UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 18th June 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-III/Science and Technology
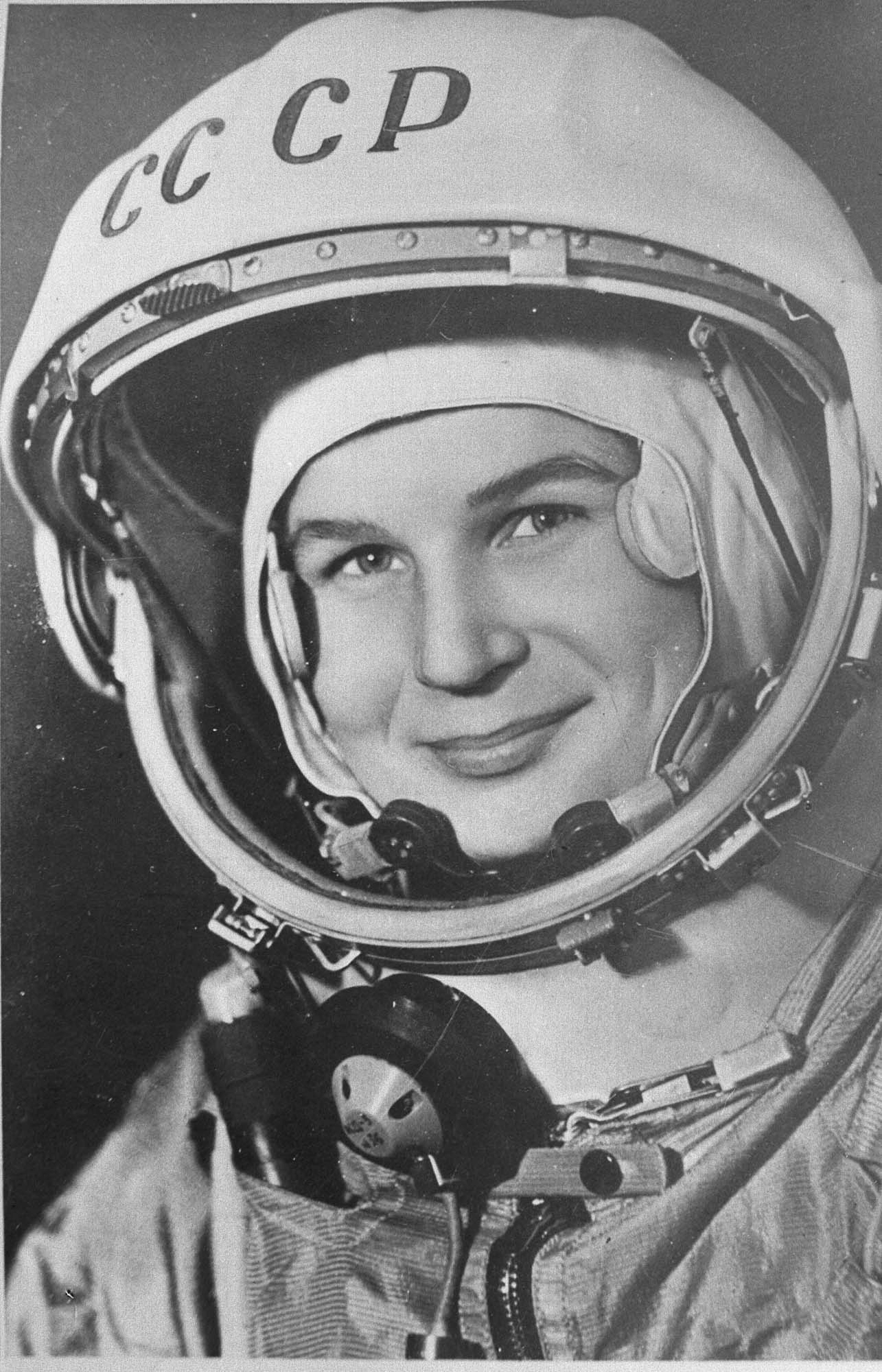
Valentina Tereshkova: The First Woman in Space
Source: Indian Express
Why in news?
On June 16, 1963, Valentina Tereshkova made history as the first woman to venture into space. Her achievement marked a significant milestone in the Space Race between the USA and the USSR during the Cold War.
About Valentina Tereshkova’s Space Journey
- In 1962, Tereshkova was selected among five women for the Soviet space program, aiming to achieve ‘gender equality’ in space exploration.
- The USSR’s decision to send a woman into space was partly influenced by the success of Yuri Gagarin’s mission in 1961 and the desire to surpass the US in space achievements.
- Her affiliation with the Communist Party and her skills as a parachutist were factors in her selection for the Vostok 6 mission.
The Mission – Vostok 6
- On June 16, 1963, Tereshkova piloted Vostok 6, becoming the first woman to orbit the Earth.
- She spent 71 hours, completing 48 orbits around the Earth during her mission.
Impact and Legacy
- Tereshkova’s mission boosted Soviet prestige in the Space Race, following earlier successes like launching Sputnik-1 in 1957 and Yuri Gagarin’s historic flight in 1961.
- Despite her pioneering role, the USA would later achieve milestones like the Apollo moon landings, surpassing Soviet achievements in manned space missions.
- Tereshkova continued to advocate for women’s participation in space exploration and held prominent positions in Soviet politics and the Air Force.
Indian Women in Space
- Kalpana Chawla: Born in Karnal, Haryana, Kalpana Chawla was the first woman of Indian origin in space. She flew on two Space Shuttle missions, including STS-87 in 1997. Tragically, she lost her life during the re-entry of the Space Shuttle Columbia in 2003.
- Sunita Williams: An American astronaut of Indian-Slovenian descent, Sunita Williams has set records for spacewalks and served as a flight engineer on the International Space Station (ISS). She has logged over 322 days in space across multiple missions.
- Sirisha Bandla: An aeronautical engineer and Vice President at Virgin Galactic, Sirisha Bandla became the second India-born woman to travel to space on the Virgin Galactic Unity 22 mission in 2021.
Women Pioneers of ISRO
- Lalitha Ramachandran: Joined ISRO in 1969 as a technical assistant at Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), becoming one of the first female chemical engineers recruited by ISRO. She retired as associate project director of the Cryogenic Upper Stage Project.
- J Geetha: Joined ISRO in 1972 after working at Bhabha Atomic Research Centre. She reminisces about the challenges of data gathering in the pre-internet era and the mentorship she received from stalwarts like Satish Dhawan and Vasant R Gowarikar.
- Radhika Ramachandran: Joined ISRO in 1984 and served in various roles, including technical liaison officer at ISRO’s New Delhi office and director of the Space Physics Laboratory. She highlights the merit-based culture and the support for open discussions and suggestions.
- T S Ramadevi: Joined ISRO in 1970 after completing her BTech from CET, Thiruvananthapuram. She was part of the communications unit and contributed to the growth of ISRO’s transmission technologies. She retired as deputy director of management systems.
- Athula Devi: Joined ISRO in 1987 and retired in January, having been part of the team that developed base software systems for the Gaganyaan launch. She emphasizes ISRO’s growth through failures and the team’s dedication to projects above personal recognition.
PYQ
[2017] India has achieved remarkable successes in unmanned space missions including the Chandrayaan and Mars Orbiter Mission, but has not ventured into manned space missions. What are the main obstacles to launching a manned space mission, both in terms of technology and logistics? Examine critically. (10)
GS-III/Environment and Biodiversity
World Crocodile Day 2024: In 50th year of India's saurian conservation
Source: Hindustan Times
Why in news?
The successful Crocodile Conservation Project in Bhitarkanika National Park is escalating the human-crocodile conflicts affecting local communities.
About the Crocodile Conservation Project
Launch and Objective:
- The Crocodile Conservation Project started in 1975 in Bhitarkanika National Park, Odisha with the main goal of safeguarding the natural habitat of crocodiles and boosting their population through captive breeding due to the low survival rate of hatchlings in the wild.
Historical Context:
- Initiated shortly after the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972, the project was a response to the looming threat of extinction caused by indiscriminate killing for commercial purposes and extensive habitat destruction.
Implementation and Success:
- Under the guidance of HR Bustard, breeding and rearing centers for saltwater crocodiles, muggers, and gharials were established in 34 locations across India. The project in Bhitarkanika, spearheaded by Sudhakar Kar and HR Bustard, has been particularly successful, boosting the crocodile population from 95 in 1975 to 1,811 in the latest reptile census.
Ongoing Efforts:
- Even after retirement, technical expertise and methodology for the annual census of saltwater crocodiles continue to be provided. Sudhakar Kar considers crocodile conservation a lifelong commitment.
About the Issues Faced by Bhitarkanika
- Human-Crocodile Conflict: The growing crocodile population has led to an increase in human-crocodile conflicts. Sudhakar Kar has expressed worry over these conflicts, cautioning locals against entering rivers, creeks, and water bodies inhabited by estuarine crocodiles.
- Impact on Local Communities: Since 2014, conflicts have resulted in 50 deaths. Local villagers have criticized politicians for not adequately addressing safety concerns, impacting political outcomes.
- Preventive Measures: Forest officials have erected barricades around 120 river ghats in and around Bhitarkanika to prevent crocodile attacks on humans.
- Political Implications: The human-crocodile conflict has influenced local political dynamics, with villagers expressing dissatisfaction with incumbents over safety concerns related to crocodile attacks.
Conclusion
- Construct and maintain more robust protective barriers around water bodies, such as reinforced barricades and secure river ghats.
- Create safe, designated areas for water-related activities to minimize the risk of crocodile attacks.
Mains PYQ
- How does biodiversity vary in India?
- How is the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 helpful in the conservation of flora and fauna?
GS3/Environment
FILOBOLETUS MANIPULARIS
Source: Times of India

Why in news?
A rare species of bioluminescent mushrooms, scientifically known as Filoboletus manipularis, has been discovered in the forests of Kasaragod.
- The discovery was made during a micro-fungal survey conducted by the Kasaragod division of the Kerala Forest and Wildlife Department and the Mushrooms of India Community in the Ranipuram forest. Scientists have warned against consuming these mushrooms due to potential toxicity.
About FILOBOLETUS MANIPULARIS
- Filoboletus manipularis is a species of agaric fungus in the family Mycenaceae.
- Filoboletus manipularis is commonly found in Australasia, Malaysia, and the Pacific islands.
- They thrive in tropical, humid environments, typically found in dense forests where there's plenty of decaying organic matter, like fallen trees and leaves. This rich, moist environment provides the nutrients and conditions necessary for their growth and their unique glowing property.
- The glow in Filoboletus manipularis is due to a chemical reaction involving luciferin (a pigment) and luciferase (an enzyme), with oxygen playing a critical role. This reaction produces light, a trait shared with other bioluminescent organisms like fireflies and certain marine creatures.
- In fungi, this glowing mechanism is thought to attract insects, which help disperse the mushroom's spores.
GS3/Economy
GOVT LOOKS AT INCOME TAX RATE CUT TO BOOST DEMAND
Source: Indian Express

Why in news?
As the Indian economy faces the challenge of declining consumption, policymakers are considering restructuring the current income tax system, especially for lower income brackets.
Key Takeaways
- Government officials suggest prioritizing tax rate reductions for lower-income earners over excessive welfare spending to promote fiscal consolidation.
- Cutting taxes for this group could effectively increase disposable income, leading to higher consumption levels and stimulating economic activities.
- Boosting consumption is crucial for revitalizing demand, which is essential for reigniting private investment, particularly in consumer-driven sectors.
- The potential revenue loss from tax cuts necessitates a comprehensive analysis to evaluate the overall impact. While there might be a loss initially, increased disposable income is expected to drive higher consumption, resulting in enhanced tax revenues.
- The government's focus on fiscal consolidation aims to reduce the fiscal deficit to 5.1% of the GDP by 2024-25 and further below 4.5% by 2025-26.
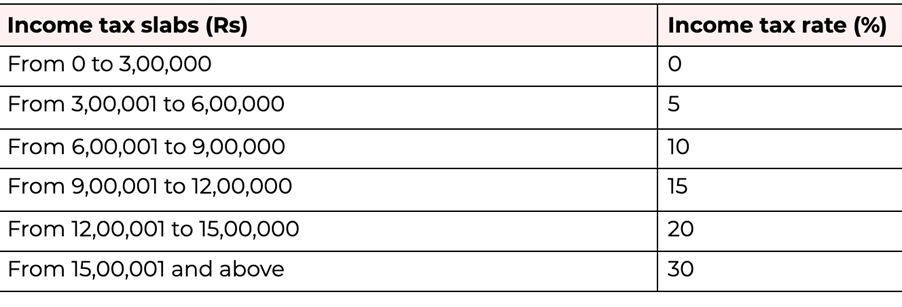
The Challenge with Marginal Income Tax
- Concerns have been raised regarding the steep increase in marginal income tax rates within the current tax structure.
- Under the new system, the tax rate escalates significantly from the 5% bracket at Rs 3 lakh to 30% at Rs 15 lakh, indicating a substantial jump.
- This steep progression poses challenges as the tax burden grows disproportionately compared to income increments.
Focus on Tax Simplification
- Simplifying the tax structure is deemed more effective than extensive spending on welfare programs, which may be susceptible to leakages.
GS-I/Indian Society
An Ageing India: The magnitude and the multitude
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
The phenomenon of ageing stands out as one of the most significant developments of this century, characterized by notable advancements in human longevity alongside historically low reproduction rates.
About the magnitude and multiplication of the aged population
The magnitude of Aging Population:
- The 21st century is witnessing a significant demographic shift marked by a notable increase in human longevity. Improved healthcare and living conditions have contributed to a rise in life expectancy, leading to a larger elderly population. By mid-century, India is projected to have around 319 million elderly people, growing at a rate of approximately 3% annually.
Multiplication of Aging Phenomenon:
- Despite longevity gains, there is a simultaneous decline in fertility rates, leading to an ageing population with a lower proportion of younger generations. This demographic shift poses challenges related to healthcare, social security, and economic sustainability. The elderly population is becoming increasingly feminized, with a higher prevalence of elderly women due to longer life expectancy and higher widowhood rates.
Aged Population as per 2011 Census
- According to the 2011 Census of India, the population of people aged 60 and older in India was 104 million, which is 8.6% of the total population. This is an increase from 5.6% in 1961.
- The census also found that 53 million of the elderly population were female and 51 million were male, with a sex ratio of 1033. 71% of the elderly population lived in rural areas and 29% lived in urban areas. Additionally, 5.18% of the elderly population, or 53,76,619 people, had some disability.
Issues and Challenges
Vulnerabilities of the Elderly:
- Many elderly individuals in India face significant vulnerabilities, including limitations in activities of daily living (ADL), multi-morbidity, poverty, and lack of financial security. A substantial proportion of the elderly report poor health conditions, with a high prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes and cancer.
- Mental health issues, particularly depression, are also prevalent among the elderly population.
Social and Economic Insecurities:
- Food insecurity affects a notable percentage of the elderly, with reports of reduced portions or skipped meals due to economic constraints.
Lack of legal protection:
- Awareness and access to welfare measures and legal protections for the elderly are low, with limited knowledge about schemes like IGNOAPS, IGNWPS, and Annapurna.
Abuse and Neglect:
- Elder abuse is a significant concern, especially for elderly women in rural areas who often experience neglect and mistreatment within their families and communities. Social exclusion and limited opportunities for productive engagement exacerbate feelings of insecurity and marginalization among the elderly.
Way Forward
- Enhancing Social Support and Welfare Measures: Strengthening awareness and accessibility of welfare schemes and legal protections for the elderly. Implementing social security measures to ensure financial stability and improve quality of life for ageing populations.
- Healthcare and Mental Well-being: Prioritizing healthcare interventions tailored to the needs of the elderly, including preventive measures against chronic diseases and mental health support. Promoting healthy ageing through lifestyle interventions and healthcare policies that address the unique challenges of an ageing population.
- Empowerment and Social Inclusion: Fostering social inclusion through community engagement and initiatives that empower the elderly to contribute actively to society. Developing innovative institutional frameworks that value the elderly as assets and promote their participation in societal development.
Mains PYQ
- Q. Critically examine the effects of globalization on the aged population in India. (UPSC IAS/2013)
GS3/Defence & Security
Kanchanjunga express accident - Human error or missing Kavach?
Source: First Post

Why in news?
Nine individuals lost their lives, and over 40 people sustained injuries following a collision involving the Sealdah-bound Kanchanjunga Express from Agartala and a goods train from the rear. This tragic incident took place in the Darjeeling district of West Bengal, approximately 11 km away from the New Jalpaiguri station.
- A combination of a signalling malfunction on the tracks preceding the New Jalpaiguri station and an error by the freight train's driver is believed to have resulted in the fatal crash. Experts stress the significance of implementing the anti-collision system 'Kavach' to mitigate human errors.
Kavach - Train Collision Avoidance System
About
The T/A912 authorization, also known as paper line clearance, provides specific instructions to train operators in case of automatic signalling system failures or defects. It delineates the necessary procedures and speed limitations to ensure safe train operations under such circumstances.
Procedures and speed restrictions
- Signal Procedure: When encountering a red signal, the driver must bring the train to a halt. The train should wait for one minute during the day and two minutes at night when faced with a red signal.
- Proceeding with Caution: After the designated waiting period, the driver can proceed cautiously. Speed should not exceed 15 kmph in good visibility conditions and 10 kmph in poor visibility conditions like during rainfall. The restricted speeds must be maintained until reaching the subsequent stop signal or clear signal indication.
Combination of faulty automatic signalling system and human error - possible reasons behind the accident
- The automatic signalling system between Ranipatra railway station and Chattar Hat junction in West Bengal was non-operational, leading the Rangapani station manager to issue a cautionary note (T/A912) to all drivers passing through that section.
- The driver of the Kanchanjunga Express adhered to the correct protocols during the automatic signalling system malfunction by stopping at red signals for a minute and proceeding at 10 kmph. Conversely, the goods train's driver disregarded these norms, resulting in the collision with the stationary passenger train.
Development of Kavach
- Kavach, formerly known as the Train Collision Avoidance System (TCAS), is an indigenous automatic protection system conceptualized in 2012 and subsequently renamed as 'Kavach' or 'armour'.
- Designed to help Indian Railways achieve Zero Accidents, Kavach is an advanced electronic system developed by the Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO) in collaboration with the Indian industry.
Functioning and Features
- The system comprises electronic devices and Radio Frequency Identification devices installed in locomotives, signalling systems, and tracks, facilitating communication using high radio frequencies to manage train brakes and alert drivers.
- Kavach automatically engages the train braking mechanism if the driver fails to adhere to speed restrictions and prevents collisions between locomotives equipped with the system.
- It assists locomotive pilots in avoiding Signal Passing At Danger (SPAD) and over-speeding, crucial factors linked to railway accidents. Furthermore, it supports train operations during adverse weather conditions such as dense fog.
Deployment strategy and Benefits
- Indian Railways planned to implement the Kavach protection system across 2000 km by 2022-23, covering about 34,000 km of the network. This initiative aims to bolster safety for Indian railways and offers the world's most cost-effective automatic train collision protection system, priced at ₹50 lakh per kilometer compared to around ₹2 crore globally.
- Kavach opens doors for exporting this indigenous technology, showcasing its potential for the Railways sector.
GS2/International Relations
EXERCISE RED FLAG 2024
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
The Indian Air Force (IAF) successfully completed its participation in Exercise Red Flag 2024. It was conducted at Eielson Air Force Base, Alaska, from June 4 to June 14.
About EXERCISE RED FLAG 2024
Exercise Red Flag is a premier air-to-air combat training exercise that serves as an advanced aerial combat training event for air forces of the United States and its allies. The 2024 edition was conducted at Nellis Air Force Base, Nevada, and Eielson Air Force Base, Alaska.
- The 2024 edition focused on offering realistic training that replicates the stresses of combat operations, improving the participants' capabilities to maintain a high level of readiness and survivability, and enhancing interoperability among allied air forces.
- Red Flag exercise is known as the most realistic air combat training, where fighter pilots refine skills against numerous targets, authentic threats, and adversary forces.
- This was the first time the IAF Rafale aircraft participated in Exercise Red Flag.
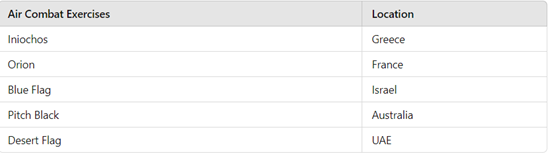
Other combat exercises in which IAF regularly participates:
GS2/International Relations
Indo-US NSA Meet
Source: Hindustan Times

Why in News?
In the first official visit from the US since Prime Minister Narendra Modi was re-elected for a third-term, US National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan met National Security Advisor Ajit Doval in Delhi.
About NSC (Composition, Functions, etc.)
- The National Security Council (NSC) of India is the principal body responsible for advising the Prime Minister on matters of national security and strategic interests.
- It was established by the former Prime Minister of India Atal Bihari Vajpayee in 1998, with Brajesh Mishra as the first National Security Advisor.
- Composition of the NSC:
- Head of the NSC: Prime Minister
- The Prime Minister oversees all aspects of national security and strategic policy.
- The NSA is the primary advisor to the Prime Minister on national security issues.
- The NSA coordinates with various ministries, agencies, and departments involved in national security.
- Members of NSC:
- National Security Advisor (NSA),
- Chief of Defence Staff (CDS),
- Deputy National Security Advisors,
- Union Ministers of Defence, External Affairs, Home, Finance, and Vice Chairman of the NITI Aayog
- Functions of NSC:
- Policy Formulation and Coordination
- Intelligence Assessment
- Strategic Planning
- Crisis Management
- International Security Cooperation
- Before the NSC was formed, these functions were carried out by the Principal Secretary to the Prime Minister.
Indo-US NSA Meet
- India's National Security Advisor, Ajit Doval, held a bilateral talk with the US' National Security Advisor, Jake Sullivan, in New Delhi.
- Both agreed to strengthen cooperation in a range of areas — Defence technology, Space, Artificial Intelligence, High-Performance Computing, critical minerals among others.
- Both also committed to take concrete action in the coming months to address long-standing barriers to bilateral strategic trade, technology, and industrial cooperation, including in the commercial and civil space sector.
- Both the NSAs chaired the second meeting of the India-U.S. initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET).
What is Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET)?
- The Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies is a framework agreed upon by India and the U.S. for cooperation on critical and emerging technologies.
- These emerging technologies include artificial intelligence, quantum computing, semiconductors, and wireless telecommunication.
- Prime Minister Modi and President Biden first announced the framework on the sidelines of the Quad meeting in Tokyo in May 2022.
- It was launched in 2023 to strengthen their strategic partnership and drive technology and defence cooperation.
- Focus Areas of iCET:
- Primarily, the iCET seeks to position New Delhi and Washington D.C. as "trusted technology partners" to build supply chains and support the co-production and co-development of items.
- Key Areas Include:
- Setting up a research agency partnership to drive collaboration in areas like Artificial Intelligence;
- Developing a new defence industrial cooperation roadmap to accelerate technological cooperation for joint development and production;
- Developing common standards in Developing a roadmap to accelerate defence technological cooperation and 'innovation bridge' to connect defence startups;
- Supporting the development of an ecosystem;
- Strengthening cooperation on human spaceflight Advancing cooperation on development in 5G 6G; and Adopting OpenRAN network technology in India.
GS1/History & Culture
TARAKNATH DAS
Source: The Telegraph

Why in news?
Birth anniversary of Shri Taraknath Das was celebrated recently. He was a pioneering immigrant in the west coast of North America and discussed his plans with Tolstoy, while organizing the Asian Indian immigrants in favor of the Indian independence movement.
About TARAKNATH DAS
- Taraknath Das (15 June 1884 – 22 December 1958) was an Indian revolutionary and internationalist scholar.
- Tarak was born at Majupara, in the 24 Parganas district of West Bengal.
- Coming from a lower-middle-class family, his father Kalimohan was a clerk at the Central Telegraph Office in Calcutta.
- At a young age Das was attracted by the revolutionary cause of the Anushilan Samiti, a secret society, and became its member.
- On the advice of Jatindranath Mukherjee, Das escaped initially to Japan and then moved to the United States of America.
- Taraknath Das reached Seattle on 12 July 1906 and subsequently got enrolled in the University of California.
- In the United States, Das was actively participating in the political activities of the South Asian immigrants.
- Following the Bellingham riots of September 1907 against South Asian immigrants, he started the publication of an anti-British newspaper, ‘Free Hindusthan’ to champion the cause of these immigrants.
- In 1913, Das came in contact with Har Dayal and got associated with the Ghadar Movement and its anti-colonial activities. In 1917, he was implicated in the Indo-German conspiracy case for which he was imprisoned in Kansas for two years.
- Das continued to be involved in revolutionary activities throughout his life, his writings maintained a strong anti-British stance, instilling nationalism in the minds of the readers.
|
38 videos|5258 docs|1111 tests
|
















