UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 15th May 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I/Geography
Geomagnetic Storms
Source: Earth.com

Why in News?
The recent occurrence of the strongest geomagnetic storm in over two decades led to radio blackouts and extended the northern lights to the southern United States.
About Geomagnetic Storms:
- A geomagnetic storm is a significant disruption of Earth's magnetosphere resulting from a highly efficient transfer of energy from the solar wind into the space environment surrounding our planet.
- These storms are triggered by fluctuations in the solar wind, leading to substantial alterations in the currents, plasmas, and fields within Earth's magnetosphere.
- Conditions conducive to geomagnetic storms include prolonged periods of high-speed solar wind and a southward-directed solar wind magnetic field at the dayside of the magnetosphere.
- The most severe storms are often linked to solar coronal mass ejections (CMEs), where vast amounts of plasma, along with its magnetic field, are ejected from the sun towards Earth.
Effects of Geomagnetic Storms:
- Geomagnetic storms lead to intense currents in the magnetosphere, alterations in the radiation belts, and modifications in the ionosphere, including the heating of the ionosphere and the thermosphere.
- These storms can result in the heating of the ionosphere, giving rise to stunning auroras on Earth.
- Due to ionospheric disturbances during storms, long-distance radio communication relying on sub-ionospheric reflection can be disrupted.
- Ionospheric expansion from these storms can elevate satellite drag, posing challenges in controlling their orbits.
- The buildup and discharge of static-electric charges during geomagnetic storms can damage satellite electronics.
- Global navigation systems may experience disruptions during these events.
- Geomagnetic-induced currents (GICs) generated in the power grid and pipelines can have detrimental effects.
What is Solar Wind?
- Solar wind is a continuous flow of protons and electrons emanating from the sun's outermost layer, the corona.
- These charged particles travel through the solar system at speeds ranging from 250 to 500 miles per second in a plasma state.
- The solar wind carries the solar magnetic field outward with it and is characterized by varying speeds and densities originating from different regions of the sun.
- Upon reaching Earth, the solar wind propels charged particles into the magnetosphere and along Earth's magnetic field lines, particularly towards the poles.
GS-I/Art and Culture
Great Pyramid of Giza
Source: Times of India

Why in News?
A recent finding of a hidden structure close to the iconic Great Pyramid of Giza has the potential to alter our perceptions of these ancient monuments.
About the Great Pyramid of Giza:
The Great Pyramid of Giza, also known as the Great Pyramid or Great Pyramid of Khufu, stands as an ancient Egyptian pyramid and is the largest among the three Pyramids of Giza.
1. Location: It is situated on the Giza plateau, approximately five miles west of the Nile River, near Cairo, Egypt.
2. Construction:
- Constructed by Khufu (Cheops), the second ruler of Egypt's 4th dynasty (around 2580 BC).
- Initiated shortly after Khufu's ascension to the throne in 2580 BC and completed around 2560 BC.
3. Historical Significance:
- Before the Eiffel Tower's completion in 1889, the Great Pyramid held the title of the world's tallest human-made structure for over 3,000 years.
- First excavated in 1880 by Sir William Matthew Flinders Petrie, a British archaeologist, using modern techniques and scientific analysis.
Features of the Great Pyramid:
- Original Height and Dimensions:
- Initially approximately 481 feet tall, now standing around 455 feet due to erosion and top piece removal.
- Each side at the base measures roughly 755 feet.
- Composition: Comprised of over two million stone blocks, each weighing an estimated 2000 pounds (907 kg).
- Internal Structure:
- Contains three primary chambers: the King's Chamber, the Queen's Chamber, and the Grand Gallery.
- Small tunnels and air shafts connect the chambers externally.
- Architectural Details:
- The pyramid's sides ascend at an angle of 51.87° and are precisely aligned with the cardinal points of the compass.
- The core comprises yellowish limestone blocks, while the inner passages are of finer, light-colored limestone.
- The burial chamber is constructed using massive granite blocks.
Key Points about the Pyramids of Giza:
- Overview: These three pyramids were built during the 4th dynasty (c. 2575–c. 2465 BCE) on a rocky plateau along the west bank of the Nile River in northern Egypt.
- Designations and Builders: Each pyramid—Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure—corresponds to the respective kings for whom they were constructed.
- Sequence of Construction:
- The oldest and northernmost pyramid was built for Khufu, the second ruler of the 4th dynasty.
- The middle pyramid was erected for Khafre, the fourth king of the 4th dynasty.
- The last and southernmost pyramid was constructed for Menkaure, the fifth ruler of the 4th dynasty.
- Significance: The Pyramids of Giza is the sole surviving Wonder of the Ancient World.
GS-II/Polity and Governance
Candid Notes on the NHRC's Status Deferral
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
The National Human Rights Commission of India (NHRC) has been informed that the deferral of its status will continue for another year. The Sub-committee on Accreditation (SCA) of the Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) extended the deferral in 2023.
About the National Human Rights Commission of India (NHRC)
- The NHRC is a statutory body established under the Protection of Human Rights Act of 1993.
- It is responsible for promoting and safeguarding human rights in India, investigating complaints of violations, and addressing human rights issues.
- The NHRC plays a vital role in ensuring accountability and justice for victims of human rights abuses.
Deferral Status:
- The deferral of NHRC's status indicates a temporary postponement of its accreditation, pending improvements in compliance with the Paris Principles.
- Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) evaluates NHRIs based on adherence to the Paris Principles, international standards for NHRIs.
About Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI)
- GANHRI is an international network of NHRIs worldwide.
- Initially known as the International Coordinating Committee (ICC) of National Institutions for the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights, it was renamed GANHRI in 2009.
Challenges Faced by Indian NHRC
- Ideological Conflict: Mentions of 'Manusmriti' in NHRC's documents have caused controversy among historically disadvantaged groups due to its association with discrimination.
- Conflict with Paris Principles: Foundational values of equality in the Indian Constitution clash with Manusmriti's caste-based principles.
- Previous Deferral: NHRC was previously placed in the deferral category by GANHRI in 2017, which was later lifted after a review.
Importance of 'A' Status
- 'A' status accreditation allows NHRC to participate in the work of GANHRI, the Human Rights Council, and other UN mechanisms.
Proposed Actions
- Comprehensive Review: Conduct an in-depth evaluation of NHRC's policies, practices, and structure to identify areas for enhancement.
- Strengthen Compliance: Implement measures to ensure compliance with the Paris Principles, enhancing autonomy and effectiveness in addressing human rights violations.
GS-II/Governance
On the importance of Regulatory Sandboxes in Artificial Intelligence
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
Regulatory sandboxes are now widely used in many countries because they allow new ideas to be tested in a controlled and supervised environment.
What are Regulatory Sandboxes?
- A regulatory sandbox allows businesses to experiment with new products under supervision.
- They are commonly used in heavily regulated sectors like Finance and Energy.
- Regulatory sandboxes can be applied to specific areas such as AI or GDPR to promote responsible innovation.
Regulatory Sandboxes around the World
- Over 50 countries are currently utilizing fintech sandboxes according to the World Bank.
- Japan introduced a sandbox regime in 2018 open to various technologies and industries.
- The UK's sandbox explores technologies like voice biometrics and facial recognition.
Significance of Regulatory Sandboxes
- Regulators gain a better understanding of innovative products, aiding in rule-making.
- Provides a controlled environment for innovators to test new technologies.
- Promotes collaboration between innovators and regulators.
- Benefits consumers by fostering innovation and access to safer products.
Need for a Balanced Approach
- Regulatory sandboxes strike a balance between innovation and regulation.
- Encourages responsible innovation through risk mitigation and ethical development.
India's Approach towards Regulatory Sandboxes
- India's strategy should consider economic, ethical, and societal factors.
- Using sandboxes as a preparatory step before imposing strict regulations.
- Advocating for adaptable and progressive AI legislation.
- Ensuring AI development aligns with India's cultural and ethical values.
Global AI Regulatory Landscape
- The EU, U.S., U.K., China, and Singapore have varying approaches to AI regulation.
- India must implement regulations to harness the potential of AI effectively.
GS-III/Defence and Security
Exercise Tarkash
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The India-U.S joint exercise in conducting coordinated operations in urban counter terrorism contingencies will conclude in Kolkata.
About Exercise Tarkash:
- It represents the seventh iteration of the joint counter terrorism exercise between India and the U.S.
- This exercise involves the elite National Security Guard (NSG) and the U.S. Special Operations Forces (SOF), commencing on April 22, 2024.
Objective:
- The primary goal of this bilateral exercise is to establish a functional relationship and boost interoperability between the two special forces. This aims at enhancing coordinated counter terror operations in urban contexts.
- Moreover, the exercise seeks to enhance bilateral cooperation between India and the U.S. concerning combating terrorism in all its forms and manifestations.
Key Activities:
- The exercise includes sharing best practices, tactics, techniques, and procedures across a broad spectrum of counter terror operations in urban environments.
- Activities encompass close-quarter battles, building intervention drills, and hostage rescue operations, among others.
GS-III/Science and Technology
Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
Source: Wionews

Why in News?
NASA's upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is set to undertake a groundbreaking mission to search for primordial black holes dating back billions of years to the Big Bang.
About Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope:
- It will offer one of the deepest-ever views into the heart of our Milky Way galaxy.
Objectives:
- Monitoring hundreds of millions of stars to detect subtle flickers indicating the presence of planets, distant stars, icy objects in the solar system's outskirts, and isolated black holes.
Instruments of the Telescope:
- Wide Field Instrument:
- Field of view 100 times greater than the Hubble infrared instrument, enabling more sky coverage with reduced observing time.
- Measurement of light from a billion galaxies throughout the mission's duration.
- Conducting a microlensing survey of the inner Milky Way to identify approximately 2,600 exoplanets.
- Coronagraph Instrument:
- Technology demonstration focusing on high contrast imaging and spectroscopy of individual nearby exoplanets.
- Galactic Bulge Time-Domain Survey:
- Concentration on the Milky Way using infrared vision to see through dust clouds obstructing the view of the central region of our galaxy.
- Plan to capture images every 15 minutes continuously for about two months, repeated six times during Roman's five-year primary mission, totaling over a year of observations.
GS-III/Environment and Ecology
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 15th May 2024
|
Download as PDF |
Armoured Sailfin Catfish
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
CSIR-Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) scientists have discovered that the armoured sailfin catfish has proliferated in 60% of the water bodies in the Eastern Ghats. This expansion has led to damage to fishing nets and the local ecosystem.
About Armoured Sailfin Catfish:
- Commonly known as the Rakashia or devil fish, the armoured sailfin catfish is scientifically labeled as Pterygoplichthys and is categorized as an invasive species.
- It has a remarkable ability to survive on a varied diet and can thrive in oxygen-depleted environments. Additionally, it can move on land using its strong fins.
- Initially introduced for its distinctive appearance and its capacity to clean algal growth in tanks and aquaria.
- Out of the 14 species identified as invasive by the National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) of India, six were introduced primarily for the ornamental fish trade.
- Within the six species listed, four belong to Pterygoplichthys, establishing it as one of the most invasive fish genera.
- It has gained notoriety due to its lack of commercial value, sharp spines, and sturdy body, posing risks to fishing nets and causing injuries to fishermen on occasions.
Impact on Biodiversity:
- The armoured sailfin catfish is known for consuming native fish species extensively, endangering the fragile aquatic ecosystem.
- The population of this species has surged significantly. This surge was identified through a unique 'eDNA-based quantitative PCR assay' developed by the institute scientists to track the presence and spread of such invasive species.
What is eDNA?
- Environmental DNA (eDNA) refers to the DNA released by all organisms into their surroundings through natural processes during their lifespan or after death.
- Source: It originates from cellular material shed by organisms (via the skin, excrement, etc.) into aquatic or terrestrial environments that can be sampled and monitored using new molecular methods.
GS-III/Science and Technology
The Challenge of Extra-Pulmonary TB
Source: The Hindu
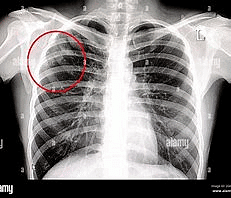
Why in News?
A tuberculosis patient receives treatment from a nurse (instead of a specialist) at a TB hospital in Guwahati.
Why is Extra-Pulmonary TB Important?
Extra-Pulmonary TB refers to tuberculosis that affects organs other than the lungs. Recently, a TB patient in Guwahati received treatment from a nurse instead of a specialist, highlighting the significance of understanding and addressing this form of the disease.
Understanding Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a severe infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) that primarily impacts the lungs but can extend to other body parts, leading to tissue destruction. It is a contagious condition affecting numerous individuals in India, representing more than 20% of TB cases.
Current Status of Extra-Pulmonary Tuberculosis in IndiaEPTB Statistics in India
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), India accounts for a substantial proportion of global TB cases, with over 10 million new cases annually. However, estimating the burden of Extra-Pulmonary TB (EPTB) is challenging due to its often stain-negative nature, making detection difficult through standard tests.
Lack of Awareness Concerning EPTB
- Physician Unawareness: Many healthcare providers are uninformed about EPTB affecting organs beyond the lungs, leading to underdiagnosis.
- Patient Unawareness: Approximately 1/5th of TB patients have EPTB, but most cases remain undiagnosed. Those diagnosed often struggle to access specialized healthcare facilities for treatment.
Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnostic Ambiguity: The lack of precise diagnostic criteria complicates accurate EPTB identification.
- Treatment Complexity: Well-defined treatment protocols for EPTB are scarce, hindering effective management. Despite initiatives like INDEX-TB by the WHO, implementation remains inadequate.
- Fragmented Data Collection: Current data collection systems for EPTB are disjointed, with various departments following disparate practices, leading to incomplete records.
Importance of Research and Development for EPTB
- In-depth Understanding Needed: Persistent disease markers post-treatment resolution pose challenges for individuals with EPTB, prompting the necessity for thorough research on infection mechanisms.
- Utilization of Advanced Tools: Leveraging advanced immunological tools like single-cell RNA sequencing can unveil immune mechanisms, enhancing treatment comprehension and potentially reducing the duration of anti-TB therapy.
|
39 videos|4560 docs|976 tests
|























