Grassroots Democracy- Local Government in Urban Areas Chapter Notes | Chapter Notes For Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Urban Local Bodies |

|
| Conclusion |

|
| Key Words |

|
Introduction
In a democracy like India, it's important for citizens to understand how the government works and their rights and responsibilities. This starts at the local level, where people can see decision-making and service delivery. Being involved helps citizens learn about administration, voting, and civic duties.
Good governance encourages participation at all levels—local, regional, and national—known as participatory democracy. Rural governance has its own structure, while urban governance is more complex due to the challenges in cities.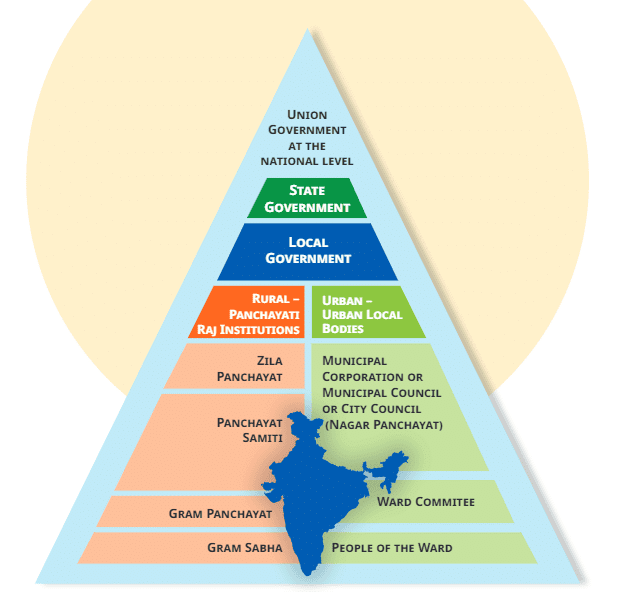
To understand city governance, it's helpful to first look at India's overall system, with local governance at the base and national governance at the top.
Urban Local Bodies
Do urban local bodies refer to local government structures in cities and towns?
Yes, Urban local bodies are the local government systems that manage cities and towns. These bodies are responsible for overseeing and addressing local issues, ensuring services like water supply, sanitation, and infrastructure are provided to the community. They function at a decentralized level, meaning the local community directly participates in decision-making for their area.

Understanding Urban Local Bodies and Their Functions
- Urban local bodies are the governing institutions responsible for managing cities and towns.
- These bodies are decentralized, allowing local communities to actively participate in managing their areas rather than relying solely on a central authority.
- This system allows residents to come together and make decisions that are best for their community.
- Cities and towns are divided into smaller sections known as wards.
- Ward committees help with various activities, including:
- Organizing health camps
- Running campaigns against single-use plastics
- Monitoring local issues like water leaks, blocked drains, or damaged roads
- The exact functioning of wards varies from State to State, based on their specific rules.
- Urban local bodies handle several key responsibilities, such as:
- Maintaining local infrastructure
- Overseeing burial grounds
- Collecting and disposing of waste
- Ensuring proper implementation of government schemes
- Collecting local taxes and fines
- Contributing to economic and social planning for the area
- For these bodies to work effectively, local residents also need to take their responsibilities seriously. This is part of a participatory democracy.
- For example:
- If residents follow guidelines for waste segregation, it helps make garbage collection easier.
- If someone notices a water leak, reporting it quickly can save a lot of water.
- In cities like Chennai and Indore, there is a Municipal Corporation at the top of their urban local bodies.
- Only cities with a population of over 10 lakhs have a Municipal Corporation, also known as Mahanagar Nigam.
- The highest governing body for cities with populations between 1 and 10 lakhs is a Municipal Council (or Nagar Palika).
- Towns with smaller populations have a Nagar Panchayat as their governing body.
The Madras Corporation: India's Oldest Municipal Institution
- The Madras Corporation, now known as the Greater Chennai Corporation, was established on September 29, 1688. It holds the distinction of being the oldest municipal institution in India.
- Before the corporation was formed, the East India Company issued a charter in 1687, granting Fort St. George and its surrounding territories (within a 16 km radius) the status of a municipal corporation.
- In 1792, a Parliamentary Act granted the Madras Corporation the authority to levy municipal taxes in the city. This marked the beginning of proper municipal administration in Madras.
Conclusion
In urban areas, decentralized governance through various urban local bodies ensures that cities and towns function efficiently and effectively. Citizens play a crucial role in this system by participating in governance, reporting issues, and following community guidelines. Just like in rural areas, urban local bodies have elected representatives who work to address the needs and concerns of the local population. By understanding and engaging in these processes, we can help create better, more livable urban environments.
Key Words
- Democracy - A system where people have the power to make decisions, often through voting.
- Governance - How the government manages and organizes things for the community.
- Civic Rights - The rights that every citizen has, such as voting and being treated fairly.
- Local Level - The smallest level of government, focusing on cities, towns, or villages.
- Participatory Democracy - When people take part in decision-making in their community.
- Urban Local Bodies - Local government bodies responsible for managing cities and towns.
- Ward - A smaller section of a city or town used to manage local areas more effectively.
- Infrastructure - Basic structures and services needed for a community, like roads and water supply.
- Decentralized - When decision-making is spread out to local areas instead of being controlled by a central authority.
- Municipal Corporation - A government body in large cities that manages urban areas.
- Municipal Council - A governing body in smaller cities (between 1-10 lakh population) that manages the area.
- Nagar Panchayat - A government body that manages small towns with a population under 1 lakh.
- Waste Segregation - The process of sorting garbage into different categories like recyclables and non-recyclables.
- Tax - Money collected by the government from residents to fund public services.
- Public Participation - When residents are actively involved in community decisions and activities to improve their area.
FAQs on Grassroots Democracy- Local Government in Urban Areas Chapter Notes - Chapter Notes For Class 6
| 1. What are Urban Local Bodies and their significance in local governance? |  |
| 2. How are Urban Local Bodies structured and governed? |  |
| 3. What are the key functions of Urban Local Bodies? |  |
| 4. How do Urban Local Bodies promote grassroots democracy? |  |
| 5. What challenges do Urban Local Bodies face in their functioning? |  |





















