Measurement of Length and Motion Chapter Notes | Chapter Notes For Class 6 PDF Download
Introduction
Measurement is a part of our daily lives. Whether we are buying fabric, cooking, or building something, measurement helps us know exactly how much we need. It also ensures that we share information correctly.
For example, if you want to buy fabric to make a dress, you need to know how much fabric to buy. Similarly, when cooking, measuring ingredients properly helps make the food taste just right.

How do we Measure?
Do you think the length of the bench would be the same if different people measured it using their hands?

How can using a scale or measuring tape help avoid mistakes in measurement?
Measuring using Body Parts
A long time ago, people used parts of their bodies to measure things. They used things like handspans, arm lengths, foot lengths, and strides for measuring.
- Handspan: The distance from the tip of the thumb to the tip of the little finger when the hand is fully stretched.

- Arm Length: The distance from the shoulder to the tip of the middle finger.

- Foot Length: The length of a person's foot could be used to measure things.

- Stride: Farmers sometimes used their steps to measure the length of fields.
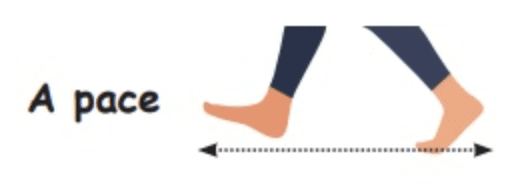 Problems with Using Body Parts for Measuring
Problems with Using Body Parts for Measuring
One big problem with using body parts to measure is that they aren’t the same for everyone. People’s body parts are different sizes, so the same length might be measured differently by different people.
For example, if you and your friend measure a table using your foot lengths, you might get different results because your feet are not the same size. This shows why we need standard units of measurement.
Ancient Indian Measurement Systems
India has a rich history of measurement systems. In ancient times, people used units like Angula (the width of a finger), Dhanusa, and Yojana to measure things like buildings, artifacts, and towns.
Even today, Angula is still used by traditional workers like carpenters and tailors. Archaeologists have also found markings on objects at Harappan Civilization sites that show how these ancient measurements were used.
Standard Units
Over time, different parts of the world created their ways of measuring things. However as people started traveling more, these different systems were confused. To fix this, countries agreed on a standard system of measurement called the International System of Units (SI).
The SI Unit of Length: Metre
- The standard unit for measuring length is the meter (m).
A meter is divided into 100 equal parts, each called a centimeter (cm).
For example, a 15-cm ruler has markings from 0 to 15 cm, and the distance between each marking is 1 cm. A 15-cm scale
A 15-cm scale - Each centimeter is further divided into 10 smaller parts, called millimeters (mm). One millimeter is equal to 0.1 cm, making it the smallest length you can measure with a regular ruler.
Measuring Large and Small Lengths
- To measure larger distances, we use kilometers (km). One kilometer equals 1000 meters.
- To measure smaller lengths, we use centimeters or millimeters.
- Examples:
- If the length of your pencil is 15 cm, it means it’s 15 times the length of one centimeter.
- If the distance between two cities is 20 km, that means the distance is 20,000 meters long.
Conversion between Units
It is important to know how to convert between different units of length:
- 1 metre = 100 centimetres
- 1 centimetre = 10 millimetres
- 1 kilometre = 1000 metres
Measuring Length in Inches
On some rulers, you may see markings in inches. One inch is equal to 2.54 centimetres.
In the past, units like inches and feet were commonly used to measure length. Even today, some people still use these units, especially in countries like the United States.

Correct Way of Measuring Length
Different scales are used for different lengths. For example:
- To measure the length of a pencil, a 15-cm ruler is perfect.
- For measuring the height of a room, a metre stick or measuring tape works best.
- If you need to measure around objects, like a tree trunk or your chest, a flexible measuring tape is the right choice.
What is the correct way to place the scale?
- The scale should be placed in contact with the object along its length.
- For example, if you are measuring the length of a paper, place the scale so that it touches the paper along its entire length.
 Method of placing the scale
Method of placing the scale
What is the correct position of the eye while reading the scale?
- The eye should be directly above the point of measurement to avoid parallax error, which can lead to incorrect readings.
- For example, if you are measuring the length of a pencil, your eye should be directly above the point where the pencil meets the scale.
 Correct position of the eye is 'B'
Correct position of the eye is 'B'
How to measure the length if the ends of the scale are broken?
- If the ends of the scale are broken, you can still measure. Start from another full mark on the scale, and then subtract the reading at the end of the object.
- For example, if you start from 1 cm and measure to 10 cm, the length of the object would be 10 cm - 1 cm = 9 cm.
 Correct method of placing the scale with broken end
Correct method of placing the scale with broken end
How Visually Challenged Students Measure Lengths
- Visually challenged students measure lengths by using special scales with raised markings.
- These markings can be felt by touch, allowing them to accurately measure without needing to see the scale.
Writing Units of Length Correctly
Symbols for length units (km, m, cm, mm) always start with lowercase letters.
Do not add an “s” for plural forms.
Do not put a full stop after the symbol (unless it is at the end of a sentence).
Always leave a space between the number and the unit. Example: 5 km (not 5km).
Measuring the Length of a Curved Line
To measure a curved line, you can use a flexible measuring tape or a piece of thread. Simply wrap the thread along the curve, then straighten it and measure the length using a ruler or metre scale.

Describing Position
A reference point is a fixed place used to describe where something is. For example, when giving directions, you might say, “The park is two blocks north of the school.” The park and the school are your reference points!
Examples of Reference Points in Real Life
- The starting line in a race
- The kilometre stones on a highway
- A landmark such as a building or a tree
Importance of Consistent Reference Points
- Using reference points helps us know exactly where we are and where we’re going.
- For example, Padma was traveling by bus to Delhi. As she passed kilometer stones, one showed "Delhi 70 km" and the next one showed "Delhi 60 km." She could tell she was getting closer to her destination.

- Further on, the next kilometer stone read "Delhi 60 km." Each kilometer stone indicated to her that she was getting closer to her grandparents' house.

Moving Things
What makes you think an object is moving or not?
What’s a fun way to check if a toy is in motion or not?
Motion and Rest of an Object
Motion
- The act, process, or state of the change in place or position of a body with respect to time and relative to the observer is said to be motion.
- For example, the blades of a rotating fan, the hands of a working wall clock, a moving car, a spinning top, and satellites are all in motion.
Rest
- When a body remains in one position for a long time, it is said to be at rest.
- For example, the chairs of the dining table are at rest unless and until they are moved, and the flower vase, table, and blackboard in the classroom are all at the position of rest.
Rest and Motion are Relative Terms
- A body seems to be at rest with respect to one object but may appear to be in motion with respect to some other object.
- For example, a person on a railway platform is at rest with respect to another person on the same platform but is in motion with reference to a person looking at him from a train crossing that platform.
- Similarly, a passenger sitting in the train will appear at rest to another passenger on the same train.

Types of Motion
1. Linear Motion
Linear motion happens when an object moves in a straight line. The direction stays the same, and the object follows a straight path. It can change speed or direction, but it doesn't go off course.
Examples include:
- A car driving on a straight road
- A runner racing in a straight line
- A train moving along straight tracks
 Linear motion
Linear motion
2. Circular Motion
Circular motion is the motion of an object that moves at a fixed distance from a fixed point. Here, all objects rotate in a circular motion. So, circular motion is a motion in which the body traverses a circular path. The hands of a clock, a merry-go-round, the blades of a fan, the wheel of a moving vehicle, satellites, a spinning top, are all good examples of circular motion.
Examples include:
- A merry-go-round spinning
- The hands of a clock moving
- A satellite orbiting the Earth
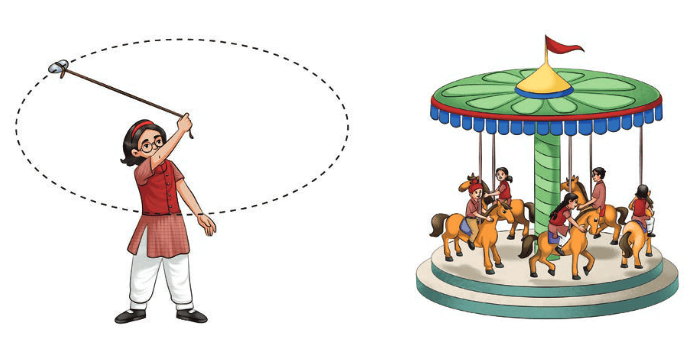 Circular motion
Circular motion
3. Oscillatory Motion
Oscillatory motion occurs when an object moves back and forth about a fixed position. The motion repeats itself in regular intervals, with the object moving to one side, then back to the other, and repeating this cycle over and over again. The path of the motion is not linear or circular but swings between two points.
Examples include:
- The motion of a swing
- A guitar string vibrating
- A pendulum swinging
 Oscillatory motion
Oscillatory motion
Periodic Motion: Circular and Oscillatory
- An object is in periodic motion if it repeats its path after a fixed amount of time. In circular motion, the object follows the same circular path again and again.
- In oscillatory motion, the object moves back and forth in a repeating pattern. Both circular motion and oscillatory motion are types of periodic motion, where the motion repeats after certain intervals.
Conclusion
Measurement is an important part of our daily lives. Whether we are cooking, building, traveling, or even playing, knowing how to measure things correctly helps us in many ways. From ancient times to modern days, people have found better ways to measure, making our lives easier and more accurate.Understanding different types of motion also helps us see the world in a new way! Everything around us moves in some way—cars on the road, swings in a park, or even the Earth spinning in space.
So, the next time you measure something or see something moving, think about what you've learned today!
Key Words
- Centimetre – A small unit of length, 1/100 of a metre.
- Measurement – Finding out how big, long, or heavy something is.
- Classify – To put things into groups based on their similarities.
- Circular motion – Movement in a round path, like a fan blade.
- Metre – A standard unit of length, 100 centimetres.
- Explore – To look at or study something carefully.
- Distance – How far one place or object is from another.
- Millimetre – A very small unit of length, 1/1000 of a metre.
- Identify – To recognize or find out what something is.
- Kilometre – A large unit of length, 1000 metres.
- Motion – When something moves from one place to another.
- Investigate – To study something in detail to understand it.
- Length – How long something is from one end to the other.
- Oscillatory motion – A back-and-forth movement, like a swing.
- Justification – A reason or explanation for something.
- Linear motion – Movement in a straight line, like a car on a road.
- Reference point – A fixed place used to compare movement.
- Observe – To watch something carefully.
- SI Unit of Length – The international system for measuring length (metre).
FAQs on Measurement of Length and Motion Chapter Notes - Chapter Notes For Class 6
| 1. What are standard units of measurement for length? |  |
| 2. How do you correctly measure the length of an object? |  |
| 3. What is the correct method for measuring the length of a curved line? |  |
| 4. How do we describe the position of an object? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of motion? |  |

















