UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 6th June 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS1/Geography
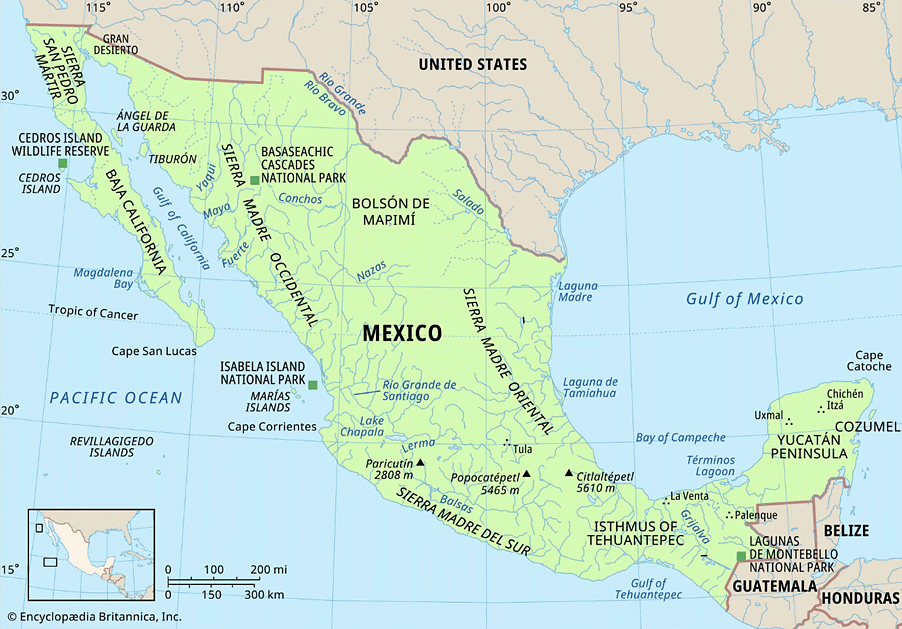
Mexico
Source: India Today
Why in news?
Claudia Sheinbaum was elected as the First Female President of Mexico. Sheinbaum will represent the left-leaning National Regeneration Movement (Morena) party when she takes office on October 1.
About MEXICO:
- Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America.
- It is the world's 13th largest country by area; with a population of almost 130 million, it is the 10th most populous country and has the most Spanish speakers in the world.
- It is the third largest country in Latin America, after Brazil and Argentina.
- Mexico is organized as a federal constitutional republic comprising 31 states and Mexico City, its capital and largest city, and among the world's most populous metropolitan areas.
- The country shares land borders with the United States to the north, with Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; as well as maritime borders with the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Caribbean Sea to the southeast, and the Gulf of Mexico to the east.
- More than half of the Mexican people live in the centre of the country, whereas vast areas of the arid north and the tropical south are sparsely settled. Migrants from impoverished rural areas have poured into Mexico's cities, and nearly four-fifths of Mexicans now live in urban areas.
- The stretch of land called the Yucatán Peninsula juts into the Gulf of Mexico from Mexico's southeastern tip. It was once the home of the Maya civilization.
- Mountains cover much of Mexico. Between the Sierra Madre Oriental mountain range in the east and the Sierra Madre Occidental in the west lie small mountain ranges on the Central Plateau. These regions are rich with valuable metals like silver and copper.
- Mexico is located in one of the Earth's most dynamic tectonic areas. It is a part of the circum-Pacific "Ring of Fire"—a region of active volcanism and frequent seismic activity.
- Mexico is situated on the western, or leading, edge of the huge North American Plate, whose interaction with the Pacific, Cocos, and Caribbean plates has given rise to numerous and severe earthquakes as well as the earth-building processes that produce southern Mexico's rugged landscape.
GS3/Economy
Greedflation
Source: Yahoo Finance

Why in news?
'Greedflation' caused more than half of last year's inflation surge in US, study finds, as corporate profits remain at all-time highs. Corporate profits drove 53% of inflation during the second and third quarters of 2023 and more than one-third since the start of the pandemic, the report found.
What is inflation?
- To begin with, inflation (or the inflation rate) is the rate at which the general price level rises. When it is reported that the inflation rate was 5% in June it implies that the general price level of the economy (as measured by a representative basket of goods and services) was 5% more than what it was in June 2022.
What causes inflation?
- For the most part, there are two main ways in which inflation happens. Either prices get pushed up because input costs have risen — this is called cost-push inflation — or they are pulled up because there is excess demand — this is called demand-pull inflation.
What is the wage-price spiral?
- If prices go up, it is natural that workers will ask for higher wages. But if wages go up, it only fuels the overall demand, while doing nothing to boost the supply. End result: inflation surges further because while a worker has more money, so does his colleague. When they go to the market then the only thing that changes is the price of the good — in other words, inflation rises.
What is Greedflation?
- Greedflation simply means (corporate) greed is fueling inflation. In other words, instead of the wage-price spiral, it is the profit-price spiral that is in play.
- In essence, greedflation implies that companies exploited the inflation that people were experiencing by putting up their prices way beyond just covering their increased costs and then used that to maximize their profit margins. That, in turn, further fueled inflation.
- In the developed countries — in Europe and the US — there is a growing consensus that greedflation is the real culprit.
GS3/Economy
Prestone Curve
Source: The Hindu Why in news?
Why in news?The Preston curve illustrates the correlation between life expectancy and per capita income within a country. Over the years, as India's per capita income increased from about ₹9,000 annually in 1947 to approximately ₹55,000 in 2011, the average life expectancy also saw a significant rise from just 32 years to over 66 years.
About PRESTON CURVE
- The Preston curve represents the empirical relationship between life expectancy and real per capita income. It was named after Samuel H. Preston, who introduced it in 1975.
- Preston's analysis covered the 1900s, 1930s, and the 1960s, consistently demonstrating that individuals in wealthier nations tend to live longer lives compared to those in economically weaker countries.
- As a poorer country experiences economic growth, there is an initial significant improvement in life expectancy due to increased access to better healthcare, nutrition, and overall living standards.
- However, this correlation between per capita income and life expectancy begins to plateau after a certain threshold is reached, indicating that increased income may not continually enhance life expectancy.
Problems in the curve
- Besides life expectancy and per capita income, other developmental indicators like infant and maternal mortality rates, education levels, and healthcare quality also tend to improve as a country's per capita income rises.
- There is a debate among experts regarding the causal relationship between income levels and human development metrics, with some advocating for economic growth as the key driver of development.
- The rapid economic expansions in countries like India and China have been cited as examples of how economic growth can positively influence life expectancy and other developmental markers.
- Contrary views suggest that advancements in life expectancy at lower income levels are often a result of investments in public healthcare and technology rather than just economic growth.
GS3/Economy
Biomass Cultivation on Degraded Land
Source: AIR

Why in news?
The Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA) to the Government of India recently convened the first meeting to discuss biomass cultivation on degraded land for green biohydrogen production and bioenergy generation.
Biomass Cultivation on Degraded Land
- Definition: Cultivating organic matter like crops or trees on land unsuitable for conventional agriculture due to factors like soil erosion, salinization, or deforestation.
Significance/Benefits of Biomass Cultivation on Degraded Land
- Rebuilding soil on degraded land improves soil quality, fertility, and structure.
- Prevents soil erosion and enhances biodiversity.
- Biomass plants absorb carbon dioxide, aiding in climate change mitigation.
- Biomass used for green biohydrogen production and energy generation.
- Promotes agri-export and food security.
Challenges/Issues in Biomass Cultivation on Degraded Land
- Degraded land lacks essential nutrients and water resources.
- Identifying suitable biomass crops for harsh conditions is challenging.
- Initial investments in land preparation and infrastructure can be high.
- Impact on local ecosystems and biodiversity.
Way Forward
- Improving soil fertility by incorporating organic matter like compost.
- Implementing multi-tiered cropping systems on degraded land.
- Using drones for assessment and mapping of degraded land.
- Developing markets for biomass and its by-products.
GS3/Defence & Security
Alleged use of White Phosphorous in Lebanon by Israel
Source: Indian Express

Why in news?
A global human rights group has claimed that Israel used white phosphorus incendiary shells on homes in at least five towns and villages in conflict-affected southern Lebanon.
- Human Rights Watch (HRW) reported no evidence of burn injuries from white phosphorus in Lebanon but noted possible respiratory damage. Human rights advocates argue that using these munitions in populated areas is a crime under international law.
- Israel claims it uses white phosphorus only as a smokescreen, not to target civilians.
- In October 2023, Israel was accused of using white phosphorus in residential areas. This occurred shortly after clashes began between the Israeli military and Hezbollah along the southern Lebanon-Israel border, following the outbreak of the Israel-Hamas war on October 7.
White Phosphorus
White phosphorus is a pyrophoric that ignites when exposed to oxygen, producing thick, light smoke as well as intense 815-degree Celsius heat. Pyrophoric substances are those which ignite spontaneously or very quickly (under five minutes) when in contact with air. Under the Globally Harmonized System of Classification & Labeling of Chemicals, white phosphorus falls under “Pyrophoric solids, category 1”. This category includes chemicals that catch fire spontaneously when exposed to air. White phosphorus emits a distinct garlic-like odour.
Military uses of white phosphorus
- White phosphorus is dispersed in artillery shells, bombs, and rockets. It can also be delivered via felt (textile) wedges soaked in the chemical. Its primary military use is as a smokescreen — used to hide troop movement on the ground. The smoke acts as a visual obscurant.
- White phosphorus is also known to mess with infrared optics and weapons tracking systems, thus protecting forces from guided missiles.
- Munitions can either be ground-burst for more concentrated smoke, or air-burst in order to cover a larger area.
- White phosphorus can also be used as an incendiary weapon.
Harmful effects of white phosphorus
- Upon exposure, white phosphorus can cause severe burns, often down to the bone. The burns are excruciatingly painful, difficult to heal, and susceptible to infections.
- Particles of white phosphorus that remain lodged in the body can reignite if in contact with air.
- Inhaling white phosphorus particles or smoke can cause respiratory damage and harm to internal organs.
- Those who survive initial injuries often experience a lifetime of suffering — with impaired mobility and painful, horrific scars.
- White phosphorus can also devastate infrastructure and property, damage crops and kill livestock, with raging fires, especially in windy conditions.
Use of white phosphorus munitions
- Irish nationalists in the late 19th century first used white phosphorus munitions, in a formulation that became known as “Fenian fire”. Fenian was an umbrella term for the Irish nationalists.
- World War I saw extensive use of the chemical by the British and Commonwealth forces in phosphorus grenades, bombs, shells, and rockets.
- These munitions have since been used in conflicts around the world, from the Normandy invasion in World War II to the US invasion of Iraq in 2004 and the long-drawn Nagorno-Karabakh conflict.
- Most recently, Russia was accused of using white phosphorus bombs during the invasion of Ukraine last year.
Legal status of white phosphorus munitions
- Use is regulated. White phosphorus munitions are not under a blanket ban, though their use is regulated under the International Humanitarian Laws.
- It is not considered a chemical weapon because its operational utility is primarily due to heat and smoke, rather than toxicity. Thus, its use is governed by the Convention on Conventional Weapons (CCW), specifically Protocol III, which deals with incendiary weapons.
- Palestine and Lebanon have joined Protocol III, while Israel has not ratified the protocol.
- Protocol III prohibits the use of airdropped incendiary weapons in concentrations of civilians. However, it restricts some but not all use of ground-launched incendiary weapons where there are concentrations of civilians. The protocol’s definition of incendiary weapons covers weapons that are primarily designed to set fire to and burn people. It excludes multipurpose munitions such as those containing white phosphorus, which are considered to primarily be “smoking” agents.
GS3/Polity and Governance
What is Special Category Status?
Source: First Post

Why in News?
With the General Elections throwing up a fractured mandate, Nitish Kumar’s Janata Dal (United) and Chandrababu Naidu’s Telugu Desam Party are set to play a key role in government formation at the Centre. As a result, their past demands for special category status (SCS) for Bihar and Andhra Pradesh, respectively, are back in focus.
To be able to get the status, states have to fulfil the following requirements (based on Gadgil formula):
- They need to have hilly and difficult terrain.
- They need to have low population density and /or a sizable share of the tribal population.
- They must be in a strategic location along borders with neighbouring countries.
- They must be economically and infrastructurally backward.
- They must have a non-viable nature of state finances.
Evolution of the idea of SCS:
- It was introduced in 1969 on the recommendations of the Fifth Finance Commission (chaired by Mahavir Tyagi) to benefit certain backward states.
- At that time, this was provided to Assam, Jammu and Kashmir and Nagaland.
- The idea of SCS was first formalised in April 1969 when the of fund allocation was cleared by the National Development Council (NDC).
- On the basis of this formula, more states were given the SCS when they attained statehood including Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Tripura, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, and Uttarakhand.
Which states have the SCS?
- Currently, 11 states have the SCS in the country including Assam, Nagaland, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Sikkim, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Uttarakhand, and Telangana.
- Odisha is another state demanding SCS.
What benefits do states with SCS enjoy?
- Benefits to these states included getting Central assistance of as much as 90% in the form of grants and 10% loan for centrally sponsored schemes.
- SCSs were also provided Special Plan Assistance for projects of special importance to the state.
- Further, unspent funds do not lapse at the end of the financial year.
- They also get tax concessions although many tax benefits have now been subsumed under the goods and services tax regime.
Bihar:
- Bihar has been asking for it ever since the mineral-rich Jharkhand was carved out of it back in 2000.
- Ranked as the poorest state in India, according to the Centre's Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) report.
- It is estimated to have nearly 52% of its population without proper access to requisite health, education, and living standards.
- While the state meets most of the criteria for the SCS, it does not fulfil the criteria of hilly terrain and geographically difficult areas.
AP:
- After its bifurcation in 2014, the then UPA government at the Centre had promised to grant SCS to AP to compensate for the loss of revenue and of Hyderabad where much of the development was concentrated.
- Today’s AP is essentially an agrarian state with low economic buoyancy, leading to huge revenue disabilities.
- SCS would mean higher grants-in-aid to the state government from the Centre.
- To illustrate, per capita grants to SCSs is Rs 5,573 crore per year, whereas AP receives only Rs 3,428 crore.
Feasibility:
- According to the 14th Finance Commission, the SCS was a burden on the Centre’s resources and this has been used by the central government to reject SCS to more states.
- In order to plug the resource gap without extending SCS, tax devolution to states has been raised to 42% as recommended by the 14th FC and has been maintained by the 15th FC (41%).
- With the 16th FC already set up and working on the formula for tax devolution between the Centre and states for the five-year period starting April 1, 2026, granting special category status to these two states may be a simpler task.
GS3/Economy
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 6th June 2024
|
Download as PDF |
Appreciation and Depreciation of Rupee
Source: Financial Express

Why in news?
Between April-end 2014 and April 2024 – roughly the time the Narendra Modi-government has been in office – the rupee has depreciated by 27.6% against the US dollar, from Rs 60.34 to Rs 83.38. India trades not only with the US. It exports goods and services to other countries as well, while also importing from them. The strength or weakness of the rupee is a function of its exchange rate with not just the US dollar, but also with other global currencies.
Key takeaways
- Appreciation of the Rupee:
- When the Rupee appreciates, it gains strength against the Dollar. This means you need fewer Rupees to buy a Dollar. For example, if the value of 1 USD decreases from ₹75 to ₹70, this change is termed as an appreciation of the Rupee.
- Here are some impacts of Rupee appreciation:
- Exports: Rupee appreciation affects exporters negatively as they may lose importers because they find imports from India more costly.
- Imports: Importers can import more quantity at a less price. This is because they need fewer Rupees to buy a Dollar.
- Depreciation of the Rupee:
- When the Rupee depreciates, it loses strength against the Dollar. This means you need more Rupees to buy a Dollar. For example, if the value of 1 USD increases from ₹70 to ₹75, this change is termed as depreciation of the Rupee.
- Here are some impacts of Rupee depreciation:
- Exports: Exporters stand to gain the most from Rupee depreciation as it makes exports more competitive.
- Imports: Imports will become costly. This is because importers need more Rupees to buy a Dollar.
- Inflation: The biggest impact of a weakening Rupee is inflation, given India imports more than 80% of its crude oil. This is because the cost of imported goods increases due to a reduction in the value of Rupee.
- IT Sector: The Indian IT sector, which focuses heavily on exports, can achieve more revenue from their global clients due to the decline of the Rupee value.
Remember, the appreciation and depreciation of the Rupee are strongly influenced by the change in demand or supply for the Rupee and the Dollar.
GS3/Economy
Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)
Source: First Post

Why in news?
The government-backed Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) recorded an all-time high of 8.9 million transactions across retail and ride-hailing segments in May. This represented a robust 23 per cent month-on-month increase in total transaction volume, the ONDC said.
About Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)
- The 'Open Network for Digital Commerce' (ONDC), is a Government of India (GoI) backed technology infrastructure. It is a network-centric model, wherein buyers and sellers can transact irrespective of the platforms/applications they use as long as "platforms/applications are connected to this open network".
- In simple terms, ONDC is like a digital road network over which different digital storefronts (in the form of buyer and seller apps) can be built. The digital road network aims to enable e-commerce traffic to travel across these different digital storefronts seamlessly, thereby allowing buyers and sellers to transact regardless of the application / platform they use.
- This is a significant departure from existing platform centric models of e-commerce where buyers and sellers can only interact within walled platforms.
- To illustrate, today, a seller on Amazon cannot reach a buyer on Flipkart, and vice versa.
- ONDC is expected to make e-Commerce more inclusive and accessible for consumers. Consumers can potentially discover any seller, product, or service by using any compatible application or platform, thus increasing freedom of choice for consumers.
- It will enable consumers to match demand with the nearest available supply. This would also give consumers the liberty to choose their preferred local businesses. Thus, ONDC would standardize operations, promote the inclusion of local suppliers, drive efficiencies in logistics, and lead to enhancement of value for consumers.
- ONDC was incorporated as a Section 8 (NON-PROFIT) company in December 2021, with the Quality Council of India and Protean eGov Technologies Limited as Founding Members.
- Various public and private sector entities have invested in ONDC, including Punjab National Bank, State Bank of India, Axis Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank, BSE Investments, Central Depository Services, ICICI Bank, and the Small Industries Development Bank of India.
- It is important to note that the relationship between the GoI and ONDC is not legally defined and it does not flow from an act of parliament.
GS3/Science and Technology
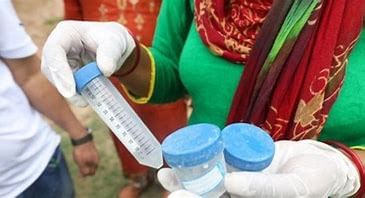
India’s TB Elimination Drive
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
A paper titled ‘Progress and challenges in achieving tuberculosis elimination in India by 2025: A systematic review and meta-analysis’ notes that India faces a daunting challenge in its fight against TB.
About TB (Description, Symptoms, Types, Treatment, TB in India, etc.)
About Tuberculosis (TB):
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection spread through inhaling tiny droplets from the coughs or sneezes of an infected person. It mainly affects the lungs, but it can affect any part of the body, including the tummy (abdomen), glands, bones, and nervous system. TB is a potentially serious condition, but it can be cured if it's treated with the right antibiotics.
Symptoms of TB:
- Persistent cough that lasts more than 3 weeks and usually brings up phlegm, which may be bloody
- Weight loss
- Night sweats
- High temperature
- Tiredness and fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Swellings in the neck
Types of TB:
- Pulmonary TB:
- Latent TB:
- Active TB:
Tuberculosis in India:
The total number of incident TB patients (new and relapse) notified during 2021 in India were 19.33 lakh as opposed to that of 16.28 lakh in 2020. In 2022, 24.22 lakh cases of TB were registered in the country. India continues to have the largest share of the global TB burden.
National TB Elimination Programme:
The National TB Elimination Programme is strengthened to meet the goal of ending the TB epidemic by 2025 from the country, five years ahead of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) for 2030.
National Strategic Plan for Tuberculosis Elimination:
Though the National Strategic Plan for Tuberculosis Elimination (2017-2025) outlined a paradigm shift in approach and strategy to achieve the ambitious goal, by 2020, it became clear that the NSP will not be able to meet these objectives. A new National Strategic Plan for Tuberculosis Elimination (2020-2025) to end TB was launched.
Challenges Associated with TB Eradication in India:
Challenges with regard to this illness in India include poor primary health care and infrastructure in rural areas, unregulated private health care, HIV induced TB cases, lack of hygiene facilities, widespread malnourishment, and poverty.
Way Forward:
Focus should be on understanding key determinants like poverty, under-nutrition, and tobacco smoking for prevention. Gaps in the public healthcare system must be addressed as this is the main medium through which millions of Indians seek treatment. Although the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program has worked toward improving the diagnosis of patients with free tests, free TB drugs, extended adherence support to increase rates of TB treatment completion, and involvement of private healthcare providers, there is more that can be done.
Challenges in achieving tuberculosis elimination in India by 2025:
The mortality rate, excluding HIV co-infected individuals, was approximately 450,000 in 2021, highlighting the severe impact of TB on the country’s public health landscape. The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is looking at reworking the protocol, specifically TB medication and its duration. The objective is to reboot the TB-free initiative with zero deaths, disease, and poverty resulting from the disease.
GS3/Science and Technology
Testing MOND with the Cassini Mission - Is Dark Matter's Rival Theory in Trouble?
Source: Psy.Org

Why in news?
The findings of Cassini mission, which orbited Saturn from 2004 to 2017, provided an opportunity to test Milgromian dynamics (MOND) - an alternative theory to dark matter.
About
Standard Model of Particle Physics
- Particles: Everything around us is made up of tiny particles. The Standard Model identifies the fundamental particles, which are the smallest building blocks of matter.
- Quarks and Leptons: There are two main families of particles:
- Quarks: These combine to form protons and neutrons, which are found in the nucleus of an atom.
- Leptons: The most famous lepton is the electron, which orbits the nucleus of an atom.
Forces
- Fundamental Forces: The Standard Model also explains how particles interact through four fundamental forces:
- Electromagnetic Force: This force is responsible for electricity, magnetism, and light. It's carried by particles called photons.
- Weak Nuclear Force: This force is responsible for some types of radioactive decay and is carried by particles called W and Z bosons.
- Strong Nuclear Force: This force holds the nucleus of an atom together, binding protons and neutrons. It's carried by particles called gluons.
- Gravity: While gravity is a fundamental force, it's not fully explained by the Standard Model. It's described separately by the theory of general relativity.
Interactions
- How They Work: Particles interact with each other by exchanging force-carrying particles. For example, when two electrons repel each other, they exchange photons.
- Higgs Boson
- Mass: The Standard Model also includes the Higgs boson, a particle that gives other particles their mass through the Higgs field.
- Challenges
- The Standard Model is incredibly successful in explaining the known particles and their interactions, but it doesn't include everything.
- For example, the Higgs boson gives mass to quarks, charged leptons (like electrons), and the W and Z bosons.
- However, it is not yet known whether the Higgs boson also gives mass to neutrinos - ghostly particles that interact very rarely with other matter in the universe.
- MOND Theory as an alternative to dark matter
- Background: Origin of MOND Theory
- One of astrophysics' biggest mysteries is why galaxies rotate faster than Newton's law of gravity predicts based on their visible matter.
- To explain this, the concept of dark matter was proposed.
- However, dark matter has never been observed directly, and it doesn't fit within the Standard Model of particle physics.
- In order to address this anomaly, an alternative theory known as Milgromian dynamics (MOND) was proposed by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom in 1982.
- MOND theory suggests that Newton's laws break down under very weak gravity, as at the edges of galaxies.
- MOND has had some success in predicting galaxy rotation without dark matter, but many of these successes can also be explained by dark matter while preserving Newton's laws.
- MOND affects gravity at low accelerations, not specific distances.
- Therefore, while MOND effects typically appear several thousand light years from a galaxy, they could become significant at much shorter distances, such as in the outer Solar System.
- MOND Theory challenged by Cassini mission
- The Cassini mission, which orbited Saturn from 2004 to 2017, provided an opportunity to test MOND.
- Saturn orbits the Sun at 10 AU, and MOND predicts subtle deviations in Saturn's orbit due to the galaxy's gravity.
- Cassini measured the Earth-Saturn distance using radio pulses, but found no anomalies expected by MOND.
- Newton's laws still hold for Saturn, putting the MOND theory in trouble.
- Further evidence against MOND
- Further evidence against MOND comes from wide binary stars.
- A study found that MOND's prediction of faster orbits was incorrect, with a probability of being right equivalent to flipping heads 190 times in a row.
- Additionally, MOND fails to explain the narrow energy distribution and orbital inclinations of comets in the outer Solar System.
- Newtonian gravity is preferred over MOND for distances below a light year.
- MOND also fails at larger scales, like galaxy clusters, where it provides too little gravity centrally and too much at the outskirts. Newtonian gravity with dark matter fits the data better.
- MOND is no longer seen as a viable alternative
- Despite issues with the standard dark matter model, such as the universe's expansion rate and cosmic structures, MOND is no longer seen as a viable alternative.
- Dark matter remains the prevailing explanation, though its nature might differ from current models, or gravity could be stronger on very large scales.
- Background: Origin of MOND Theory
|
39 videos|4566 docs|979 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 6th June 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is Greedflation mentioned in the article? |  |
| 2. What is the Prestone Curve and how is it related to the article? |  |
| 3. What is the Alleged use of White Phosphorous in Lebanon by Israel? |  |
| 4. What is the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) mentioned in the article? |  |
| 5. What is India’s TB Elimination Drive mentioned in the article? |  |


























