Getting to Know Plants Chapter Notes | EVS Class 3: The World around us (Our Wondrous World) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Explanation |

|
| Points to Remember |

|
| Difficult Words |

|
Introduction
The chapter "Getting to Know Plants" follows the journey of Gopu, Simmi, and Raj as they see different types of plants while walking to school. They talk about the beauty of plants, their size and shape.
 The chapter explores various types of plants like trees, shrubs, herbs, climbers, and creepers, explaining structure of stems, leaves, and roots.
The chapter explores various types of plants like trees, shrubs, herbs, climbers, and creepers, explaining structure of stems, leaves, and roots.
Explanation
So Many Kinds of Plants
Gopu, Simmi and Raj see many different plants on their way to school. They see trees, shrubs, herbs, grasses, climbers, and creepers. Trees are big with trunks and branches. Shrubs are smaller with many stems. Herbs have soft stems, and grasses have thin, green stems. Climbers grow up other plants, and creepers spread on the ground. They also learn about the parts of a plant, like roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and seeds.
They talk about different types of trees. Firstly they talk jamun tree, which is Raj's favourite tree.
Trees

Trees are large plants with thick, woody trunks and have branches, leaves, and deep roots that help them stay stable and absorb water.
An example is the jamun tree, which has shiny leaves and small fruits. Trees provide shade, shelter for animals, and help the environment by producing oxygen and absorbing carbon dioxide.
Shrubs
 Shrubs are medium-sized plants that are smaller than trees and have many stems. Shrubs have no single main trunk.
Shrubs are medium-sized plants that are smaller than trees and have many stems. Shrubs have no single main trunk. 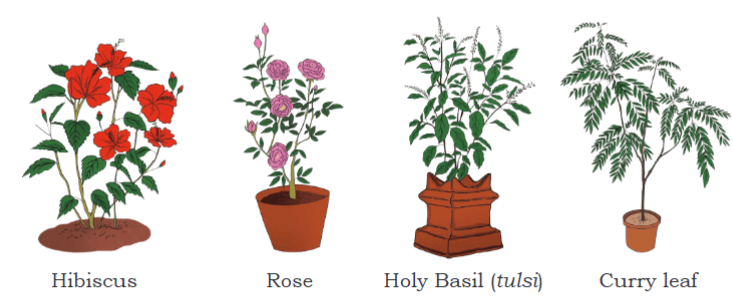 They can be found in gardens and wild areas, have bushy appearance.
They can be found in gardens and wild areas, have bushy appearance.
Examples of shrubs include the tulsi plant. Shrubs serve as habitats for smaller insects.
Herbs and Grasses
 Herbs are small plants with tender, green stems that do not become woody.
Herbs are small plants with tender, green stems that do not become woody. 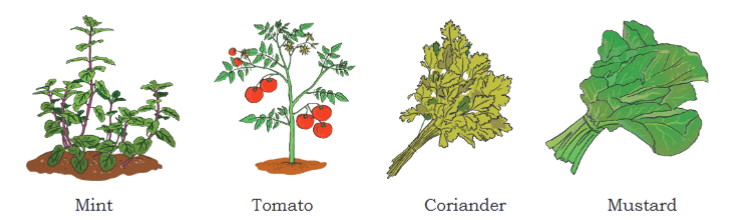 HerbsThey are usually short-lived and can be found in gardens, kitchens, and the wild. Herbs are used for medicinal purposes. Examples of herbs include mint and tomato plants. They are known for their soft, flexible stems and are used in cooking.
HerbsThey are usually short-lived and can be found in gardens, kitchens, and the wild. Herbs are used for medicinal purposes. Examples of herbs include mint and tomato plants. They are known for their soft, flexible stems and are used in cooking.
Grasses are a type of herb with soft stem. They have long, thin, and flat leaves. Grasses are commonly found in lawns, and fields.  Grasses They are important for preventing soil erosion and providing food for many animals. Examples of grasses include lawn grass and wild grasses.
Grasses They are important for preventing soil erosion and providing food for many animals. Examples of grasses include lawn grass and wild grasses. 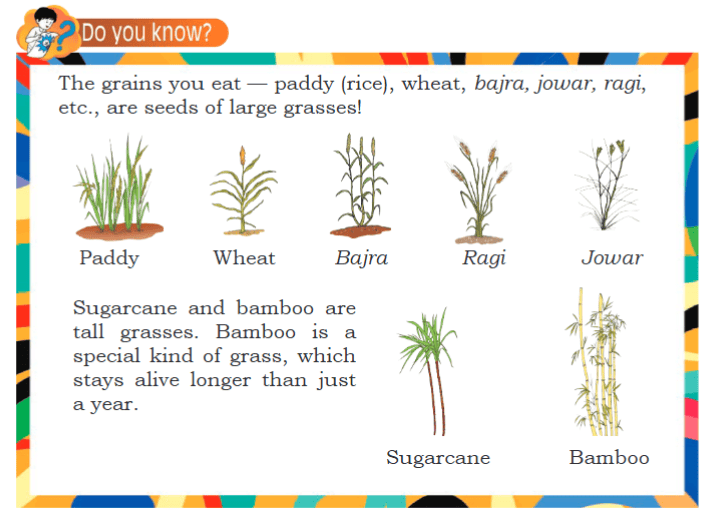
The pulses we eat, such as toor, masoor, moong, and urad, are type of grasses.
Climbers
Climbers are plants with thin, flexible stems that need support to grow. They use other plants to climb and reach sunlight. Examples include the money plant, which climbs walls or trees.  Climbers Climbers often attach to other plants. Examples: Money plant, grapevines.
Climbers Climbers often attach to other plants. Examples: Money plant, grapevines.
Creepers
Creepers are similar to climbers but grow horizontally along the ground. They have thin, flexible stems that spread out and cover the soil surface. CreepersSuch as the pumpkin plant, which has branches that spread across the ground. Creepers are important for ground cover and can help prevent soil erosion. Examples: Pumpkin plant, watermelon vines.
CreepersSuch as the pumpkin plant, which has branches that spread across the ground. Creepers are important for ground cover and can help prevent soil erosion. Examples: Pumpkin plant, watermelon vines.Leaves
Leaves of different plants come in various colors, shapes, and sizes.
They also have different smells, as noticed by Raj. He mentions plants like tulsi, coriander, curry leaves, mint, and lemon grass, each having a distinct fragrance. 
Simmi shares that she loves the smell of mango leaves when rubbed. 
Raj tells his brother is unable to see, can easily identify the smell of fruits like mango, pineapple, jackfruit, guava, and jamun due to their strong aroma.
Parts of a Plant
- Roots: Anchor the plant in the soil and absorb water and nutrients.
- Stems: Support the plant and transport nutrients and water between roots and leaves.
- Leaves: Perform photosynthesis to produce food for the plant.
- Flowers: Reproductive part of the plant that produces seeds.
- Fruits: Contain seeds and help in their dispersal.
- Seeds: Contain the embryo of a new plant and are essential for plant reproduction.
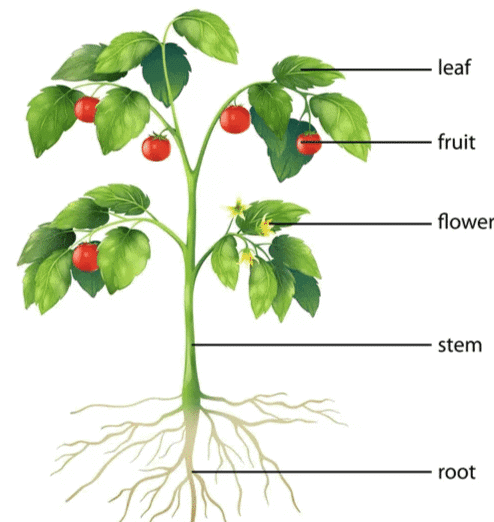
By observing the parts of the plant, we can identify the plants.
Points to Remember
- Trees have thick wooden trunks with branches that spread out. They grow tall and have deep roots to support them.
- Herbs are small plants with soft, green stems that don’t become woody. Examples: Mint and Tomato.
- Grasses are a type of herb with long, thin leaves and hollow stems.
- Climbers grow by climbing on other plants or structures for support, like the money plant.
- Creepers spread along the ground, like the pumpkin plant, which cannot stand upright by itself.
- A plant consists of several parts: roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds, each playing a crucial role.
- The bark of a tree is the hard outer covering that protects the trunk.
- Plants have a variety of textures and smells, like the smooth leaves of the Jamun tree.
- Plants can grow in different sizes and shapes: tall and straight, bushy, thin, curvy, or tiny depending on the type of plant.
Difficult Words
- Exclaimed – Said something suddenly and with strong emotion.
- Creeper – A plant that spreads along the ground as it grows.
- Climber – A plant that grows upward by support of another plant.
- Tender – Soft and easily breakable.
- Hollow – Having an empty space inside.
- Flexible – Capable of bending easily without breaking.
- Trunk – The main, thick stem of a tree.
- Shade – An area with no direct sunlight.
- Observe – To carefully watch or examine something.
|
26 videos|163 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Getting to Know Plants Chapter Notes - EVS Class 3: The World around us (Our Wondrous World)
| 1. What are the main parts of a plant? |  |
| 2. How do plants make their food? |  |
| 3. Why are roots important for plants? |  |
| 4. What is the role of flowers in plants? |  |
| 5. How do plants adapt to their environment? |  |




















