UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 24th May 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I/Geography
Baltic Sea
Source: BBC
Why in News?
A recent proposal by the Russian defense ministry to alter Russia's maritime border in the eastern Baltic Sea caused confusion and concern among NATO members like Finland, Sweden, Lithuania, and Estonia.
Background:
- Finland and the Baltic states are part of both the EU and NATO, with the military alliance dedicated to safeguarding their borders.
About Baltic Sea
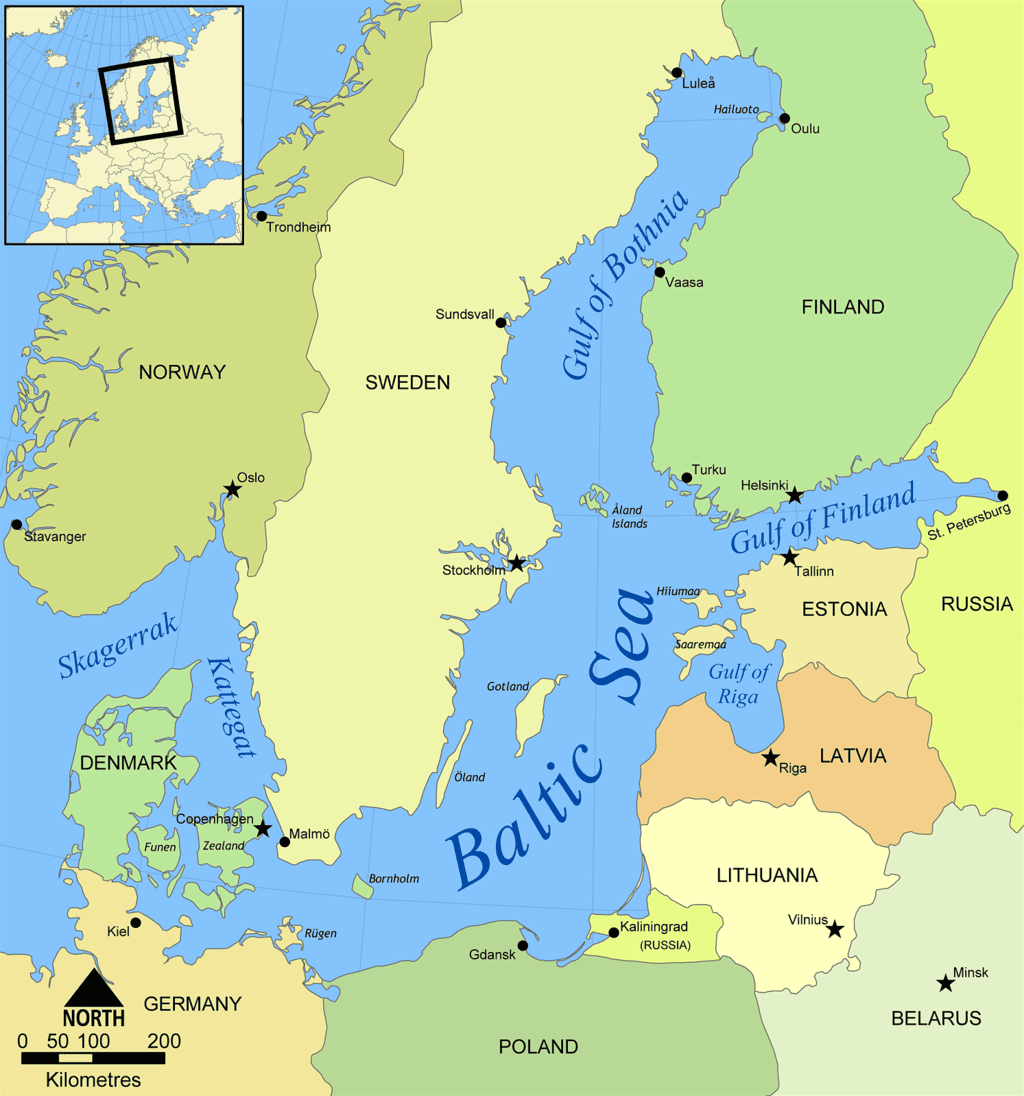
- The Baltic Sea is an extension of the North Atlantic Ocean, stretching from southern Denmark's latitude towards the Arctic Circle. It acts as a barrier between the Scandinavian Peninsula and the rest of continental Europe.
- Surrounded by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North and Central European Plain, the Baltic Sea is both a shelf sea and a marginal sea of the Atlantic. Limited water exchange between the two bodies of water characterizes it as an inland sea.
- Outflows from the Baltic Sea occur through the Danish Straits into the Kattegat via the Øresund, Great Belt, and Little Belt. Notable parts of the Baltic Sea include the Gulf of Bothnia (comprising the Bothnian Bay and Bothnian Sea), the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga, and the Bay of Gdańsk.
Additional Information
- The term "Baltic states" or "Baltic countries" collectively refers to Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. These nations are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD.
- Geographically located on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, these three independent countries are sometimes denoted as the "Baltic nations."
GS-I/Geography
Key Facts about Neanderthals
Source: Times of India

Why in News?
Recent research has revealed that Neanderthals, who lived around 50,000 years ago, were infected with three viruses that continue to impact modern humans today.
About Neanderthals:
- Species: Neanderthals, scientifically known as Homo neanderthalensis, were an extinct relative of modern humans who resided across Europe and parts of Central and Southwest Asia.
- They are our closest extinct human relatives, with evidence suggesting a separation of their lineage from modern humans at least 500,000 years ago.
- The last known Neanderthal populations are believed to have vanished approximately 40,000 years ago, following the migration of modern humans further into Europe.
- Even though Neanderthals are no longer in existence, traces of their genetic material persist in the DNA of present-day humans.
Distinctive Features:
- Neanderthals possessed unique skull characteristics, including a prominent mid-face, angled cheekbones, and a large nose that aided in humidifying and warming cold, dry air.
- Their physical bodies were shorter and more robust compared to modern humans, an adaptation suited for cold climates.
- Despite their sturdy build, Neanderthals had brains comparable in size to or even larger than modern humans, relative to their more muscular physique.
- Analysis of their bones suggests they were highly muscular and robust individuals who frequently endured injuries.
- Unlike modern humans, Neanderthals lacked a distinct chin in their facial structure.
Behavior and Adaptations:
- Neanderthals exhibited advanced behaviors such as crafting intricate tools, controlling fire, constructing shelters, creating and wearing clothing, excelling as hunters of large animals, consuming plant-based diets, and occasionally producing symbolic or ornamental items.
- Evidence suggests that Neanderthals engaged in deliberate burial practices for their deceased, sometimes including offerings like flowers, showcasing a level of symbolic behavior unparalleled among earlier human species.
GS-I/Geography
Mount Ibu
Source: BBC
Why in News?
Recently, Mount Ibu erupted once again, projecting ash up to a height of 4 km, accompanied by streaks of purple lightning flashing around its crater.
About Mount Ibu:
- The Ibu volcano is an active stratovolcano situated along the northwest coast of Halmahera Island in Indonesia.
- Ibu's volcanic activities align with a series of eruptions across various volcanoes in Indonesia, a country positioned on the Pacific "Ring of Fire" boasting 127 active volcanoes.
What is Stratovolcano?
Definition:
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is characterized by a conical shape crafted from layers of volcanic material deposited during successive volcanic eruptions.
Characteristics:
- These volcanic formations typically exhibit a gentle slope at the base, transitioning into a rapid rise near the summit, culminating in tall mountain peaks.
- Stratovolcanoes are commonly situated above subduction zones and are integral components of expansive, volcanically active zones like the Ring of Fire, which envelops a significant portion of the Pacific Ocean.
- The construction of stratovolcanoes involves the layering of lava, ash, and tephra, resulting in a gradual buildup of height. They are distinguished by alternating layers of pyroclastic material and lava.
- Notable examples of stratovolcanoes include the Nevado del Ruiz Volcano and the Ubinas Volcano located in the Andes Mountains of Colombia.
GS-I/Geography
Understanding La Nina and Its Impact on Global Weather
Source: Times of India
Why in News?
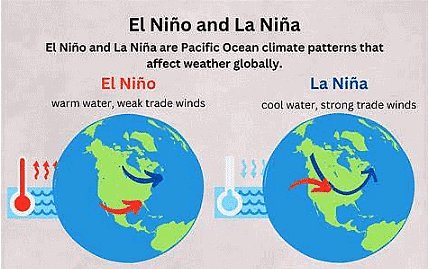
La Nina is a significant climate phenomenon that affects global weather patterns. It involves strong trade winds pushing warm water towards Asia, leading to cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures along South America.
El Nino vs La Nina
- El Nino and La Nina are climate phenomena in the tropical Pacific Ocean, influencing global weather patterns.
- El Nino results in warmer sea surface temperatures, while La Nina leads to cooler temperatures.
Temperature Impacts
- During La Nina, global temperatures are expected to decrease compared to the recent El Nino event.
- Despite cooling effects, temperatures remain higher due to long-term greenhouse gas emissions.
Rainfall Patterns
- La Nina brings drier conditions to Southeast Asia, Australia, and the southern US.
- Wetter conditions are expected in South America and eastern Africa during La Nina.
Tropical Storm Activity
- La Nina increases tropical storm activity in the Atlantic and reduces storms in the Pacific.
- The 2023 Atlantic hurricane season may see more intense storms due to La Nina conditions.
Economic Impacts
- La Nina-related droughts and floods can harm agriculture and infrastructure.
- Fishing communities in the eastern Pacific may face reduced catches due to cooler temperatures.
Impact on India
- La Nina generally leads to above-average monsoon rainfall in India.
- However, heavy rains can cause floods in parts of India and affect crop cultivation.
Climate Change and ENSO
- Climate change may alter the frequency and intensity of El Nino and La Nina events.
- Global warming could lead to more severe weather events associated with ENSO.
Way Forward for Understanding La Nina
- Develop more accurate climate models for predicting ENSO events.
- Promote international collaboration to manage challenges related to ENSO.
GS-II/International Relations
Arab League
Source: BBC

Why in News?
The Arab League recently advocated for the deployment of UN peacekeeping forces in the Palestinian territories during a summit in Manama, Bahrain.
About the Arab League:
- The Arab League, also known as the League of Arab States (LAS), is a regional organization comprising Arab states in the Middle East and portions of Africa.
Formation:
- Established on March 22, 1945, in Cairo.
- Originated as a response to concerns regarding postwar colonial territorial divisions and strong opposition to the establishment of a Jewish state on Palestinian lands.
Objectives:
- The primary objective of the league is to advance Arab interests.
- Main goals include enhancing and coordinating the political, cultural, economic, and social initiatives of its members and resolving conflicts among them or with external parties.
- In 1950, member states additionally committed to providing military assistance for mutual defense.
Headquarters:
- Located in Cairo, Egypt.
Official Language:
- Arabic is the official language of the Arab League.
Membership:
- Comprising 22 current members.
- Founding members include Egypt, Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen.
- Later joined by Libya, Sudan, Tunisia, Morocco, Kuwait, Algeria, Bahrain, Oman, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Mauritania, Somalia, the Palestine Liberation Organization, Djibouti, and Comoros.
- The League recognizes Palestine as an independent state.
- Observer status granted to Brazil, Eritrea, India, and Venezuela.
Council:
- The Council serves as the league's highest authority, comprising representatives of member states, typically foreign ministers, their delegates, or permanent envoys.
- Decisions within the Council are made based on majority agreement, although there is no mechanism to enforce compliance with resolutions.
- Each member holds one vote on the Council, with decisions being binding solely on supporting states.
GS-II/International Relations
Strengthening India's Negotiating Capabilities for FTA with UK, EU
Source: The Print

Why in News?
The Ministry of Commerce and Industry in India is focusing on enhancing the country's negotiation abilities for free trade agreements with the UK, EU, and other nations.
- Experts have highlighted the necessity for a dedicated service to handle trade negotiations rather than relying on generalist civil servants.
Major Pending FTAs of India
- India is in the process of negotiating FTAs with various countries such as the United Kingdom, European Union, Oman, Australia, and reviewing the trade pact with ASEAN.
- Post general elections, there are intentions to reopen discussions with the Eurasian Economic Union, led by Russia.
- India has withdrawn from the RCEP agreement, led by China, after prolonged discussions.
- Challenges exist in finalizing trade agreements with countries like the UK and EU due to issues such as high tariffs and lengthy negotiations.
Challenges with India's Negotiating Capabilities for FTA
- Loss of institutional memory due to frequent transfers of key civil servants involved in trade negotiations.
- Inefficient file management at the Ministry of Commerce leading to a lack of institutional memory.
- Absence of a permanent institutional framework affecting India's negotiations with subject matter experts, particularly from developed nations.
- Lack of accountability among Indian negotiators, hindering the identification of shortcomings.
Strategies to Enhance India's Negotiating Capabilities for FTA
- Clarity in objectives is crucial, understanding the purpose and benefits of FTAs.
- Streamlining tariffs, focusing on Mutual Recognition Agreements to address non-tariff barriers can enhance trade benefits.
- Regular reporting to Parliament and the Cabinet for transparency and accountability.
- Implementation of a structured approval process before and after negotiation meetings.
- Establishment of permanent institutions like Centre for WTO Studies, Centre for Trade and Investment Laws, and Centre for Regional Trade.
- Development of standard operating procedures for trade talks.
- Adaptation to evolving trade dynamics including non-traditional areas like labor and environment.
- Emphasis on record-keeping to preserve institutional memory and third-party audits for transparency.
GS-II/International Relations
BIMSTEC Charter
Source: Hindustan Times

Why in News?
BIMSTEC achieves 'legal personality' following charter enactment
- Ministry of External Affairs announces acceptance of new members and observers
Charter Adoption Details
- Leaders adopted BIMSTEC's inaugural charter during the 5th summit
- Charter establishes legal framework, granting 'legal personality' to the group
- 'Legal personality' allows structured diplomatic dialogue with other entities
Significance for Member Countries
- Enhanced Cooperation
- Strengthened Regional Integration
- Diplomatic Dialogue Opportunities
Challenges in the Current Scenario
- Historical Discord among Member States
- Geopolitical Complexities
- Stagnation of SAARC
Proposed Solutions
- Conflict Resolution Mechanisms Implementation
- High Diplomatic Engagement Advocacy
GS-II/Polity and Governance
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 24th May 2024
|
Download as PDF |
Personality Rights and Their Protection
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
Recently, Scarlett Johansson raised concerns about her voice allegedly being used in OpenAI's GPT-4o without her consent.
Background
- OpenAI introduced GPT-4o, an upgraded AI model enhancing features like Voice Mode for voice interactions.
- One voice option, 'Sky', was accused by Johansson of mimicking her voice.
- OpenAI responded by halting the availability of 'Sky', clarifying it was not Johansson's voice.
Personality Rights
- Definition: Aspects like name, voice, images identifying a celebrity constitute personality rights.
- Examples: Usain Bolt's 'bolting' pose is a trademarked aspect of his personality.
Types of Personality Rights
- Right of Publicity: Protects against unauthorized commercial use of one's likeness.
- Right to Privacy: Safeguards against public representation without consent.
Personality Rights in India
- Legal Basis: Not explicitly outlined in Indian law but rooted in the right to privacy and property.
- Recent Developments: Personality rights recognized as constitutional rights post the 2017 Puttaswamy case.
Legal Precedents
- Shivaji Rao Gaikwad vs Varsha Production: Courts in India acknowledge personality rights.
- ICC Development vs Arvee Enterprises: Right of publicity tied to constitutional rights in India.
Personality Rights on the Internet
- Delhi HC Ruling: Online fame is akin to real-world popularity, with names becoming personal marks.
Personal Rights vs Consumer Rights
- Protection for Celebrities: Shielded from commercial exploitation but liable for misleading endorsements.
- Regulatory Measures: Ministry of Consumer Affairs issued guidelines to curb deceptive endorsements.
Recent Cases
- Delhi HC Orders: Protected personality rights of Anil Kapoor and Jackie Shroff, curbing unauthorized use of their identities.
GS-III/Economy
PRODUCTION LINKED INCENTIVE SCHEME
Source: Financial Express

Why in News?
Smartphone PLI (production-linked incentive), the most successful of all 14 such schemes, may be extended by a couple of years beyond 2025-26 when it officially ends.
Background:-
- The scheme aimed to attract significant foreign investment in the sector while encouraging domestic mobile phone makers to expand their units and presence in India.
Key Takeaways
- The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme is an initiative by the Government of India to boost domestic manufacturing and reduce imports.
- The scheme provides companies with incentives on incremental sales from products manufactured in domestic units.
Key Details about the PLI Scheme
- The scheme was announced with an outlay of INR 1.97 Lakh Crores across 14 key sectors to create national manufacturing champions, create 60 lakh new jobs, and an additional production of 30 lakh crore during the next 5 years.
- It aims to attract foreign companies to set up units in India while encouraging local companies to expand their manufacturing units.
- The scheme targets labor-intensive sectors in the hope to create new jobs for the ballooning employable workforce of India.
List of Sectors under PLI Scheme
- Mobile Manufacturing and Specified Electronic Components
- Critical Key Starting Materials/Drug Intermediaries & Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
- Manufacturing of Medical Devices
- Automobiles and Auto Components
- Pharmaceuticals Drugs
- Specialty Steel
- Telecom & Networking Products
- Electronic/Technology Products
- White Goods (ACs and LEDs)
- Food Products
- Textile Products: MMF segment and technical textiles
- High efficiency solar PV modules
- Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery
- Drones and Drone Components
Implementation Status of PLI Schemes
- PLI Schemes for all 14 Sectors have been notified by the concerned Ministries/Departments after due approval.
- These Schemes are in various stages of implementation by the implementing Ministries/Departments.
Impact of PLI Scheme
- The PLI scheme is expected to have a cascading effect on the country's MSME ecosystem.
- All the approved sectors identified under PLI Schemes follow the broad criteria of focusing on key technologies where India can leapfrog and multiply employment, exports, and overall economic benefits for the economy.
Additional Information
- The smartphone PLI has seen domestic production of phones rising to Rs 4.1 trillion in FY24 from Rs 2.14 trillion in FY20, the year before the scheme was announced.
- Smartphones exports from the country rose to Rs 1.2 trillion in FY24, compared to Rs 27,225 crore in FY20.
GS-III/Environment and Ecology
DEMISE OF RANGELANDS
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
About 50% of the world's rangelands are degraded and require intervention, as per the UNCCD.
- Communities reliant on these lands need targeted assistance.
Understanding Rangelands
- Rangelands span 80 million sq km, encompassing 54% of Earth's land surface.
- They consist of areas with sparse vegetation like grasslands, shrublands, and more.
- India's rangelands cover approximately 1.21 million sq km, ranging from the Thar Desert to Himalayan meadows.
Rangelands Definition
- Rangelands are natural or semi-natural ecosystems grazed by livestock or wild animals.
- These areas contain various vegetation types influenced by climate factors like rainfall and temperature.
- They serve as crucial carbon sinks, reservoirs of freshwater, and barriers against desertification.
Impacts and Findings
- UNCCD reveals that nearly half of the world's rangelands are degraded.
- Primary causes include climate change, poor land and livestock management, biodiversity loss, and land use changes.
- Unclear land rights among pastoralist communities exacerbate degradation.
Role of Pastoralists
- Pastoralists engage in livestock production, including farming of various animal types.
- They heavily rely on quality rangelands for their livelihoods.
- In India, pastoralists contribute significantly to livestock farming and the preservation of indigenous breeds.
Economic Significance
- India hosts 20% of the global livestock population, with 77% managed by pastoralists.
- Pastoralists play a crucial role in milk, buffalo meat, and sheep/goat meat production in India.
- They also safeguard traditional knowledge in animal husbandry.
GS-III/Environment and Ecology
COASTAL REGULATION ZONE
Source: Times of India
Why in News?
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has instructed the Chennai Metropolitan Development Authority (CMDA) to seek approval from the Tamil Nadu State Coastal Zone Management Authority (TNSCZMA) before undertaking any activities on the beaches of the city, in addition to cleaning and removing encroachments.
Background:
Under the ₹100-crore Chennai Shoreline Renourishment and Revitalization Project, the CMDA had outlined plans for 'integrated coastal community development' in Kasimedu, Tiruvottiyur, and Injambakkam-Akkarai stretches. This entailed facilities like a prefab building, cycle track, food court, landscape, open-air theatre, open parking, pedestrian walkway, and a play area in Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) II areas where such activities are prohibited.
Key Takeaways
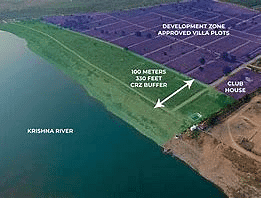
- The Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) is a protective area along India's coastline established by the Indian Government to safeguard the coastal environment and ecosystem.
- The CRZ was initially designated under Section 3 of the Environment Protection Act, 1986 of India in February 1991.
COASTAL REGULATION ZONE NOTIFICATION, 2019
Aside from conserving and safeguarding the coastal environment, the 2019 notification aims to boost activities in coastal regions, fostering economic growth, employment opportunities, and an improved standard of living.
Salient features of the 2019 Notification:
- CRZ-I: Further categorized as CRZ-I A, representing the most environmentally critical zones. CRZ-I B includes the Intertidal zone, between the Low Tide Line (LTL) and High Tide Line (HTL).
- CRZ-II: Encompasses developed land areas near the shoreline, within existing municipal limits or other legally designated urban areas with substantial construction.
- CRZ-III: Comprises relatively undisturbed land areas like rural regions, excluding CRZ-II. Classified into:
- CRZ-III A: Densely populated areas with a population density exceeding 2161 per sq km as per the 2011 census.
- CRZ-III B: Areas with a population density less than 2161 per sq km as per the 2011 census.
- CRZ-IV: Designated as Water area, further split into CRZ-IV A and CRZ-IV B.
- Clearance procedures for projects or activities in CRZ-I and CRZ-IV are overseen by the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change. State-level authorities handle clearances for CRZ-II and CRZ-III with appropriate guidance.
- Temporary tourism facilities like shacks, toilets, change rooms, and drinking water facilities are now permitted in the No Development Zone of CRZ-III areas, with a minimum distance of 10m from the HTL, propelling the tourism industry.
- Critically Vulnerable Coastal Areas (CVCA): Identified regions such as the Sundarbans in West Bengal and ecologically sensitive areas like the Gulf of Khambat and Gulf of Kutchh in Gujarat, among others, are designated as CVCA. These areas involve the engagement of coastal communities, particularly fisherfolk, dependent on coastal resources for sustainable livelihood.
GS-III/Science and Technology
Naegleria fowleri or Brain-Eating Amoeba
Source: NDTV Why in News?
Why in News?
Naegleria fowleri, a tiny organism found in warm freshwater, can enter the body through the nose when people swim or dive in contaminated water.
Overview:
- Naegleria fowleri, commonly known as the "brain-eating amoeba," is a single-cell organism that thrives in warm freshwater environments like lakes, hot springs, and poorly maintained swimming pools.
- Discovered in Australia in 1965, this microorganism is microscopic in size and can only be seen under a microscope.
- Among the various species of Naegleria, only Naegleria fowleri poses a threat to humans by causing a rare and often fatal brain infection.
Infection Process:
- The amoeba typically enters the human body through the nasal passages and then migrates to the brain.
- Infections can occur during activities like swimming, diving, or even by exposing the nasal passages to contaminated freshwater sources.
- Notably, Naegleria fowleri does not spread through water vapor or aerosol droplets.
Symptoms and Effects:
- The onset of symptoms, resembling those of meningitis, usually begins within one to 12 days after infection.
- Initial symptoms may include headaches, nausea, and fever, progressing to more severe manifestations like a stiff neck, seizures, hallucinations, and coma.
- Once the amoeba reaches the brain, it causes primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), a severe and often fatal infection.
Survival Rates and Treatment:
- Survival rates for individuals infected with Naegleria fowleri are distressingly low, with a mortality rate of 97%.
- Early diagnosis and immediate treatment are crucial, although the prognosis remains bleak even with prompt medical intervention.
- Treatment protocols recommended by the CDC involve a combination of drugs like amphotericin B, azithromycin, fluconazole, rifampin, miltefosine, and dexamethasone.
Preventive Measures:
- Limiting activities in warm freshwater bodies unless they are properly disinfected with chlorine is advisable.
- When engaging in water activities, using nose protection, maintaining clean swimming pools, and practicing proper hygiene by washing hands thoroughly are essential preventive steps.
- It is recommended to use sterile water for nasal cleaning and to be cautious, especially during hot summer months when the risk of infection is higher.
|
39 videos|4566 docs|979 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 24th May 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are some key facts about Neanderthals? |  |
| 2. How does La Nina impact global weather patterns? |  |
| 3. What is the Arab League and its purpose? |  |
| 4. How does the Production Linked Incentive Scheme work? |  |
| 5. What is BIMSTEC and what is its charter? |  |


























