Second Moment of Area | Civil Engineering Optional for UPSC PDF Download
The area moment of inertia, also known as the second area moment or the 2nd moment of area, is a property of a two-dimensional plane shape that describes how its points are distributed relative to an arbitrary axis in the cross-sectional plane. This property characterizes the deflection of the shape under load.
The area moment of inertia is typically denoted by the letter I when the axis lies in the plane and J when the axis is perpendicular to the plane. Its dimensional unit is length to the fourth power (L4). In the International System of Units, this is measured in meters to the fourth power (m4), while in the Imperial System, it is measured in inches to the fourth power (in4).
This concept frequently arises in structural engineering, where the area moment of inertia measures a beam's flexural stiffness. It is a critical property used to determine a beam’s resistance to bending and to calculate its deflection. There are two primary cases to consider:
- A beam’s resistance to bending is described by the planar second moment of the area, where the force is perpendicular to the neutral axis.
- The polar second moment of the area is used to determine a beam’s resistance when the applied moment is parallel to its cross-section, indicating the beam’s ability to resist torsion.
Area Moment of Inertia Formulas
If we consider the second moment of area for the x-axis, then it is given as,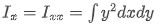
Meanwhile, the “product” moment of area is defined by
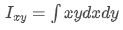
Determining Area Moment of Inertia
1. Parallel Axis Theorem
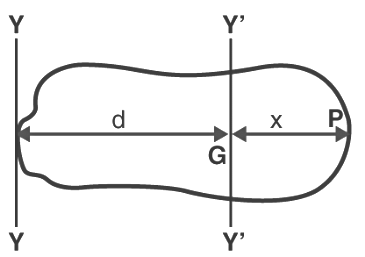
The moment of inertia of a body about any axis is equal to the sum of the moment of inertia of the body about a parallel axis that passes through the centre of mass and the product of its mass and the square of the distance between the two lines.
I = Ig + Md2
M = Mass of the body
D = The perpendicular distance between the two lines
2. Perpendicular Axis Theorem
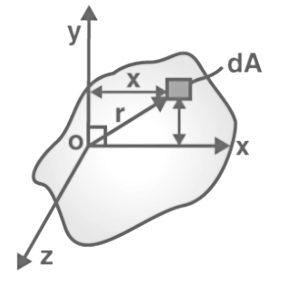
For the planar body, the moment of inertia about a perpendicular axis is equal to the sum of the moment of inertia about two perpendicular axes concurrent with this perpendicular axis, and it lies on the plane of the body. It is given by the expression,
IZ = Ix + Iy
Area Moments of Inertia for Some Common Shapes
Here is a list of area moments of inertia of some shapes.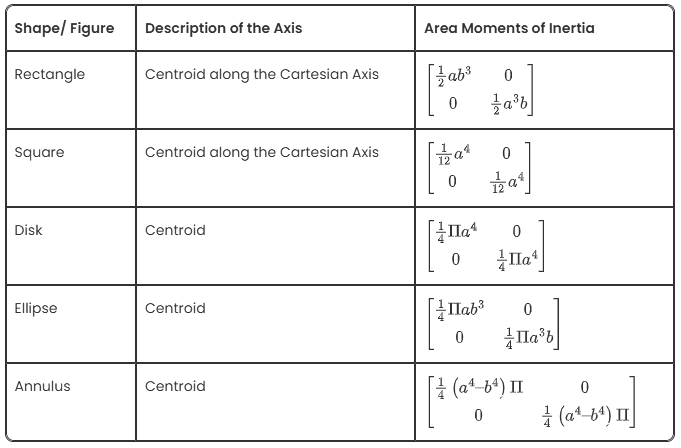
|
352 videos|468 docs|2 tests
|
FAQs on Second Moment of Area - Civil Engineering Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the formula for calculating the second moment of area for common shapes? |  |
| 2. How is the second moment of area used in engineering and design? |  |
| 3. Can the second moment of area be different for the same shape with different orientations? |  |
| 4. How does the second moment of area differ from the first moment of area? |  |
| 5. What are some common applications of the second moment of area in real-world engineering projects? |  |




















