UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 20th May 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I/Geography
Speculoos-3b: A New Earth-Sized Exoplanet Discovered
Source: Times of India

Why in News?
Astronomers recently found a new exoplanet, Speculoos-3b, which is similar in size to Earth. It orbits around an ultracool red dwarf star.
Back2Basics: Red Dwarf Star
- Red dwarfs are the most common type of stars in our Milky Way galaxy.
- These stars have low luminosity, making them difficult to observe individually.
- Examples of red dwarfs include Proxima Centauri, the closest star to the Sun, and fifty out of the sixty nearest stars to our solar system.
- Approximately three-quarters of the fusing stars in the Milky Way are estimated to be red dwarfs.
About Speculoos-3b
- Speculoos-3b, an Earth-sized exoplanet, was recently discovered orbiting an ultracool dwarf star.
- The discovery was led by Michael Gillon's team from the University of Liege in Belgium.
- Located around 55 light-years away from Earth, Speculoos-3b receives nearly ten times more solar energy per second compared to Earth due to its short orbital period.
SPECULOOS Project
- The SPECULOOS project aims to explore exoplanets orbiting ultra-cool dwarf stars.
Project Overview
- The discovery of Speculoos-3b was made under the SPECULOOS project.
- The project is conducted by the University of Liege (Belgium) and the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge (United Kingdom).
Astrophysical Significance of the Discovery
- Ultracool dwarf stars, like the host star of Speculoos-3b, make up about 70% of all stars in the galaxy and have long lifespans of up to 100 billion years.
Importance for Life's Potential
- The extended lifespan of ultracool dwarf stars offers a stable environment that could potentially support life development on orbiting planets.
GS-I/Geography
Summer Solstice
Source: Live Science

Why in News?
The summer solstice heralds the start of astronomical summer in the Northern Hemisphere and marks the day with the most daylight for the year.
- Definition: The summer solstice signifies the beginning of astronomical summer in the Northern Hemisphere and represents the day with the longest daylight period of the year.
- Meaning of Solstice: In Latin, "Solstice" translates to "sun stands still".
- Annual Phenomenon: It is an annual astronomical event that brings about the longest day of the year.
- Position of Northern Hemisphere: During the summer solstice, the Northern Hemisphere is inclined towards the sun, receiving the full intensity of its rays.
- Earth's Axis Tilt: During the solstice, the Earth's axis, around which the planet rotates, is tilted in a manner that the North Pole is inclined towards the Sun while the South Pole moves away from it.
- Axis Tilt Angle: The Earth's axis is typically tilted at 23.5 degrees concerning the Sun.
- Energy Reception: The Earth receives a higher amount of energy from the Sun on this day.
- Variation in Dates: The summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere falls on either June 20 or June 21, while in the Southern Hemisphere, it occurs on Dec. 21 or Dec. 22. This variation is due to the Gregorian calendar having 365 days, with an additional leap day every four years in February.
- Light Distribution: The quantity of light received during the summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere varies according to the latitude of the location. Moving farther north from the equator results in receiving more light. For instance, at the Arctic Circle, the sun does not set during the solstice.
GS-I/Geography
Godavari River
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
Three individuals from Konaseema district, Andhra Pradesh, tragically lost their lives in the recent incident in the Godavari River.
About Godavari River:
- India's second-longest river after the Ganga and the third-largest in India, draining approximately 10% of the country's total geographical area.
- Referred to as 'Dakshina Ganga,' meaning the South Ganges River.
Course:
- The river originates from Brahmagiri Mountain at Trimbakeshwar in Nashik district.
- It spans a length of around 1,465 kilometers.
- The river ultimately meets the Bay of Bengal at Narasapuram in West Godavari district, Andhra Pradesh.
- Its mainstem traverses through Maharashtra, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh, with its basin including parts of Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Chattisgarh, and Odisha.
- The drainage basin covers about 121,000 square miles (313,000 square km).
Geographical Features:
- The basin is bordered by the Satmala hills, the Ajanta range, and the Mahadeo hills in the north, the Eastern Ghats in the south and east, and the Western Ghats in the west.
- The Godavari basin experiences its highest rainfall during the Southwest monsoon.
Tributaries:
- Key tributaries of the river include the Pravara, Purna, Manjra, Penganga, Wardha, Wainganga, Pranhita (formed by Wainganga, Penganga, Wardha), Indravati, Maner, and Sabri.
GS-II/International Relations
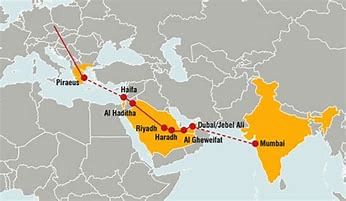
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) Project
Source: Financial Express
Why in News?
An Indian inter-ministerial delegation visited the UAE to discuss the operational aspects of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC), marking a significant step forward since the signing of the agreement.
About IMEC Project
- IMEC is part of the broader Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII), which focuses on infrastructure development in economically developing regions.
- The MoU for IMEC was formally endorsed on September 10, 2023, during the 2023 G20 New Delhi summit.
- Signatories to this agreement: India, United States, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, Italy, and the European Union.
Aim
To integrate Asia, Europe, and the Middle East, enhancing economic cooperation across these regions.
Objectives
- Improve transportation efficiency, lower costs, and promote economic cohesion among participating nations.
- Generate employment opportunities and reduce Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions.
- Facilitate trade and connectivity, thereby reshaping regional integration among Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
Significance
- IMEC, upon completion, will establish a dependable and cost-efficient cross-border ship-to-rail transit network, complementing existing maritime and road transport networks.
- The IMEC Project holds significant promise in redefining regional trade dynamics and fostering sustainable economic growth and cooperation among the involved countries.
GS-II/International Relations
Renew the Generalized System of Preferences
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
Renewing the Generalised System of Preferences (GSP) program is seen as a crucial step that could lead to extensive trade negotiations between the United States and India, potentially taking their bilateral trade relations to new levels.
Generalised System of Preferences (GSP) Program Overview
- What is the Generalised System of Preferences (GSP) Program about?
- The GSP is a trade initiative established by developed nations to support the growth of developing countries.
- Almost all developed countries have their versions of the GSP, customized to align with their economic and policy objectives.
- The program focuses on reducing import tariffs from these nations to boost their economic progress. It is not formally a part of the World Trade Organization.
Origin and Evolution of the GSP
- Conceptualization during the 1960s:
- The idea of the GSP originated in the 1960s as a part of broader initiatives within the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) to enhance developing countries' market access in developed economies.
- Establishment in 1968:
- In 1968, UNCTAD introduced the GSP to provide unilateral, non-discriminatory tariff preferences to developing countries, aiming to foster their economic advancement and industrialization.
- Formation in 1974:
- The United States officially launched its GSP program under the Trade Act of 1974. This act empowered the U.S. to offer duty-free treatment for specific products imported from chosen beneficiary developing countries (BDCs).
Importance of Renewing the GSP
- Unique Features of the GSP program:
- The GSP program stands out as it necessitates periodic approval from the U.S. Congress. Despite bipartisan backing, the program expired in 2020 and awaits renewal.
- Ensuring Market Stability:
- Renewal is essential for maintaining stable market access for developing nations, especially in today's politically polarized environment.
- Promoting Diversification:
- The GSP aids small businesses and women-led enterprises, promoting economic empowerment and reducing dependence on Chinese imports.
- Encouraging Reforms:
- Renewing the GSP can drive labor and environmental reforms while cutting tariff burdens for American businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises.
Significance of the US - India Trade Relationship
- Enhancing Trade Agreements:
- The U.S. and India share a substantial trade partnership, with bilateral trade valued at approximately $200 billion. Renewing the GSP could pave the way for expanded negotiations and potentially a comprehensive trade deal.
- Importance of GSP Renewal:
- Prior to the GSP's expiration, the U.S. and India were close to finalizing a trade agreement covering various sectors like medical devices, agriculture, ethanol, and IT products.
- Current Trade Scenario:
- Despite ongoing trade talks, the U.S. is not actively engaged in new Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), making GSP renewal a crucial mechanism for enhancing trade ties.
Strategic Importance and the Way Forward
- Impact in the Indo-Pacific Region:
- Revitalizing the GSP could significantly boost trade and economic collaboration between the U.S. and India, underlining their dedication to deepening trade relations and addressing broader economic issues.
- Proposed Strategies:
- Utilize GSP as a Negotiation Tool:
- Leverage the renewal of GSP to kickstart broader trade discussions between the U.S. and India, potentially culminating in a more extensive trade agreement.
- Focus on Strategic Sectors:
- Identify and prioritize sectors such as technology, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture where both countries share mutual interests and complementary strengths.
GS-III/Science and Technoloy
Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (LUPEX)
Source: Science and Technology

Why in News?
The India-Japan collaboration for their joint lunar mission, Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (LUPEX), is set to launch in the near future, as per a recent statement by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
About Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (LUPEX)
- The project is a joint initiative between the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
- Scheduled for liftoff in 2025, the mission will be launched using Japan's H3 rocket.
Primary Goal: The main objective is to investigate the moon's southern polar region to study the presence of water and other substances, potentially including surface ice.
The mission aims to demonstrate advanced technologies for surface exploration, particularly focusing on transportation mechanisms and survival during lunar nights.
Comprising a lander and a rover, the mission divides responsibilities between the two agencies: JAXA will oversee the development and operation of the rover, while ISRO will handle the lander that carries the rover.
The rover will autonomously navigate the lunar surface to identify water-rich areas, extract soil samples using a drill, and analyze them with onboard equipment.
Equipped with tools for measuring water content in lunar sand, drilling, and sampling, the rover will also feature cutting-edge technologies for propulsion and power storage.
In addition to ISRO and JAXA instruments, the rover will carry equipment from NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA
GS-III/Environment
Green Credit Program (GCP)
Source: MSN

Why in News?
The Centre has approved 12 greening projects under the Green Credit Program (GCP) and estimates of 24 plans submitted by different state forest departments are under consideration.
Background
- The Green Credit Initiative was initiated by the Indian Prime Minister during COP 28 in Dubai, UAE in 2023.
- It is part of the government's Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE) movement, introduced earlier at COP26 in Glasgow in 2021.
About GCP
- The program employs a market-based approach to incentivize eight specific environmental activities.
- Participants can earn incentives known as 'Green Credits' for their actions.
- It encourages voluntary environmental efforts by various entities.
Aim and Objectives
- The primary goal is to promote sustainable lifestyles and environmental conservation.
- Objectives include enhancing forest and tree cover, identifying degraded land for plantation, and encouraging pro-environment actions.
Implementing Agency and Targeted Sectors
- The Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) oversees the implementation.
- Sectors targeted for implementation include water management, afforestation, sustainable agriculture, waste management, air pollution reduction, mangrove conservation, eco mark label development, and sustainable building and infrastructure.
Compensatory Afforestation and GCP
- GCP allows the exchange of credits to fulfill compensatory afforestation requirements.
- Industries and government bodies are mandated to plant trees on non-forest land to compensate for deforestation.
Greening Projects under GCP
- 12 greening projects have been approved under the program, with 24 more under consideration.
- Public-sector undertakings (PSUs) are encouraged to participate, particularly in states with heavy mining activities.
- Guidelines for third-party project verification are being developed by the government.
- As of April 2024, 13 states have offered nearly 10,983 hectares of degraded forest land for restoration.
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 20th May 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of the discovery of Speculoos-3b, the new Earth-sized exoplanet? |  |
| 2. What is the Summer Solstice and why is it important? |  |
| 3. What is the Godavari River known for and where is it located? |  |
| 4. What is the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) Project and its objectives? |  |
| 5. What is the Green Credit Program (GCP) and how does it contribute to environmental sustainability? |  |