an electrical insulator.
Ans: Non-metal, as it is used as an insulator, a property typical of non-metals.
Q5. The cables coming out of a television are made of copper covered in plastic. Suggest why these two materials are chosen.
Ans: Copper is used because it is an excellent conductor of electricity, making it ideal for transmitting electrical signals efficiently. Plastic is used as insulation to protect against electric shocks and to prevent short circuits, as it is a good electrical insulator.
Q6. Brass is a metal but it is not listed on the Periodic Table. Explain why.
Ans: Brass is not listed on the Periodic Table because it is an alloy, which is a mixture of metals (primarily copper and zinc), rather than a pure element.
Q7. If you mix iron with other metal elements or carbon it forms an alloy called steel. Explain why steel, and not pure iron, is used to build bridges.
Ans: Steel is used instead of pure iron because it is stronger and more durable. The addition of carbon and other elements to iron in steel improves its mechanical properties, making it more resistant to wear and corrosion, which is essential for the structural integrity of bridges.
End of chapter review
Q1. What is meant by a chemical property of a substance?
Ans: A chemical property of a substance refers to its ability to undergo a specific chemical change or reaction due to its composition. For example, flammability, reactivity with water, and acid-base behavior are all chemical properties.
Q2. Hydrogen is a colourless gas. It has a low density and is highly reactive. Give one chemical property and two physical properties of hydrogen.
Ans: Chemical property: Hydrogen reacts explosively with oxygen. Physical properties: Hydrogen is colorless and has a low density.
Q3. State the meaning of the following hazard symbols:
(a) The symbol indicates that the material is corrosive. It can cause chemical burns to the skin and eyes, and it can also corrode metals.
(b) The symbol indicates that the material is harmful or an irritant. It can cause harm to health without being immediately dangerous.
Q4. Universal Indicator turns a range of colours in acids and alkalis. The table shows the pH range for the different colours of Universal Indicator. A student tested five substances with Universal Indicator solution. Copy the table and put one tick (✓) in each row to state whether the results show the substance is acidic, alkaline or neutral.
| Substance | Colour of indicator | Acid? | Alkali? | Neutral? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toothpaste | Blue | ✓ | ||
| Vinegar | Red | ✓ | ||
| Milk | Yellow | ✓ | ||
| Water | Green | ✓ | ||
| Oven cleaner | Purple | ✓ |
Q5. Describe the difference in movement of particles in solids and liquids.
Ans: In solids, particles are tightly packed and only vibrate in fixed positions. In liquids, particles are less tightly packed than in solids and can move around freely, allowing the liquid to flow.
Q6. What is a vacuum?
Ans: A vacuum is a space devoid of matter, including air, resulting in no atmospheric pressure or any other substances present.
Q7. A chemical reaction between hydrochloric acid and magnesium produces magnesium chloride (MgCl2). Is magnesium chloride an element, compound or mixture?
Ans: Magnesium chloride is a compound because it consists of magnesium and chlorine chemically bonded together.
Q8. What is an alloy?
Ans: An alloy is a mixture composed of two or more elements, at least one of which is a metal, which exhibits metallic bonding and enhanced properties compared to the individual constituent elements.
Q9. Name two physical properties that are typical of metals and two physical properties typical of non-metals.
Ans: Physical properties of metals: Good conductors of heat and electricity, and malleable. Physical properties of non-metals: Poor conductors of heat and electricity, and brittle.
Q10. Explain why scientists might find Universal Indicator more useful than litmus.
Ans: Scientists might find Universal Indicator more useful than litmus because it can provide a more comprehensive indication of the pH level of a substance, showing a wide range of colors that correspond to different pH levels, unlike litmus paper which only indicates whether a substance is acidic or alkaline.
Q11. The table below shows the pH of four different soil samples which are labelled A–D. Use letters from the table to answer the following questions:
(a) Which soil sample is neutral? Ans: None of the soil samples are neutral as they do not have a pH of 7.
(b) Cabbages grow better in an alkaline soil. Which soil sample would be the best to grow cabbages in? Ans: Soil sample B with a pH of 7.4.
(c) Potatoes grow better in slightly acidic soil. Which soil sample would be the best to grow potatoes in? Ans: Soil sample D with a pH of 4.7.
Q12. Amin fills a balloon with air. Use the particle model to explain why he can squash the balloon.
Ans: Amin can squash the balloon because the air particles inside are not rigidly fixed but are free to move around, allowing the shape of the balloon to be changed when compressed.
Q13. Draw diagrams to show the particles in:
(a) a piece of solid copper Ans: In solid copper, the particles are closely packed in a regular lattice structure.
(b) carbon dioxide gas (CO₂) Ans: In carbon dioxide gas, the particles are spaced far apart and move freely at high speeds.
Q14. For each of these elements, use a Periodic Table to state whether it is a metal or non-metal:
(a) magnesium – Metal
(b) neon – Non-metal
(c) nitrogen – Non-metal
(d) barium – Metal
Q15. Draw and label diagrams to explain the difference in hardness between pure metals and alloys.
Ans: Pure metals have a uniform lattice structure that allows layers of atoms to slide over each other easily, making them relatively soft. Alloys have different sizes of atoms that disrupt this lattice, making it harder for layers to slide and thus making alloys harder.
Q16. Helium is the second element in the Periodic Table. Tin is the 50th. Suggest how tin atoms and helium atoms are different.
Ans: Tin atoms are larger, have more protons, electrons, and neutrons, and have more complex electron arrangements compared to helium atoms, which are smaller and simpler with fewer protons, electrons, and neutrons.
Q17. Stainless steel is an alloy of iron, carbon and other metals (mainly chromium). It has different chemical and physical properties from pure iron. One chemical property is that it does not rust.
(a) Explain two reasons why many bridges are made from stainless steel, and not pure iron. Ans: Stainless steel does not rust, providing longevity and lower maintenance costs, and it is stronger and more durable than pure iron, making it more suitable for structures that bear heavy loads.
(b) Suggest one reason why more bridges are made from normal steel and not stainless steel. Ans: Normal steel is less expensive than stainless steel and is sufficient for many applications where the superior properties of stainless steel are not necessary.
|
31 videos|34 docs|22 tests
|
FAQs on Textbook Solution: Structure and Properties of Material - IGCSE Cambridge Science for Year 6 - Class 6
| 1. What are some examples of physical properties of materials? |  |
| 2. How do acidity and indicators relate to the structure and properties of materials? |  |
| 3. How does the particle model help us understand the structure and properties of materials? |  |
| 4. How are elements organized on the Periodic Table and how does this relate to their properties? |  |
| 5. What are the differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures in terms of their structure and properties? |  |

















