UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly > The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 22nd July 2024
The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 22nd July 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download

Focus on Female Employment to Counter Unemployment
Why in News?
The Institute for Human Development and the International Labour Organization (ILO) recently released the India Employment Report 2024.
- The research is mostly based on data analysis from the National Sample Surveys and Periodic Labour Force Surveys conducted between 2000 and 2022.
Key highlights of the India Employment Report 2024
- Shifting of Workforce in Non-farm Sectors: The period from 2000 to 2019 saw a gradual move of workers from farming to other types of jobs, a shift that is still ongoing.
- Employment Trends in India: In India, most people are either self-employed or working in temporary jobs. About 82% of workers are part of the informal sector, and around 90% have informal jobs.
- Stagnant Wages: While wages for temporary workers went up slightly from 2012 to 2022, the actual pay of regular employees stayed the same or even decreased.
- The Rate of Youth Not Engaged in Work, School, or Training: In South Asia, there was an average of 29.2% of young people not involved in work, education, or training between 2010 and 2019, the highest rate in the region.
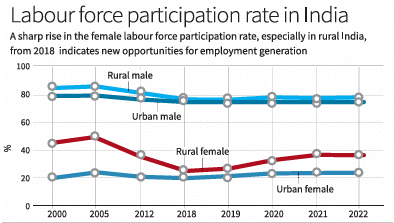
Outlook on Women Employment in India
- Female Labour Force Participation Rate:
- The percentage of women participating in the workforce was 37 in 2023, while for men it stood at 78.5. Globally, women's participation rate is 49 according to the World Bank.
- From 2000 to 2019, the female labour force participation rate saw a steady drop, reaching 24.5 before showing a slight increase, especially in rural regions.
- Increase in Engagement:
- Women played a significant role in the rise of self-employment and unpaid family work.
- Post-2019, around two-thirds of new jobs were self-employed positions, with a notable presence of unpaid female family workers.
- The proportion of regular employment, which had been on the rise since 2000, started declining after 2018.
- Youth Employment Situation:
- India has a considerable number of young individuals not engaged in employment, education, or training. This group is more prominent among young women compared to men.
Reasons for Low Women’s Participation
- Gross enrollment in higher education: The enrollment rate for women was 47.3% in the 2021-22 period, causing delays in joining the workforce.
- Overall lack of paid work: India's economic growth has not generated many job opportunities, favoring men for skilled jobs over women.
- Traditional Indian social norms: Women are typically expected to be primary caregivers at home, restricting their movement and limiting their freedom to pursue available opportunities. Women's choices are often constrained by marriage and responsibilities towards their households and families.
- Limited options: Concerns about public safety and inadequate transportation confine women to seeking work close to their homes, thus restricting their choices.
- Supply and demand dynamics in female labor: Factors influencing women's decisions about combining work and family responsibilities include education, childcare, technological advancements, laws, societal norms, and changes in the economy's structure.
What Needs to Change?
- Focus growth in labour-intensive sectors: Policies that support labor-intensive industries (like Textiles and IT) are necessary.
- Increase public investment: Public funds for safety measures (such as street lighting and CCTVs) and transportation (affordable last-mile public transport) are crucial, as is investment in affordable childcare and elderly care.
- Safe Accommodation: Investments in building hostels for working women to facilitate commuting to work from outside their homes.
- Recognizing unpaid care work as a type of economic activity.
The document The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 22nd July 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
Related Searches















