UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 19 July 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/International Relations
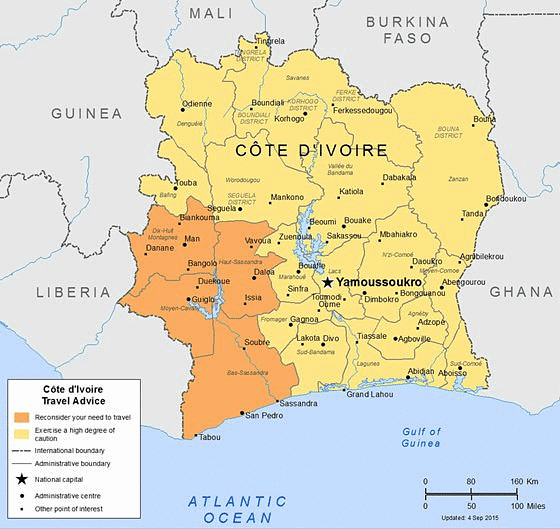
Places in News: Niger, Ivory Coast and Pacific Island States
Source: AP News
Why in news?
Turkish delegation visited to strengthen military cooperation with the junta, shifting alliances to Turkey and Russia.
Geography:
Landlocked in West Africa, bordered by Algeria, Libya, Chad, Nigeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, and Mali. Population ~26.3 million; capital Niamey.
Niger
- Gained independence from France in 1960.
- Political instability with coups and a military junta in 2023.
- Faces challenges including desertification, water scarcity, and economic development issues.
- One of the world’s poorest nations despite having large uranium reserves.
Ivory Coast
- Located on the southern coast of West Africa; bordered by Liberia, Guinea, Mali, Burkina Faso, Ghana, and the Gulf of Guinea. Population ~30.9 million; capital Yamoussoukro.
- Experienced political instability but now relatively stable since 2016.
- Economy dependent on cocoa, coffee, gold mining, and oil refining.
- Abidjan is a major hub for West African economic activities.
Pacific Island States
- Vast region in the Pacific Ocean, categorized into Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia; diverse climates and ecosystems.
- Challenges include climate change impacts, biodiversity loss, and varying levels of development.
- Economic activities include tourism, agriculture (especially coconut and palm oil), and fishing.
- Play a crucial role in global biodiversity and climate resilience efforts.
Key Points:
- Ivory Coast has substantial oil reserves estimated at six billion barrels.
- The Baleine field, operated by Eni, aims to reach significant production levels by 2026.
- Participated in a summit with Japan expressing concerns over military build-ups and the need for regional peace and security.
GS-III/Environment and Biodiversity
845 Elephant Deaths recorded in Kerala in eight years
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
Kerala’s forests have witnessed 845 elephant deaths between 2015 and 2023. Studies show a rising trend in the death rate over time.
Habitat and Population Challenges
- Elephants are increasingly vulnerable due to shrinking habitats and rising fragmentation worsened by climate change.
- Factors contributing to their susceptibility include:
- Decreasing population sizes
- Sensitivity to high temperatures
- Competition from invasive plant species disrupting food sources
- Increased vulnerability to diseases
Elephant Mortality: Key Trends
- Younger elephants, particularly those under 10 years of age, face the highest risk of mortality.
- The mortality rate for calves is about 40%.
- The rise in calf deaths is mainly due to Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesviruses – Haemorrhagic Disease (EEHV-HD).
Influence of Herd Size on Survival
- A recent study in Sri Lanka highlights potential mitigating factors against the herpesvirus.
- Calves in larger herds exhibit better survival rates due to shared immunity.
- Exposure to various virus strains within larger herds helps calves develop antibodies, enhancing their chances of survival.
About Elephants in India
- Population Estimate: India harbors the largest population of wild Asian Elephants (Elephas maximus), with around 29,964 individuals, comprising approximately 60% of the global population as per the 2017 census.
- Leading States: Karnataka boasts the highest number of elephants, followed by Assam and Kerala.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Endangered; CMS: Appendix I; Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Listed under Schedule I; CITES: Conservation Initiatives
- Conservation Initiatives: Project Elephant was initiated in 1992, encompassing 23 states in India. The country hosts over 60% of all wild Asian elephants and has contributed to an increase in the wild elephant population from about 25,000 in 1992 to roughly 30,000 in 2021. Additionally, 33 Elephant Reserves have been established, totaling about 80,777 sq.km.
GS3/Environment
The Issue with India's Tree Planting Schemes
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
India's tree planting schemes have garnered attention as part of the country's efforts to combat climate change and restore degraded ecosystems. However, these initiatives face several challenges and criticisms.
Recent Trends of Special Conservation Drives
Increased Initiatives
- There has been a surge in global and national tree planting drives, such as the "One Trillion Project" by the World Economic Forum, Pakistan's "10 Billion Tree Tsunami," China's "Great Green Wall," and the "Bonn Challenge" to restore degraded landscapes.
High Media Attention
- These drives often feature catchy slogans and glamorous campaigns that attract substantial media attention and public involvement.
Annual Events
- India celebrates Van Mahotsava annually in July, aiming to promote tree planting and environmental conservation.
Issues Associated with These Drives
Limited Community Participation
- Many programs lack significant involvement from local communities, affecting their effectiveness and sustainability.
Post-Planting Measures
- Insufficient focus on post-planting care and monitoring hinders the success of tree planting efforts.
Monoculture Risks
- Some drives promote monoculture, which can be detrimental to biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
Ecological Impact
- Inappropriate tree planting in non-deforested areas like grasslands or animal habitats can damage ecosystems, increase wildfire risk, and exacerbate global warming.
India's Accountability and Challenges Toward Environmental Goals
Achievements
- India claims to have fulfilled its Paris Agreement commitments and achieved an additional carbon sink of 1.97 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent.
Encroachment and Loss
- Approximately 10 million hectares of Indian forests are under encroachment, and about 5.7 million hectares have been lost for non-forestry purposes.
Dependence on Forests
- Nearly 27.5 crore people rely on forests for subsistence, highlighting the importance of sustainable management.
Restoration Goals
- India aims to restore 26 million hectares of degraded forests by 2030, but faces challenges such as encroachment and the need for effective tree planting strategies.
Way Forward
Community Involvement
- Need to foster local participation in tree planting drives by involving communities in planning, execution, and ongoing maintenance.
Monitoring and Maintenance
- Try to implement robust post-planting monitoring and care systems to ensure the survival and growth of planted trees.
Policy and Strategy Improvements
- To address criticism of mass planting drives, India needs to prioritize adequate financing, active community participation, and technical considerations in forestry and restoration strategies.
GS3/Economy
NITI Aayog Suggests Measures to Revitalize Electronics Industry
Source: Business Standard

Why in news?
NITI Aayog has released a report titled “Electronics: Powering India’s Participation in Global Value Chains”. Through this report, the Aayog has recommended a slew of measures to help grow India’s electronics sector from $100 billion to $500 billion by 2030.
Electronics sector in India
- India's electronics manufacturing currently focuses on the final assembly of electronic goods.
- Brands and design firms are increasingly outsourcing assembly, testing, and packaging tasks to Electronic Manufacturing Services (EMS) companies in India.
- The ecosystem for design and component manufacturing is still at a nascent stage.
Statistics
- India’s electronics sector has seen rapid growth, reaching USD 155 billion in FY23.
- Production almost doubled from USD 48 billion in FY17 to USD 101 billion in FY23, driven mainly by mobile phones, which now make up 43% of total electronics production.
- This includes USD 86 billion in finished goods production and USD 15 billion in components manufacturing.
Global scenario
- The global electronics market, valued at USD 4.3 trillion, is dominated by countries like China, Taiwan, USA, South Korea, Vietnam, and Malaysia.
- India currently exports about USD 25 billion annually, representing less than 1% of the global share despite having a 4% share in global demand.
Various initiatives by the government
- 100% FDI is allowed under the automatic route.
- Initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive Scheme (PLI) for Large Scale Electronics Manufacturing and others have been introduced to position India as a global hub for ESDM.
Challenges
- Relatively high import tariffs increase costs of input parts, making the assembled product uncompetitive globally.
- India lacks a robust electronics component ecosystem, especially for high-complexity components.
USD 500 billion in electronics manufacturing by 2030
- India aims to achieve USD 500 billion in electronics manufacturing by 2030, creating employment for about 6 million people.
Projection in a business as usual (BAU) scenario
- The report projects that India's electronics manufacturing could reach USD 278 billion by FY30 in a BAU scenario.
Strategic interventions
- Interventions needed include promoting components and capital goods manufacturing, incentivizing R&D and Design, tariff rationalization, skilling initiatives, facilitation of technology transfers, and infrastructure development.
- Emphasize scaling up production in established segments and diversifying into emerging areas like wearables, IoT devices, and automotive electronics.
GS3/Economy
Decline in popularity of Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS)
Source: Business Line

Why in news?
Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS) are mutual fund schemes that offer tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. Recently, ELSS has seen a decline in popularity, with more money being withdrawn from these schemes than invested.
What is Section 80C of the Income Tax Act?
Section 80C permits certain investments and expenses to be tax-exempted. By well-planning the 80C investments that are spread diversely across various options like National Savings Certificate (NSC), Unit Linked Insurance Plan (ULIP), Public Provident Fund (PPF), etc., an individual can claim deductions up to Rs 1,50,000. By taking tax benefits under 80C, one can avail of a reduction in tax burden.
About Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS)
- An ELSS fund or an equity-linked savings scheme is the only kind of mutual funds eligible for tax deductions under the provisions of Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Investors can claim a tax rebate of up to Rs 1,50,000 and save up to Rs 46,800 a year in taxes by investing in ELSS mutual funds.
- ELSS mutual funds' asset allocation is mostly (65% of the portfolio) made towards equity and equity-linked securities such as listed shares.
- They may have some exposure to fixed-income securities as well.
- These funds come with a lock-in period of 3 years only, the shortest among all Section 80C investments.
- Being market-linked, they are subject to market risk, but may offer potentially higher returns compared to traditional tax-saving instruments like National Savings Certificate (NSC) or Public Provident Fund (PPF).
Recent Trends in ELSS
- In the past few months, more money has been taken out of ELSS than put in.
- For example, last month ₹445 crore was withdrawn, while in April it was ₹144 crore.
- In the last fiscal year, only ₹1,041 crore was invested in ELSS, compared to ₹7,744 crore the previous year.
Impact of the New Tax Regime
- New tax regime introduced in 2020-21, which is now the default option.
- The old tax regime offered various tax exemptions and deductions, helping to reduce income tax.
- Benefits are not available under the new tax regime, making ELSS less attractive to investors.
PYQ:
[2021] Indian Government Bond Yields are influenced by which of the following?
1. Actions of the United States Federal Reserve
2. Actions of the Reserve Bank of India
3. Inflation and short-term interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
GS3/Defence & Security
How do Assam's Foreigners Tribunal Function?
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
On July 5, the Assam government directed the Border wing of the State's police not to forward cases of non-Muslims who entered India illegally before 2014 to the Foreigners Tribunals (FTs) in accordance with the Citizenship (Amendment) Act of 2019, which offers a citizenship application window for non-Muslims fleeing persecution in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, and Pakistan.
About Foreign Tribunal:
Foreign Tribunals (FTs) are quasi-judicial bodies established under the Foreigners (Tribunals) Order of 1964, operating under Section 3 of the Foreigners’ Act of 1946.
Composition of an FT
- Each FT is headed by a member who is a judge, advocate, or civil servant with judicial experience.
- In 2021, the Ministry of Home Affairs informed Parliament that Assam has 300 FTs, with only 100 currently operational as per the State's Home and Political Department website.
Powers of Foreign Tribunal:
- Authorized by the 1964 order, FTs possess powers akin to civil courts, including summoning individuals, enforcing attendance, examining under oath, and requesting documents.
- Upon suspicion of foreign nationality, a notice must be served within 10 days, with the individual having 10 days to respond and present evidence supporting their citizenship claim.
- FTs must resolve cases within 60 days; failure to prove citizenship may lead to detention and eventual deportation.
Role of Assam Police Border Organisation:
- Initially part of the State police’s Special Branch under the Prevention of Infiltration of Pakistani (PIP) scheme, the Assam Police Border Organisation evolved into an independent wing in 1974.
- Responsible for detecting and deporting illegal foreigners, patrolling the India-Bangladesh border, maintaining a secondary defense line, and monitoring riverine areas.
- Refers individuals with questionable citizenship to FTs for nationality determination based on documentation.
- Election Commission of India and 'D' voters excluded from the National Register of Citizens (NRC) draft can also appeal to FTs to validate citizenship.
About the Recent Controversy:
- In July 2024, the Supreme Court overturned an FT decision declaring Rahim Ali a foreigner, emphasizing that authorities lack the mandate to arbitrarily demand citizenship proof.
- An FT member in central Assam highlighted concerns about cases becoming commercialized and accused individuals being unaware due to improper notice placement.
GS3/Science and Technology
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 19 July 2024
|
Download as PDF |
Vasco da Gama’s Toxic Legacy
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
On July 8th, 1497, Vasco da Gama’s historic voyage began, reshaping global maritime routes and leaving a lasting impact on trade and culture. This era of exploration introduced and disseminated tobacco, profoundly affecting societies in numerous ways.
Cultivation and Production of Tobacco
- Historical Introduction: Tobacco was originally cultivated by Native Americans and brought to Europe in the 16th century. It was introduced to South Asia by European traders and colonizers, notably the Portuguese, Dutch, and British.
- Economic Significance: Tobacco is a drought-tolerant crop providing livelihoods to many. It accounts for about 2% of India’s agricultural exports and employs over 45 million people.
- Revenue Generation: The tobacco industry is a major source of revenue through taxation and exports, generating over ₹22,000 crores annually.
Implications on Human Health
- Health Issues: Tobacco use contributes to various cancers (lung, mouth, throat, esophagus, pancreas, and bladder), respiratory diseases (COPD, emphysema, chronic bronchitis), cardiovascular problems (heart disease, stroke, hypertension), and other conditions like diabetes, infertility, weakened immune system, and complications in pregnancy.
- Addiction: Nicotine, a highly addictive substance in tobacco, alters brain function leading to severe addiction.
- Health Crisis: In India, tobacco use causes over 1.2 million deaths annually. It is responsible for 27% of all cancers and adds significant costs to healthcare and productivity losses, totaling approximately ₹1.82 trillion annually.
Ethical and Revenue Considerations
- Economic Benefits vs. Health Costs: While tobacco provides economic benefits and employment, it comes with tremendous human and financial costs due to tobacco-related illnesses.
- Constitutional Provisions: Under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution guarantees the right to life and health. The Directive Principles of State Policy mandate the state to improve public health and living standards. So, the government has a responsibility to prevent tobacco consumption.
Indian Needs to Stack Up Its Priorities
- Institutional Conflict: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) focuses on eliminating tobacco to mitigate health impacts, while the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) aims to increase tobacco crop yields.
- Policy and Ethical Dilemma: The conflicting priorities between ICMR and ICAR create significant policy challenges. The constitutional mandate to prioritize public health should guide policy decisions.
Will CRISPR Make a Difference?
- Gene Editing Potential: CRISPR technology offers potential solutions by developing genetically modified tobacco plants with reduced nicotine content.
- Research Developments: Studies have shown promise in using CRISPR to significantly lower nicotine levels in tobacco plants. However, further characterization is needed to ensure these modifications do not negatively impact other important traits.
- Collaborative Efforts: Collaboration between ICMR and ICAR is crucial to align scientific advancements with public health goals and agricultural sustainability.
The Tobacco Lobby and Surrogate Advertising
- Circumventing Regulations: The tobacco industry employs surrogate advertising to promote its products despite stringent advertising bans. These tactics perpetuate tobacco consumption, especially among youth, undermining public health efforts.
- Aggressive Lobbying: The tobacco industry has a large network of 1,027 registered lobbyists at the state level in 2024, many of whom are former government employees. They engage in extensive lobbying to weaken, delay, or block life-saving tobacco control measures.
Way Forward
- Implement Stricter Regulations: Enforce stringent regulations on tobacco advertising, including surrogate advertising, and ensure compliance through regular monitoring and penalties.
- Ban on Public Smoking: Implement and strictly enforce smoking bans in public places to reduce exposure to second-hand smoke.
Main PYQ
- What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of society? (UPSC IAS/2021)
GS3/Economy
Green Revolution in Maize
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
India has experienced a remarkable success story in the green revolution in maize, primarily driven by the private sector. Over the last two decades, maize production in the country has more than tripled.
Green Revolution in India
About:
- The history of the Green Revolution in India dates back to the 1960s when high-yielding rice and wheat varieties were introduced to boost food production.
- This period marked a significant transformation of Indian agriculture into a modern industrial system, incorporating technologies such as:
- High yielding variety (HYV) seeds
- Mechanised farm tools
- Irrigation facilities
- Pesticides and fertilisers
- Primarily championed by agricultural scientist M.S. Swaminathan in India, this effort was part of the broader Green Revolution initiative spearheaded by Norman Borlaug to enhance agricultural productivity in the developing world through research and technology.
Impact:
- Crop varieties were selectively bred to exhibit various beneficial traits, such as high yields, disease resistance, fertiliser responsiveness, and quality.
- The Green Revolution led to a surge in food grain production, especially in regions like Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh, reducing the need for imports and fostering self-sufficiency.
- Other outcomes included industrial growth, the creation of rural employment opportunities, among others.
Criticism:
Despite its initial success, the Green Revolution faced significant criticism in India, primarily due to:
- Escalating input costs, which burdened small farmers with debt as they transitioned from traditional seed varieties.
- Environmental degradation and soil fertility depletion resulting from excessive and inappropriate use of fertilisers and pesticides.
- Exacerbation of regional inequalities since the revolution was limited to irrigated and high-potential rainfed areas.
- The focus on wheat and rice, neglecting other crops.
Green Revolution in Maize
Maize Crop in India:
- In India, maize cultivation primarily occurs during two seasons: rainy (kharif) and winter (rabi).
- Kharif maize accounts for approximately 83% of maize cultivation in India, while rabi maize constitutes the remaining 17%.
- India ranks fourth globally in terms of maize cultivation area and seventh in production, representing about 4% of the world's maize cultivation area and 2% of total production.
Maize Production in India:
- India has witnessed a significant transformation in maize production between 1999-2000 and 2023-24, with annual maize production more than tripling and average yields per hectare rising from 1.8 to 3.3 tonnes.
- Maize serves primarily as a fuel crop rather than a direct human food source. Only a small portion is consumed directly, while the majority is utilized as feed for poultry and livestock, indirectly reaching households in the form of meat, eggs, or milk.
- Approximately 14-15% of India's maize output is allocated for industrial applications. Due to its starch content, maize finds applications in various industries such as textiles, paper, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage.
New Varieties of Maize:
- The Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) has developed India's first "waxy" maize hybrid with high starch content, tailored for ethanol production.
- The CIMMYT has established a maize doubled haploid (DH) facility in Kunigal, Karnataka, producing genetically pure maize for further hybridization and breeding.
Advantages of Maize over Wheat and Rice:
- Unlike rice and wheat, which are self-pollinating plants, maize's cross-pollination ability makes it conducive to hybrid breeding, offering significant advantages in crop improvement.
Role of Private Sector in Green Revolution in Maize:
- More than 80% of India's maize cultivation is driven by private sector hybridization efforts.
- The CIMMYT collaborates with both public institutions and numerous private seed companies, sharing improved inbred lines to enhance maize productivity.
GS2/Polity
Call for ruthless action against drugs syndicate
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
While chairing the 7th apex level meeting of Narco-Coordination Centre (NCORD), Union Home Minister Amit Shah has called for ruthless action against drug smuggling syndicates.
- The Minister launched a toll-free helpline called MANAS (Madak Padarth Nishedh Asuchna Kendra) with the number 1933. Along with this, a web portal and a mobile app were introduced to allow citizens to connect with the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) 24/7.
- People can use these platforms to share anonymous information about drug dealing and trafficking or to seek advice on issues like drug abuse, quitting drugs, and rehabilitation.
About:
- NCB is the apex drug law enforcement and intelligence agency of India, established in 1986 under the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (NDPS Act), 1985
- The NCB is responsible for combating drug trafficking and the abuse of illegal substances.
Nodal ministry:
- Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India.
The NCORD mechanism was formed in 2016 for better coordination between states and Ministry of Home Affairs.
It has been further strengthened through a four-tier system in 2019.
Aim
- NCORD has been established to enhance coordination among various central and state agencies involved in combating drug trafficking and abuse.
- It is designed to facilitate better communication, cooperation, and intelligence sharing among law enforcement and drug control agencies.
Structure
- Apex Level NCORD Committee, headed by Union Home Secretary;
- Executive Level NCORD Committee, headed by Special Secretary, Ministry of Home Affairs;
- State Level NCORD Committees, headed by Chief Secretaries; and
- District Level NCORD Committees – headed by District Magistrates.
Article 47 of the Indian Constitution
- The National Policy on Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances is based on the Directive Principles, contained in Article 47 of the Indian Constitution.
- The Article directs the State to endeavour to bring about prohibition of the consumption, except for medicinal purposes, of intoxicating drugs injurious to health.
Signatory to international conventions
India is a signatory to:
- the single Convention on Narcotic Drugs 1961, as amended by the 1972 Protocol, the Conventions on Psychotropic Substances, 1971 and
- the United Nations Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988.
Existing Laws
- The broad legislative policy is contained in the three Central Acts:
- Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940,
- The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985, and
- The Prevention of Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1988.
Institutions involved
- was created in 1986 as a nodal agency to fight against this menace.
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) and Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MSJE) are involved with alcohol and drug demand reduction policies and drug de-addiction programme.
In order to prevent misuse of dual-use drugs
- permanent inter-ministerial committee
- has been formed with the ministry of health and family welfare and the ministry of chemicals.
Technological intervention
- The NCORD portal has been launched as an effective mechanism for information exchange between various institutions/agencies.
- A toll-free helpline called
- with the number 1933 has been launched.
Other measures
- The government aims to achieve
- drug-free India by 2047
- through a 3 points strategy - strengthening of institutional structure, coordination among all narco agencies and extensive public awareness campaign.
As part of this strategy a number of steps have been taken which includes:
- Establishment of a dedicated Anti-Narcotics Task Force (ANTF) in each state/UTs.
- High priority to Drug Disposal drive.
- Launch of NIDAAN Portal
- for Narco offenders.
- Creation of canine squads for drug detection.
- Strengthening the forensic capabilities.
- Establishment of Special NDPS Courts and Fast Track Courts.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan
- (NMBA) for generating Awareness against drug Abuse.
Highlighted major challenges posed by synthetic drugs
- The entire business of such substances is getting linked with terrorism and the money coming from drugs has emerged as the most serious threat to the security of the country.
- Due to the drugs trade, other channels of economic transactions meant to weaken the economy have also been strengthened.
- Many such organisations have been formed that are getting involved not only in drugs trade but also in illegal hawala dealings and tax evasion.
- Maritime routes were being used for smuggling drugs
- Maritime routes were being used for smuggling drugs thereby threating India’s maritime security as well.
Need to shift from a "Need to Know" policy to a "Duty to Share" approach
- The Minister emphasized that agencies should shift from a "Need to Know" policy to a "Duty to Share" approach.
- He stated that there should be a strict approach to cutting off drug supply, a strategic approach to reducing demand, and a compassionate approach to minimizing harm.
- He highlighted that although these three aspects are different, all must be addressed to achieve success in combating drug issues.
Drug seizure statistics
- The Minister said that from 2004 to 2023, 1.52 lakh kg of drugs worth ₹5,933 crore were seized.
- In the 10 years from 2014 to 2024, this quantity increased to 5.43 lakh kg, which is worth more than ₹22,000 crore.
GS-III/Science and Technology
What is OpenAI’s secret Project ‘Strawberry’?
Source: News week
Why in News?
US-based OpenAI emerged as a major player with its AI chatbot ChatGPT, capable of answering questions and processing images. OpenAI is now reportedly developing a new AI model with improved reasoning capabilities, potentially changing the AI landscape.
What is Project Strawberry?
Nearly six months ago, OpenAI’s secretive Project Q* (Q-Star) gained attention for its innovative approach to AI training. OpenAI is now working on a new reasoning technology under the code name “Strawberry” believed to be the new name for Project Q*. Strawberry aims to enable AI models to plan ahead, autonomously search the internet, and conduct deep research.
What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
LLMs are advanced artificial intelligence (AI) systems designed to understand, generate, and process human language. They are built using deep learning techniques, particularly neural networks, and are trained on vast amounts of text data.
Difference from Existing AI Models
- Existing Large Language Models (LLMs) can summarize texts and compose prose but struggle with common sense problems and multi-step logic tasks.
- Current LLMs cannot plan ahead effectively without external frameworks.
- Strawberry models are expected to enhance AI reasoning, allowing for planning and complex problem-solving.
- These models could enable AI to perform tasks that require a series of actions over an extended time, potentially revolutionizing AI’s capabilities.
Potential Applications of Strawberry Models
- Advanced AI models could conduct experiments, analyze data, and suggest new hypotheses, leading to breakthroughs in sciences.
- In medical research, AI could assist in drug discovery, genetics research, and personalized medicine analysis.
- AI could solve complex mathematical problems, assist in engineering calculations, and participate in theoretical research.
- AI could contribute to writing, creating art and music, generating videos, and designing video games.
Ethical Considerations
- Impact on Jobs: Improved AI capabilities may intensify concerns about job displacement and the ethical implications of AI reproducing human work.
- Power Consumption and Ethics: The vast amounts of power required to run advanced AI models raise environmental and ethical questions.
PYQ
[2020]
With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following?
1. Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units.
2. Create meaningful short stories and songs.
3. Disease diagnosis.
4. Text-to-Speech Conversion.
5. Wireless transmission of electrical energy.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
|
39 videos|4566 docs|979 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 19 July 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. How many elephant deaths have been recorded in Kerala in the past eight years? |  |
| 2. What are some of the habitat and population challenges faced by elephants in India? |  |
| 3. How does herd size influence the survival of elephants? |  |
| 4. What are some key trends in elephant mortality in India? |  |
| 5. What are some issues with India's tree planting schemes in relation to elephant conservation? |  |




























