Measuring angles | Year 6 Mathematics PDF Download
Types of angles
- An angle represents the space between two lines originating from the same point and is measured in degrees.
- Angles can range from 0° to 360°.
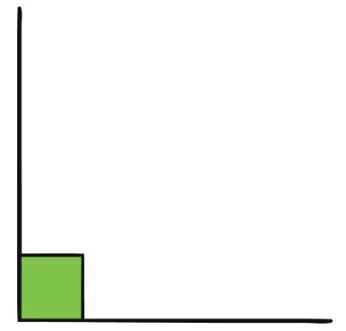
Right Angle
- A right angle resembles the corner of a square or the edge of a book.
- It measures a perfect 90°, often denoted by a small square drawn between the two lines.
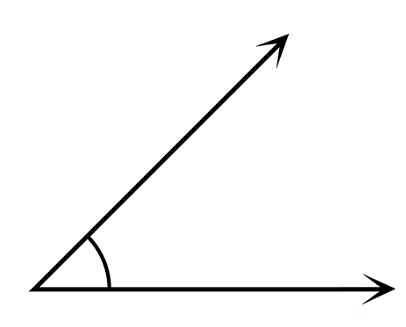
Acute Angle
- An acute angle is less than 90°, smaller than a right angle.
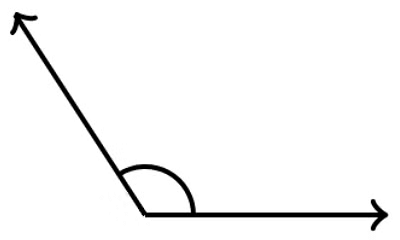
Obtuse Angle
- An obtuse angle is greater than 90° but less than 180°.
 |
Download the notes
Measuring angles
|
Download as PDF |
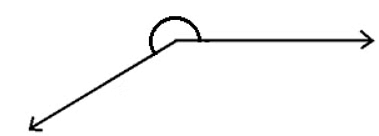
Reflex Angle
- A reflex angle is greater than 180°.
Examples
Example 1: Use the protractor to measure this angle. The protractor has already been lined up correctly.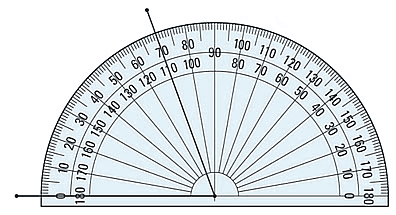
The zero line is on the left this time, so you need to read the outside numbers.
The other angle line goes directly through 70° and 110°.
The angle must be 70° degrees since it is the outside number.
Example 2: You can measure an angle using a protractor. Let's look at how you do this…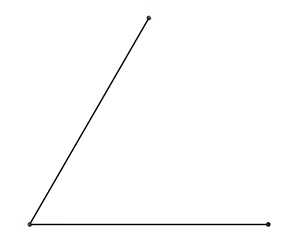
Step 1: Line up the vertex (corner) of the angle with the cross section of the protractor.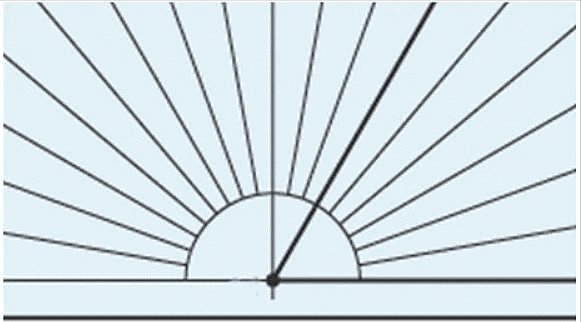 Step 2: Make sure that one of the angle lines goes right through the zero.
Step 2: Make sure that one of the angle lines goes right through the zero.
Step 3: See which number the other line of the angle reaches on the protractor.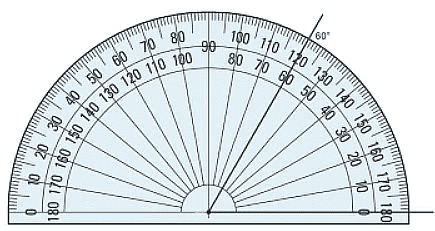
Step 4: Take your measurement.
The line goes through both 120° and 60°. Always read from the zero. Since the zero is on the inside line, you continue to read the inside numbers - the angle must be 60°.
You can also tell that the angle is an acute angle so it has to be less than 90°.
|
54 videos|54 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Measuring angles - Year 6 Mathematics
| 1. What are the different types of angles that can be measured? |  |
| 2. How are angles measured in degrees? |  |
| 3. What is the sum of the interior angles in a triangle? |  |
| 4. How can we determine if two angles are complementary or supplementary? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between adjacent and vertical angles? |  |






















