Points and Crossings: Learn their Functions & Types | Civil Engineering Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Component Parts of Points and Crossings |

|
| Functions of Points & Crossing |

|
| Important Terms in Points and Crossings |

|
| Types Of Crossing |

|
Points and crossings are essential components of railway infrastructure designed to enable the safe and efficient movement of trains from one track to another. Here's a breakdown of each:
Points (Switches): Points, also known as switches in some regions, are movable sections of rail that allow trains to switch from one track to another. They consist of two movable rails called switch rails, which can be aligned to guide a train either straight ahead or onto a diverging track. Points are typically controlled by a lever mechanism operated manually or electronically by a signaling system.
Crossings: Crossings are sections of track where two rails intersect at an angle. They provide a smooth transition for train wheels to pass from one track to another, whether those tracks are parallel, diverging, or converging. Crossings are designed to accommodate the flanged wheels of railway vehicles, which have a small flange on the inside of the wheel that keeps the train on the track. Crossings feature diamond-shaped plates where the rails intersect, allowing the wheels to roll smoothly over them.
Both points and crossings are crucial for railway operations, allowing trains to change tracks safely and efficiently. They are often combined to form turnouts, which are the junctions where tracks diverge or converge. Proper maintenance and operation of points and crossings are essential for ensuring the smooth flow of train traffic and minimizing the risk of derailments or accidents.
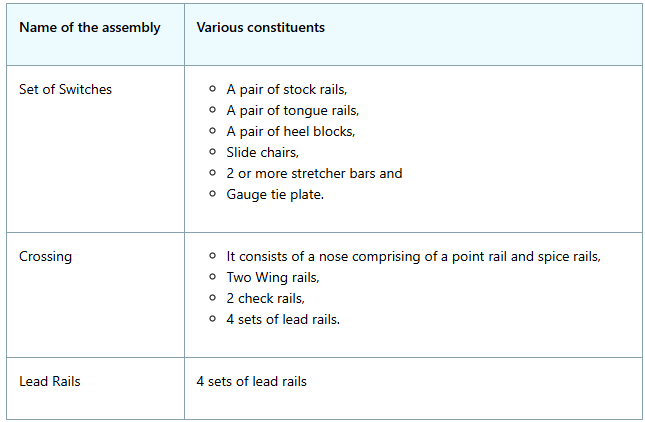
Component Parts of Points and Crossings
- Switch Rails: Movable rails guiding trains between tracks.
- Stock Rails: Fixed mainline rails connecting to switch rails.
- Frog: Diamond-shaped component at rail intersection.
- Check Rails: Side rails guiding train wheels at crossings.
- Switch Drive Mechanism: Operates points and moves switch rails.
- Switch Lever: Controls switch rail position manually.
- Tie Plates and Fasteners: Secure rails to sleepers (ties).
- Crossings and Crossing Nose: Allow trains to cross tracks safely.
Necessity of Points and Crossings
- The wheels of rolling stock have flanges on the inside of the rails to prevent the lateral movement of the trains.
- When trains are diverted along different tracks, these flanges may cause hindrance. Due to this, points and crossings are necessitated to facilitate the transfer and uninterrupted movement of trains when moving from one track to another.
Some of the major functions of Points and Crossings are:
- They facilitate in receiving the trains that approach the railway station.
- Facilitating shunting operations and marshalling of trains.
- Connecting the dispatched train to the designated route.
Functions of Points & Crossing
1. Track Switching: Enables trains to switch between tracks.2. Route Flexibility: Provides multiple track options for efficient train routing.
3. Intersections and Crossovers: Facilitates safe train crossings.
4. Train Routing Optimization: Optimizes routes for improved efficiency.
5. Safety and Risk Mitigation: Ensures safe operations and minimizes accidents.
6. Train Flow Management: Manages train movements and reduces delays.
Important Terms in Points and Crossings
The following terms are often used in the design of points and crossings.Turnout
- It is the arrangement of points and crossings along with the lead rails.
- It facilitates the diversion of the rolling stock from one track to another.
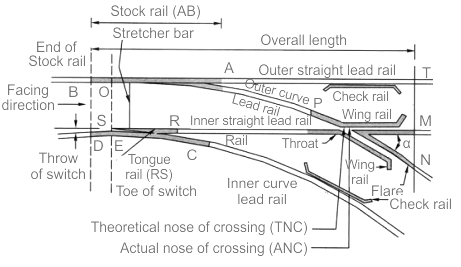 Constituents of a Turnout
Constituents of a Turnout
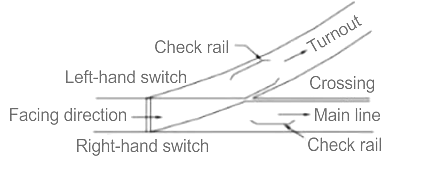
Direction of a turnout
 Left-Hand Turnout
Left-Hand Turnout
- A turnout can be a right-hand or a left-hand turnout on the basis of whether the diversion is to the right or left side.
- The turnout is a right-hand when it facilitates the diversion of trains towards the right side.
- The direction of a turnout is known as the facing direction when the rail vehicle approaches the turnout. In other words, the turnout is in the facing direction when the point first faces the thin end of the switch.
- The direction is called trailing direction when the vehicle negotiates a switch in the trailing direction. In such a case, the rail vehicle first negotiates the crossing and, after that, traverses the switch from the thicker end to the thinner end.
- When an observer stands at the toe of a switch and looks in the direction of the crossing, it is called the facing direction.
- On the other hand, when the observer looks in the opposite direction, it is called the trailing direction.
Tongue rail
- It is a tapered movable rail that is composed of high carbon or high manganese steel.
- It is attached to a running rail at the thicker end.
- A tongue rail is also called a switch rail.
Stock rail
- The running rail against which the tongue rail operates is called the Stock rail.
Points or switch
- A pair of tongue and stock rails alongside the connections and fittings are called Points or Switches.
Crossing
- A crossing is an arrangement provided at the junction/intersection where the two rails cross each other.
- The objective of providing crossing is to allow the passing of the wheel flange of the vehicle from one track to another.
Types Of Crossing
The different types of crossings are:
- Square crossing
- Acute angle or V-crossing or Frog
- Obtuse angle or Diamond crossing
Square Crossing
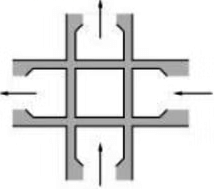
Square Crossing
- Square Crossing is an arrangement formed when two straight tracks cross each other at right angles.
- This crossing is avoided on main lines due to the heavy wear of rails.
Acute Angle Crossing
- This crossing is formed when the right-hand rail of one track crosses the left-hand rail of another track at an acute angle.
- The Acute angle crossing consists of a pair of check rails, a pair of wing rails, and a splice rail. It is used extensively and is also called V-crossing or frog crossing.
Obtuse Angle Crossing
- This crossing is also called Diamond Crossing.
- It is an obtuse angle crossing that is formed when a left-hand rail from one track crosses a right-hand rail of another track at an obtuse angle.
- A typical diamond crossing consists of two acute and two obtuse angle crossings.
|
352 videos|468 docs|2 tests
|
FAQs on Points and Crossings: Learn their Functions & Types - Civil Engineering Optional for UPSC
| 1. What are the functions of points and crossings in railway systems? |  |
| 2. What are the important terms associated with points and crossings? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of crossings used in railway systems? |  |
| 4. How do points and crossings contribute to the overall efficiency and safety of railway operations? |  |
| 5. Why is it important for railway personnel to have a thorough understanding of points and crossings? |  |



















