UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 9th May 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| INDIAN OCEAN DIPOLE (IOD) |

|
| The ‘Muslim Quota’ Question |

|
| African Union (AU) |

|
| Cloud Seeding |

|
| AlphaFold3 |

|
| Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting |

|
| Climate Migration |

|
| Forest Fire |

|
GS-I/Geography
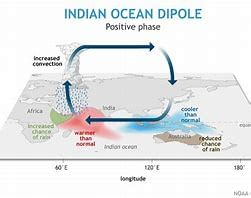
INDIAN OCEAN DIPOLE (IOD)
Source: Hindu Business Line
Why in News?
Recent Reports: Positive Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) may re-emerge in late 2024, marking the second consecutive year since 1960.
Background
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), also referred to as the Indian Niño, involves irregular sea surface temperature oscillations.
- During the positive phase, warmer waters accumulate in the western Indian Ocean, contrasting with colder temperatures in the eastern region.
- Conversely, the negative phase of the IOD witnesses a reversal in this pattern, with warm waters shifting eastward.
- The IOD's interplay with El Niño can mitigate the latter's adverse effects on the Indian monsoon.
- Notably, a positive IOD alongside an El Niño occurrence can counterbalance some of El Niño's negative impacts.
- The IOD significantly influences local weather patterns, triggering intense rainfall or droughts in regions like Africa and Australia.
- Furthermore, associated sea-level alterations heighten coastal flooding risks, amplifying related consequences.
GS-II/Polity and Governance
The ‘Muslim Quota’ Question
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
In the midst of election season, India is engaged in a critical discussion regarding fundamental constitutional aspects concerning reservation policies. The core query revolves around whether a secular nation like India should implement reservation based on religion. Additionally, there is deliberation on whether Muslims have ever received reservation benefits through a reduction in quotas allocated for Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), or Other Backward Classes (OBCs).
Background Information
- The findings of the Justice Rajinder Sachar Committee in 2006 highlighted that the overall status of the Muslim community was nearly as underprivileged as SCs and STs, and even more so than non-Muslim OBCs.
- The Justice Ranganath Misra Committee report from 2007 proposed a 15% reservation quota for minorities, with a specific 10% allocation for Muslims.
Key Concepts and Takeaways
- The Constitution of India transitioned from the principle of equality, which focuses on uniform treatment for all, to equity, which ensures fairness and may necessitate distinct treatment or special provisions for certain groups.
- The Supreme Court has emphasized that equality is a multifaceted concept with diverse dimensions, not confined within traditional limits, as evidenced in the case of E P Royappa vs State Of Tamil Nadu in 1973.
- While formal equality stresses equal treatment for all individuals regardless of outcomes, substantive equality concentrates on ensuring equality of results. Affirmative action advocates for substantive equality.
- The initial constitutional amendment introduced Article 15(4), empowering the state to make special provisions for the advancement of socially and educationally backward classes or for SCs and STs.
- Article 15 explicitly prohibits discrimination by the state solely based on religion, caste, as well as other factors like sex, race, and place of birth. Following the Supreme Court's ruling in State of Kerala vs N M Thomas in 1975, reservation is viewed not as a deviation from equality principles but as an extension of equality.
- The term 'only' in Articles 15 and 16 implies that if a religious, racial, or caste group is identified as a 'weaker section' per Article 46 or is categorized as a backward class, it is eligible for special provisions for advancement.
- Certain Muslim castes received reservation not solely due to their religious affiliation but because they were classified within the backward class category. This reservation was granted without diminishing the quotas for SCs, STs, and OBCs by establishing a sub-quota within the OBCs.
- Following the example of numerous states, the Mandal Commission incorporated several Muslim castes in the OBC list.
- As per the Supreme Court's directive in the Indra Sawhney case of 1992, any social group meeting the criteria of backwardness, irrespective of its identifying traits, deserves consideration as a backward class.
GS-II/International Relations
African Union (AU)
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
The African Union recently expressed concerns over the Israeli military actions in southern Gaza's Rafah, urging the global community to halt this dangerous escalation of conflict.
About African Union (AU):
- Established in 2002, the African Union (AU) is a continental organization comprising 55 member states from across Africa.
- It succeeded the Organization of African Unity (OAU) established in 1963.
- Primary Objective: The AU aims to foster unity, cooperation, and development among African nations while advocating for the continent's interests globally.
- Guided by the vision of "An Integrated, Prosperous, and Peaceful Africa," the AU strives to be a significant global player driven by its citizens.
- Agenda 2063 serves as a strategic roadmap for Africa's socio-economic and integrative transformation, emphasizing collaboration and African-led initiatives for the continent's progress.
Structure:
- Assembly: Comprising heads of state and government, it serves as the highest decision-making body within the AU.
- Executive Council: Consisting of foreign affairs ministers, the council addresses policy issues and provides recommendations to the Assembly.
- AU Commission: Located in Addis Ababa, this administrative body executes the decisions of the Assembly and Executive Council.
- Peace and Security Council: Responsible for ensuring peace and security across the continent.
- The AU's structure encourages the involvement of African citizens and civil society through bodies like the Pan-African Parliament and the Economic, Social & Cultural Council (ECOSOCC).
GS-III/Science and Technology
Cloud Seeding
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
The Supreme Court recently informed the Uttarakhand government that cloud-seeding would not extinguish the forest fires that had resulted in five casualties in the State.
- Cloud Formation: Water vapor condenses around tiny particles to create the droplets that form a cloud.
- Rain Formation: These droplets collide, grow, and when they become heavy and the cloud reaches saturation, it rains.
- Rainfall Limitations: Not all clouds result in rain; even those that do, only a few can produce sufficient moisture to form large raindrops.
- Reasons for Limited Rainfall: Inadequate ice particles within a cloud can lead to insufficient cloud droplets combining to form raindrops.
What is Cloud Seeding?
- Cloud seeding is a scientific method that enhances a cloud's capacity to generate rain or snow and influence other weather phenomena.
- Process Description: It involves intentionally introducing various substances (seeds) into clouds to serve as condensation or ice nuclei in order to stimulate precipitation.
- Seed Dispersal: Cloud seeding introduces additional ice crystals or cloud nuclei into clouds, commonly carried out via aircraft, rockets, cannons, or ground generators.
- Effective Substances: Solid carbon dioxide (dry ice) and silver iodide have proven to be the most successful substances. When deployed in supercooled clouds (composed of water droplets at temperatures below freezing), they create nuclei around which water droplets evaporate.
- Rain Formation Process: The resulting water vapor transforms into ice crystals, which rapidly grow as water droplets adhere to them. Once the ice crystal becomes a hefty raindrop, it descends through the cloud and precipitates onto the ground as rainfall.
Conditions Required for Cloud Seeding
- Essential Cloud Conditions: Cloud seeding necessitates appropriate cloud types, as not all clouds are suitable for seeding.
- Optimal Cloud Depth: Clouds must possess adequate depth and maintain a specific temperature range (between -10 and -12 degrees Celsius) for effective seeding.
- Wind Speed Consideration: Wind speed should not exceed a certain threshold for successful cloud seeding, with these conditions often prevalent in mountainous regions.
Benefits of Cloud Seeding
- Global Utilization: Cloud seeding is employed worldwide to augment winter snowfall and boost mountain snowpack, supplementing the natural water reservoirs accessible to nearby communities.
GS-III/Science and Technology
AlphaFold3
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
Google Deepmind has introduced the third iteration of its AlphaFold artificial intelligence model, aiming to aid scientists in enhancing drug design and disease targeting.
About AlphaFold3
- AlphaFold3 is a newly developed AI model by Google DeepMind and Isomorphic Labs.
- This revolutionary model can predict the structure and interactions of various molecules in life with exceptional accuracy. For instance, it can even map the behavior of human DNA.
- It has the capability to generate joint 3D structures of molecules, illustrating how they interconnect.
- AlphaFold3 can model a wide range of biomolecules like proteins, DNA, RNA, and small molecules like ligands (including numerous drugs).
- Moreover, it can simulate chemical alterations in molecules that regulate cellular functions. Disruptions in these modifications can lead to diseases.
- It constructs its forecasts using a diffusion network, similar to those utilized in AI image generators.
Significance of AlphaFold3
- AlphaFold3 enables scientists to observe cellular systems comprehensively, encompassing structures, interactions, and modifications.
- This advanced perspective on life's molecules elucidates their interconnectedness and aids in comprehending how these connections impact biological functions.
- For example, it assists in understanding the effects of drugs, the synthesis of hormones, and the DNA repair mechanisms that preserve health.
GS-III/Environment and Ecology
Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
The 46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM) and the 26th Meeting of the Committee for Environment Protection (CEP) will be held in Kochi from May 20-30.
About Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting:
- It plays a crucial role in safeguarding Antarctica's delicate ecosystem and promoting scientific research in the region.
- Convened annually under the Antarctic Treaty System, these meetings provide a platform for Antarctic Treaty Consultative Parties and other stakeholders to address environmental, scientific, and governance issues concerning Antarctica.
What is the CEP?
- Established in 1991 under the Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty (the Madrid Protocol).
- Advises the ATCM on matters related to environmental protection and conservation in Antarctica.
Key facts about the Antarctic Treaty:
- Initial signing in 1959 with enforcement beginning in 1961.
- Designated Antarctica for peaceful purposes, scientific collaboration, and environmental preservation, with 56 countries currently party to the Treaty.
Provisions of the treaty:
- Stipulates that Antarctica should be utilized solely for peaceful endeavors.
- Ensures freedom for scientific research in Antarctica and promotes cooperation towards that objective.
- Mandates the exchange and free availability of scientific observations and outcomes from Antarctica.
India's involvement:
- India became a Consultative Party to the Antarctic Treaty in 1983.
- Participates in decision-making processes alongside 28 other Consultative Parties.
- Operates two permanent research stations in Antarctica: Maitri (established in 1989) and Bharati (established in 2012).
- Conducts Indian Scientific Expeditions to Antarctica annually since 1981.
- In 2022, India reinforced its commitment to the Antarctic Treaty by enacting the Antarctic Act.
Antarctic Treaty Secretariat (ATS):
- Established in 2004, the ATS serves as the administrative center for the Antarctic Treaty System.
- Coordinates ATCM and CEP meetings, manages information, and facilitates diplomatic communication and negotiations regarding Antarctic governance and management.
GS-III/Environment and Ecology
Climate Migration
Source: DTE

Why in News?
The issue of climate migration has garnered significant attention, yet the world still lacks a comprehensive legal framework to protect individuals forced to flee their homes due to increasingly severe weather disasters.
Overview
- Climate migration is when individuals are forced to leave their homes due to environmental changes caused by climate change. This movement can be temporary or permanent and can occur within a country or across borders.
- Climate migrants are primarily those who have little choice but to leave their homes due to the impacts of climate change.
Causes of Climate Migration
- Sudden-onset disasters like floods, hurricanes, and earthquakes cause internal displacement, making it difficult for people to return home due to destroyed infrastructure.
- Slow-onset disasters like droughts and desertification degrade land and water resources, pushing people to migrate for better opportunities.
- Rising sea levels threaten coastal communities, leading to permanent displacement as homes become submerged.
- Climate change-induced migration is often influenced by factors like poverty, political instability, and lack of social safety nets.
Challenges Faced by Climate Migrants
- Climate migrants often lose skills and assets, making it hard for them to find new jobs in unfamiliar environments.
- They may end up in informal work sectors with low wages and poor conditions, facing exploitation.
- Access to basic services like healthcare and education can be challenging, leading to social exclusion.
- Adapting to new cultures and languages can hinder integration into new communities.
- Climate migrants lack a clear legal framework for protection and may not qualify for refugee status.
- Displacement can lead to psychological distress, trauma, new health risks, and statelessness.
Way Forward
- Aggressive mitigation strategies are crucial to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and slow climate change.
- Adaptation strategies help communities become resilient to climate impacts and reduce displacement risks.
- Disaster preparedness plans, early warning systems, and risk reduction measures can minimize displacement.
- Legal frameworks are needed to protect climate migrants, possibly by extending refugee status or creating new protection categories.
- Planned relocation and resettlement programs may be necessary for uninhabitable areas due to climate change.
- Investing in sustainable development and climate-smart agriculture is essential for adaptation.
- Encouraging labor migration among countries can help mitigate climate change impacts on vulnerable communities.
GS-III/Environment and Ecology
Forest Fire
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
- At least five individuals have lost their lives in the fires, which have now affected over 1,000 hectares of forests in parts of Uttarakhand.
- There is a risk of the fires spreading to densely populated urban areas like Nainital city, with poor visibility hindering the Air Force's firefighting operations.
Background
- India witnesses a surge in forest fire incidents during March, April, and May due to the abundance of dry biomass following the end of winter and the onset of summer.
Key Takeaways
- Experts attribute the spread of forest fires to three main factors: fuel load, oxygen, and temperature. Dry leaves serve as fuel for these fires.
- Approximately 36% of India's forests are deemed prone to frequent fires, according to data from the Forest Survey of India (FSI).
- Burning forests intensifies heat and results in black carbon emissions, impacting water systems and air quality negatively. Nevertheless, some level of combustion is essential for forest regeneration; for instance, burning litter encourages the growth of fresh grasses.
- Human activities have been identified as the primary cause of forest fires, prompting the state government to implement emergency measures like banning the burning of fodder and solid waste near forests.
- Historically, around 95% of forest fires in India, including those in Uttarakhand, are initiated by human actions. Pine needle accumulation during summer months has been a major catalyst for fires in the Himalayan region.
- Forest fires pose a significant challenge that cannot be solely addressed through bans and punitive actions. The widespread devastation of Uttarakhand's forests reflects the worsening climate crisis.
- Severe fires are prevalent in certain forest types such as dry deciduous forests, while others like evergreen and montane temperate forests are less susceptible.
- Uttarakhand experienced a notably dry April last year, following deficient monsoon patterns. In such moisture-deficient conditions, fires spread rapidly, particularly in oxygen-rich environments like forests.
Prevention and Control of Forest Fires
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) advocates several methods for forest fire prevention and management, including constructing watch towers for early detection, deploying fire watchers, involving local communities, and establishing and maintaining fire lines.
- Two types of fire lines are commonly used: Kachha or covered fire lines, where undergrowth and shrubs are cleared while retaining trees to reduce fuel load, and Pucca or open fire lines, which are clear-felled areas separating forest blocks to prevent fire spread.
- Satellite-based remote sensing technology and GIS tools, as highlighted by the FSI, have proven effective in enhancing fire prevention and management. These technologies aid in creating early warnings for fire-prone regions, monitoring fires in real-time, and estimating burnt areas.
|
38 videos|5253 docs|1107 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 9th May 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) in the context of climate change? |  |
| 2. How does cloud seeding work and what is its role in influencing precipitation patterns? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of the Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting and what are some of the key discussions held during these meetings? |  |
| 4. How does the concept of Climate Migration relate to climate change and its impact on human populations? |  |
| 5. What is AlphaFold3 and how does it contribute to advancements in scientific research and technology? |  |




















