Notes: Motivation & Learning | Child Development and Pedagogy for CTET Preparation - CTET & State TET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Motivation |

|
| Principles of Motivation in Learning |

|
| Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs |

|
| Suggestions for Application to Education |

|
| Motivation and Learning |

|
Motivation serves as the mental fuel that sparks the mind's desire to achieve greatness. It plays a crucial role in the teaching and learning process, significantly influencing its success. The level of motivation in students can determine how well they reach their learning goals. Thus, motivation is fundamental to the success of the teaching and learning process. Without it, achieving learning objectives becomes challenging. When students are motivated, they approach the teaching and learning process with enthusiasm, driving them to study effectively. Consequently, motivation and learning are closely linked, working together harmoniously.

Motivation
Motivation is a key concept in psychology, referring to the factors that move or activate individuals. We recognize motivation when people work towards specific goals. For instance, observing a student diligently working on every task suggests a strong motive to achieve. Human behavior generally responds to internal (physiological) or external (environmental) stimuli, often with a specific purpose or goal in mind. Motivation is defined as the process of activating, maintaining, and directing behavior towards a particular goal.
Various thinkers have defined motivation in different ways:
- Skinner: “Motivation is the super highway to learning.”
- Good: “Motivation is the process of arousing, sustaining, and regulating activity.”
Types of Motivation
Motivation can be driven by internal or external factors. Internal motivation arises from within us, such as the desire for food or sex (intrinsic motivation), while external motivation is influenced by our environment, like the need for recognition or approval (extrinsic motivation). Based on this, motivation is categorized into two types:
1. Intrinsic (Internal) Motivation:
- It is an internal force or motive within the individual that propels them to display certain behaviors.
- It is an innate or genetically predetermined disposition to behave in a particular way in specific situations.
- This type of motivation fosters feelings of self-confidence and competence. For example, a student who is intrinsically motivated may engage in a task because they enjoy it.
2. Extrinsic (External) Motivation:
- It is driven by external or environmental factors that set an individual’s behavior into motion. Incentives or reinforcements drive behavior towards a goal.
- A student who is extrinsically motivated will perform an action to receive a reward or avoid punishment. For instance, a student may study hard to achieve a better grade, or a runner may practice to win a prize.
- Extrinsic rewards should be used cautiously as they can potentially decrease intrinsic motivation. For example, while extrinsic incentives might encourage a student to participate in an uninteresting task, they could undermine their intrinsic and ongoing motivation.
- Student motivation relates to their desire to participate in the learning process and the reasons or goals underlying their involvement or lack thereof in academic activities.
Characteristics of Motivation
From the definition of motivation, we can identify the following characteristics:
1. Motivation is a Psychological Phenomenon:
- Motivation is an internal feeling generated within an individual. Motivating factors are usually unconscious but are aroused by other actions.
2. Motivation is Based on Needs:
Needs may be consciously or unconsciously felt and can be:
- Fundamental needs such as food, clothing, and shelter.
- Ego-satisfaction needs such as self-development and self-actualization.
- These needs vary among individuals and can change over time.
3. Goals are Motivators
- Motivation leads to goal-directed behavior. When a person feels a need, they behave in ways to satisfy that need.
4. Motivation is Different from Satisfaction:
Motivation is a drive towards an outcome, whereas satisfaction involves outcomes already experienced. Satisfaction is the contentment felt when a desire is fulfilled.
5. Motivation is a Continuous Process:
- Wants are innumerable and cannot be satisfied all at once. As the satisfaction of needs is an ongoing process, so is the process of motivation.
6. Motivation is Related to the Person in Totality:
- A person’s basic needs are interrelated, as each individual is an integrated, organized whole.
Principles of Motivation in Learning
Motivating students is a complex task, regardless of their age. When students are eager to complete their work and succeed, the classroom environment becomes more positive and productive. Here are some useful strategies for teaching:
- All Learning Must Have a Purpose: Teachers and students should collaborate to set long-term goals, ensuring that the work is relevant to students’ lives and driven by a purpose. Rarely do students work just for the sake of working.
- Students Need Skills and Knowledge: All students require the necessary knowledge to complete their work and achieve their goals. Helping students achieve their short-term goals helps develop the competencies they need to be successful. Skills such as listening carefully and paying attention are crucial for making learning accessible.
- Specific Directions Empower Students: When students know exactly what they need to do to complete assignments, they approach their work with confidence and interest. Providing clear, concise, and logical directions requires practice.
- Students Want to Have Fun While They Work: Teachers who offer enjoyable learning activities find that students are less likely to be bored.
- Offer Activities that Involve Higher-Order Thinking Skills: Students find open-ended questions and critical thinking more engaging than activities that merely require recalling facts. While rote drills have a place in any learning environment, higher-level thinking skills inspire more enthusiasm.
- Curiosity is an Important Component of Motivation: When students want to learn more about a topic, they are more willing to tackle challenging assignments to satisfy their curiosity. Even something as simple as posing a provocative question can spark curiosity.
- A Blend of Praise and Encouragement is Effective in Building Self-Reliance: Teachers who offer sincere praise and encouragement create a positive, nurturing classroom atmosphere. When students know they are on the right track, they are more inclined to continue their efforts.
- A Combination of Extrinsic and Intrinsic Rewards: Rewards help increase students’ focus and engagement. While both types of rewards can motivate students independently, their combined effect is more significant.
- Involve Students in Collaborative Activities: When students work together, both motivation and achievement increase.
- Students Tend to Work Harder When They Believe Their Teacher Likes Them: Students are more inclined to work for a teacher who they believe cares about them. Building a positive relationship with students is crucial for maintaining their motivation and engagement.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow's theory of motivation suggests that human behavior is driven by both internal and external motivational factors, which he calls 'needs'. He emphasized that humans have the unique ability to make choices and exercise free will. These needs, present in all cultures, are both physiological and psychological. Maslow described these needs as hierarchical, meaning that some needs are more basic or powerful than others, and as these needs are satisfied, higher needs emerge. He classified them into basic needs and growth needs, with additional levels of needs proposed by other psychologists.
Basic Needs
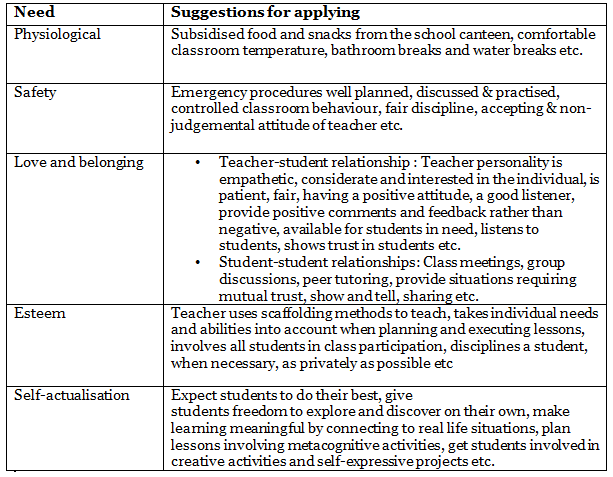
- Physiological: These are the needs for sleep, rest, food, drink, shelter, sex, and oxygen.
- Safety: These needs involve being safe from harm, having a predictable world with consistency, fairness, routine, and a sense of stability and security.
Growth Needs
1. Love and Belonging:
- The need for love and affectionate relationships, belonging to a group, and caring for others.
2. Esteem:
This has two parts:
- Self-respect: The desire for confidence, competence, adequacy, achievement, and mastery.
- Respect of others: The desire for acceptance, recognition, reputation, appreciation, status, and prestige.
3. Understanding and Knowledge:
- The need to satisfy curiosity, explore, discover, find solutions, look for relationships and meaning, and seek intellectual challenges.
4. Aesthetics:
- The need for beauty in one’s surroundings.
5. Self-Actualization:
- The need for growth, development, and the utilization of one’s potential, achieving what one wants to achieve in life, and self-fulfillment.
Suggestions for Application to Education
 |
Download the notes
Notes: Motivation & Learning
|
Download as PDF |
Motivation and Learning
Motivation plays a crucial role in a student’s learning and behavior in several ways:
- Guides Behavior Towards Goals: Motivation directs students towards specific objectives, influencing their choices, such as whether to take up physics or art, complete a difficult homework assignment, or spend time playing video games with friends.
- Boosts Effort and Energy: It determines the amount of effort and energy learners invest in activities that align with their goals and needs. Motivated students engage in tasks with enthusiasm and dedication rather than indifference.
- Encourages Task Initiation and Persistence: Students are more likely to start tasks they are genuinely interested in and persist in completing them despite challenges or interruptions.
- Influences Cognitive Processes: Motivation affects what learners focus on and how efficiently they process information. Highly motivated students strive to understand concepts deeply and think about their practical applications in real life.
- Determines Perception of Rewards and Consequences: Students with high academic motivation take pride in achieving high grades and feel disappointed with low scores, shaping their learning behavior.
- Enhances Performance: By driving goal-oriented behavior, increasing effort, sustaining engagement, improving cognitive processing, and influencing reactions to outcomes, motivation ultimately leads to better academic performance.
Important Suggestions to Keep Students Motivated for Learning
- Plan for every class; never teach without preparation.
- Consider the strengths and limitations of each student. Reward strengths and help strengthen weaknesses.
- Vary instructional strategies, such as lectures, demonstrations, discussions, case studies, and group activities.
- Review learning objectives with students so they know what they are expected to learn and achieve.
- Encourage students to share ideas and comments, even if incorrect. Involve them in teaching and ask for feedback.
Importance of Motivation for Teachers
- Make your classes relevant to students and the world around them.
- Ensure consistency in treating students.
- Ensure that tests are current, valid, and reliable.
- Align assessments with course objectives.
- Provide opportunities for students to speak in class.
- Plan for 30 to 40 minute periods to maintain student attention.
- Be expressive and productive in your teaching.
- Create a competitive class environment.
|
69 videos|101 docs|29 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Motivation & Learning - Child Development and Pedagogy for CTET Preparation - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are the key principles of motivation in learning? |  |
| 2. How does Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs relate to education? |  |
| 3. What are some practical suggestions for applying motivation principles in education? |  |
| 4. Why is motivation important in the learning process? |  |
| 5. How can teachers assess student motivation effectively? |  |





















