Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 31st July 2024) Part - 2 | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
SC Verdict on GM Mustard Approval
 Why in news?
Why in news?
- Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) delivered a split verdict on the validity of the Centre's decision to grant conditional approval for the environmental release of Genetically Modified (GM) mustard crops. Now, the case will be referred to a Supreme Court's three-judge Bench.
Key Highlights of SC Verdict on GM Mustard
Reason Behind Split Judgement:
- Justice Nagarathna criticized the GEAC for clearing the project without relying on any indigenous studies on the crop's effect in India and its possible environmental ramifications. Only foreign research studies were considered while making the recommendation.
- Justice Karol upheld the GEAC's clearance for GM mustard's commercial release. Both judges concurred on certain points raised during the arguments, emphasizing the need for a national policy and judicial review of GEAC decisions.
Directive for National Policy:
- The judges asked the Union Ministry of Environment and Forest to formulate a policy within four months, covering research, cultivation, trade, and commerce, developed in consultation with stakeholders.
GEAC's Role:
- GEAC approved the environmental release of the transgenic mustard hybrid Dhara Mustard Hybrid-11 (DMH-11) in October 2022.
What is GM Mustard?
About:
- GM Mustard was developed in India by hybridizing the Indian mustard variety 'Varuna' and 'Early Heera-2' (Eastern European variety). It contains two alien genes ('barnase' and 'barstar') isolated from a soil bacterium called Bacillus amyloliquefaciens.
- It is classified as a Herbicide Tolerant (HT) mustard variety engineered to withstand specific herbicides, aiding in weed control and crop yield enhancement.
Significance:
- Mustard plays a vital role in India's edible oil production, contributing 40% of the total production.
- GM Mustard demonstrates a yield increase of approximately 28% compared to the national standard and surpasses zonal benchmarks by around 37%, with varieties like DMH-11 capable of significantly enhancing yields per hectare.
Concerns Associated with GM Mustard
Biodiversity Concern:
- Potential effects on honeybees due to altered flowering and pollen production, impacting other beneficial insects, soil microbes, and wildlife essential for agriculture.
Food Security and Health Concerns:
- Monoculture cropping enabled by GM varieties could increase vulnerability to crop diseases and climate change impacts, posing threats to long-term food security.
- Potential creation of novel proteins with unknown impacts on human health, raising ethical concerns about agricultural sovereignty and access to technologies.
Regulatory Challenges:
- Ensuring compliance with bio-safety protocols and monitoring long-term environmental impacts require robust institutional capacity and infrastructure.
Way Forward
Biodiversity Mitigation:
- Conduct extensive research to understand ecological impacts of GM mustard on non-target organisms and implement adaptive management strategies.
Food Safety and Human Health:
- Risk assessment of allergenicity and toxicity of novel proteins introduced into the crop, investing in long-term studies to monitor impacts on food security and crop diseases.
Ethical Considerations:
- Ensure equitable access to GM technologies, protect traditional farming practices, and promote farmer autonomy in decision-making.
Capacity Building:
- Strengthen institutional capacity through training regulators, enhancing laboratory facilities, and establishing transparent regulatory frameworks.
GS2/International Relations
Kargil Vijay Diwas
 Why in news?
Why in news?
- Is celebrated every year on July 26 to pay tribute to the bravery of Indian soldiers who made the ultimate sacrifice for the country during the Kargil War (1999). This event marks the conclusion of the Kargil War between India and Pakistan that started in May 1999.
What is Kargil Vijay Diwas?
About:
- Kargil Vijay Diwas, or Kargil Victory Day, is a significant day observed annually in India.
- The day commemorates India's triumph in the 1999 conflict with Pakistan and honors the bravery and sacrifices of Indian soldiers during the war.
- The Kargil war of 1999 was the first military confrontation in a nuclearized South Asia, and arguably the first real war between two Nuclear States.
Background:
- India and Pakistan have a history of conflicts, including a significant one in 1971 that led to the creation of Bangladesh.
- Post-1971, both nations faced ongoing tensions, particularly vying for control over the Siachen Glacier through military outposts on nearby mountain ridges.
- In 1998, both countries conducted nuclear tests, escalating tensions.
- The Lahore Declaration in February 1999 aimed to resolve the Kashmir conflict peacefully and bilaterally.
Significance of Kargil War Diwas:
- Since 1999, July 26 has been observed as Kargil Vijay Diwas to remember and honor supreme sacrifices made by Indian soldiers during the war.
- Kargil War memorial in Dras was built in 2000 by the Indian Army to commemorate the success of Operation Vijay in 1999.
- National War Memorial, inaugurated in 2019, is dedicated to soldiers who sacrificed their lives in various conflicts and missions.
Impact of Kargil War:
- Global Recognition of the Line of Control (LoC)
- Strengthened Strategic Partnerships
- Diplomatic Gains
- Highlighting Nuclear Diplomacy
- Impact on Global Perception
What Reforms were Undertaken After the Kargil War?
- Security Sector Reforms
- Creation of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS)
- Establishment of Tri-Service Commands
- Intelligence Reforms
- Border Management Enhancements
- Operational Reforms
- Improved Coordination and Communication
- Counter-Terrorism Measures
- Indigenous Satellite Navigation System
- Doctrinal Changes
Conclusion
The Kargil War of 1999 was a pivotal event for India, significantly impacting its military strategy and national security policies. Operation Vijay's success restored control over strategic areas and strengthened India's defence capabilities. The war highlighted the need for robust security measures and prompted major reforms in national security infrastructure. It reaffirmed the Line of Control (LoC) as an effective international border and accelerated the development of new military doctrines, such as the Cold Start Doctrine. The conflict’s legacy continues to shape India's defence strategies and diplomatic relations.
Mains Question:
Q. The Kargil War of 1999 made a significant impact on the regional dynamics of the South Asian region. Discuss.
GS3/Environment
Climate Change and Impact on Children's Education
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Recently, a new report by the Global Education Monitoring Report of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) has highlighted the long-term impact of climate shocks experienced in early childhood.
How does Climate Change Impact Children and Their Education?
Vulnerability of Children:
- The report states that young children are particularly vulnerable to physical hazards like floods, droughts, and heat waves, which can negatively impact physical abilities, cognitive abilities, emotional well-being, and educational opportunities.
Impact on Cognitive Abilities of Children:
- In Ecuador, children exposed to severe El Nino floods in utero were shorter and performed worse on cognitive tests later in life. In India, rainfall shocks during early life negatively impacted vocabulary at age 5 and mathematics and non-cognitive skills at age 15. An analysis of disasters affecting over 140,000 children in seven Asian countries showed a negative correlation with school enrollment for boys and mathematics performance for girls by age 13-14.
School Closures and Infrastructure Damage:
- Climate-related stressors cause frequent school closures, with 75% of extreme weather events in the past 20 years resulting in such disruptions. Natural disasters, including floods and cyclones, have led to deaths and significant damage to educational infrastructure.
Impact of Heat and Environmental Variability:
- Higher-than-average temperatures during prenatal and early life are linked to fewer years of schooling. Studies show reduced high school graduation and college entrance rates in China due to heat. In Maharashtra, India, drought led to a 4.1% reduction in mathematics scores and a 2.7% reduction in reading scores. In Pakistan, children in flooded districts were 4% less likely to attend school compared to those in non-flooded areas.
What are the Recommendations of the Report?
Need for Adaptation:
- The report emphasizes the need for comprehensive climate adaptation strategies, including improved school infrastructure, curriculum reforms, and community engagement.
Curriculum Integration:
- The report underscores the need for incorporating climate change education into school curricula to provide both climate science knowledge and skills in resilience, adaptation, and sustainable development.
Proactive Measures:
- To mitigate climate impacts on education, proactive measures are recommended, including strengthening school infrastructure, training educators for psychological and academic support, and promoting community resilience through awareness and adaptation initiatives.
Investing in Education:
- There is a call for increased investment in educational systems to enhance their resilience to climate-related disruptions, ensuring continuity of education despite environmental challenges.
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the multifaceted impacts of climate change on schooling in developing countries. Examine how extreme weather events, rising temperatures, and environmental degradation disrupt educational access, quality, and outcomes.
GS3/Economy
India AI Mission
 Why in news?
Why in news?
- The Indian government is focusing on advancing artificial intelligence (AI) technology, as seen in the recent budget allocation for the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology. The allocation of Rs 551.75 crore in the Union Budget 2024-25 is aimed at enhancing AI infrastructure, including the procurement of high-performance Graphic Processing Units (GPUs). This move intends to boost domestic AI development and reduce dependence on expensive foreign hardware.
What is the India AI Mission?
Objective
- The mission's goal is to establish a robust AI computing infrastructure in India to facilitate the development and testing of AI systems. It aims to improve data quality, develop indigenous AI technologies, attract top talent, foster industry collaboration, support impactful AI startups, and promote ethical AI practices.
Financial Support
- The Union Cabinet approved the Rs 10,372 crore IndiaAI Mission to create a computing capacity of over 10,000 GPUs and develop foundational models with a capacity of more than 100 billion parameters trained on datasets covering major Indian languages for priority sectors like healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
Current Focus
- The initial phase involves procuring 300 to 500 GPUs to kickstart the project, highlighting the importance of GPU procurement for training and building large-scale AI models.
Key Components of the IndiaAI Mission
- India AI Compute Capacity: Creation of a high-end AI computing ecosystem with over 10,000 GPUs to support AI startups and research, along with an AI marketplace for resources.
- India AI Innovation Centre: Development of indigenous Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) and foundational models for various sectors, with significant financial allocation.
- India AI Datasets Platform: A unified platform to provide seamless access to non-personal datasets for startups and researchers.
- India AI Application Development Initiative: Promotion of AI applications focusing on governmental problem statements for socio-economic transformation.
- India AI FutureSkills: Expansion of AI education programs and the establishment of Data and AI Labs in smaller cities.
- India AI Startup Financing: Provision of funding access for deep-tech AI startups to support innovative projects.
- Safe & Trusted AI: Development of guidelines and frameworks to ensure responsible AI practices and tools for project assessment.
Key Highlights of India's AI Market
- Adoption Across Sectors: AI adoption is increasing in various sectors in India, supported by initiatives like the National AI Strategy and the National AI Portal.
- Focus on Data Analytics: Companies are leveraging AI-driven data analytics to enhance operations and innovation, supported by programs like AI for All.
- Government Initiatives: Initiatives such as Digital India and Smart Cities Mission are driving AI adoption.
- Research and Development: Indian research institutions are actively involved in AI R&D, contributing to the global knowledge base.
- Clusters: AI clusters are emerging in Indian cities, with Bengaluru being a prominent hub known for its AI research and industry presence.
Opportunities in India's AI Market
- AI in Agriculture: IoT and AI-powered precision farming can boost productivity.
- AI in Finance: Applications for fraud detection, risk assessment, and customer service automation are in demand.
- AI in Healthcare: Opportunities for predictive diagnostics, personalized treatment, and drug discovery.
- AI in Retail: Technologies like recommendation engines and chatbots are reshaping the retail sector.
Challenges for India AI Mission
- Limited GPU Capacity and Infrastructure: Concerns about timely procurement and deployment of GPUs for AI applications.
- Data Access and Quality: Need for diverse datasets for effective AI model development.
- Limited AI Expertise and High Costs: Shortage of skilled AI professionals in India.
- High Implementation Costs: Capital investments for AI deployment can be prohibitive.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Lack of advanced cloud computing infrastructure for scaling AI applications.
- Ethical and Integrity Concerns: Ensuring responsible AI practices and avoiding biases in AI models.
- Geopolitical and Regulatory Issues: Restrictions on essential AI technologies due to geopolitical tensions.
- Environmental Concerns: AI's energy consumption and environmental impact.
Way Forward
- Incentivize Hardware Manufacturing: Expand initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive scheme for IT hardware.
- Start-up Support: Provide financial incentives and mentorship for AI startups.
- Comprehensive Data Ecosystem: Develop a national data platform for standardized data sharing.
- Prioritize Ethical AI: Establish comprehensive AI ethics guidelines and regulations.
- AI Applications for Societal Impact: Focus on developing AI solutions for critical sectors.
- Promote Sustainable AI: Invest in energy-efficient AI algorithms and hardware.
- Talent Gap: Foster partnerships and attract AI talent to India.
Mains Question
Discuss the objectives and key components of the IndiaAI Mission. How does it aim to transform India's AI landscape?
GS3/Economy
India's First Offshore Mineral Auctions
 Why in News?
Why in News?
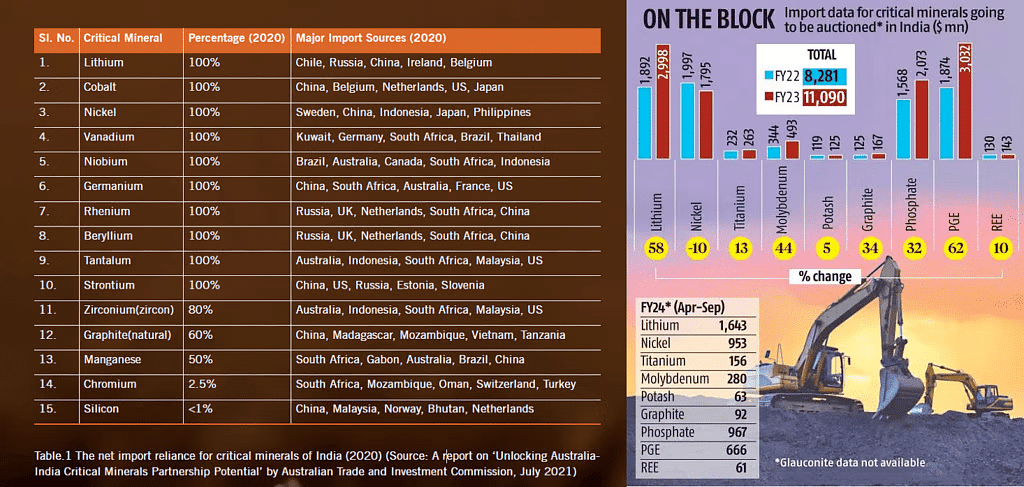
- India is set to launch its first offshore mineral auctions, marking a significant step in resource management. This initiative, part of the proposed National Critical Minerals Mission (NCCM), aims to enhance the supply chain for critical minerals. Union Minister of Mines announced the identification of 10 blocks, marking a pivotal moment in the nation’s quest for self-reliance in mineral resources, in line with the vision of an Atmanirbhar Bharat.
What are the Key Details of the Offshore Mineral Auctions?
Mineral Blocks Identified:
- Exploration reports of 10 blocks located in India’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) are available for auction for grant of composite license. Of these, 7 blocks of poly-metallic nodules and crusts are located in Andaman Sea, 3 blocks of lime-mud are located off the Gujarat coast.
Types of Minerals:
- The mineral blocks which contain critical minerals like Cobalt and Nickel which are key to manufacturing low-carbon technologies to generate, store and transmit clean energy and steel manufacturing.
Regulatory Framework:
- The auctions will be conducted under the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act (OAMDR), 2002. Composite licenses will be issued for mineral resource determination, exploration, and commercial production.
What is the National Critical Mineral Mission?
Need:
- Increasing demand for electronic gadgets and clean energy technologies has led to India's heavy reliance on importing critical minerals, primarily from China. This import dependency has negative economic impacts, contributing to the current account deficit and affecting domestic production. Economic Survey 2023-24 has highlighted strategic concerns regarding India's dependence on China for critical minerals.
Objective:
- Ensure a sufficient supply of critical minerals, including copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt and rare earth elements. These minerals are essential components in almost all electronic gadgets ranging from laptops to electric cars.
Applications:
- Electronics: Essential for manufacturing laptops, electric cars, and other electronic gadgets.
- Clean Energy Technologies: Vital for wind turbines and other renewable energy sources.
- High-Priority Sectors: Nuclear energy, renewable energy, space, defense, telecommunications, and high-tech electronics.
Legislative and Budgetary Measures to Support NCCM:
- Mines and Minerals (Development & Regulation) Amendment Bill 2023: Allows awarding of exploration licenses for 30 deep-seated and critical minerals, including antimony, beryllium, lithium, and more.
Budgetary Support:
- Union Budget 2024-2025 proposed increased allocations for the Geological Survey of India (GSI), Indian Bureau of Mines (IBM), National Mineral Exploration Trust (NMET).
- Rs.1,300 crore for GSI to improve geoscience data and strategic planning.
- Rs.135 crore for IBM to enhance regulatory efficiency and environmental protection.
- Rs. 400 crore for NMET to accelerate mineral exploration and support startups in the sector.
Waiver of Customs Duty:
- The Union Budget 2024-2025 proposed the elimination of customs duties on 25 critical minerals and reductions for two others. This move aims to lower costs for industries reliant on these minerals, attract investments in processing and refining, and foster the growth of downstream industries. Zero import duty on blister copper will stabilize the supply chain for copper refiners, crucial for electronics and construction industries.
How Does Offshore Mineral Auctions Align with the Proposed National Critical Minerals Mission?
Expanding Capabilities:
- Tapping into offshore mineral resources will significantly enhance India's capabilities in sectors like clean energy and steel manufacturing.
Supply Chain Approach:
- The proposed will oversee the entire supply chain of critical minerals, from domestic production to recycling. It will also shield the country from elevated levels of import reliance and supply risks owing to global geo-political turbulence.
Focus on Research and Development:
- The mission will address trade and market access, scientific research, and technology development in the critical minerals value chain.
Encouraging Recycling Initiatives:
- The initiative aims to incentivise the Indian industry to develop recycling capacities for critical minerals, reducing reliance on primary sources.
Mains Question:
Q. Evaluate the potential impact of the National Critical Minerals Mission (NCCM) on India's industrial and technological sectors.
GS3/Economy
The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2024
 Why in news?
Why in news?
- Recently, the "State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2024" (SOFI 2024) report, published by FAO, IFAD, UNICEF, WFP, and WHO, presents a critical analysis of global food security and nutrition trends. This year's report emphasizes the urgent need for increased financing to end hunger, food insecurity, and malnutrition in all its forms.
What are the Key Findings of the SOFI 2024 Report?
Global Prevalence of Undernourishment:
- Between 713 and 757 million people faced hunger in 2023, with one out of eleven people in the world and one out of every five in Africa facing hunger.
- Asia, despite having a lower percentage, still harbors the largest number of undernourished people (384.5 million).
Food Insecurity:
- Approximately 2.33 billion people experienced moderate or severe food insecurity in 2023. Severe food insecurity affected more than 864 million people globally.
Cost of a Healthy Diet:
- The global average cost of a healthy diet rose to USD 3.96 in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms per person per day in 2022.
- Regional Disparities: The cost of a healthy diet is highest in Latin America and the Caribbean and lowest in Oceania.
Stunting and Wasting:
- Improvements in reducing the prevalence of stunting and wasting among children under five have been noted, but progress is insufficient to meet the SDG targets.
Obesity and Anaemia:
- Obesity rates are rising globally, while anaemia in women aged 15 to 49 years is increasing.
Current Levels and Gaps:
- Public spending on food security and nutrition remains inadequate, particularly in low-income countries.
What are the Key Highlights Related to India in the Report?
- India is home to 194.6 million undernourished individuals, the highest in the world.
- The number of undernourished people has decreased from 240 million in the 2004-06 period to the current figure.
- 55.6% of Indians, translating to 790 million people, cannot afford a healthy diet.
- 13% of India's population suffers from chronic undernourishment.
Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2023
- India ranked 111, highlighting significant issues in food security.
- India has the highest prevalence of wasting (18.7%) in South Asia and a high prevalence of stunting (31.7%) in children under five years.
- 27.4% of babies born in India have low birth weight, the highest in the world, reflecting maternal malnutrition.
Public Spending in India
- India's public spending on food security and nutrition has seen some increases, but there is still a need for more effective allocation and utilization of resources to address the root causes of food insecurity and malnutrition.
Impact of Covid-19 in India
- The pandemic has exacerbated food insecurity and malnutrition issues in India, leading to lasting impacts on food access and affordability.
What are the Key Recommendations in the Report?
Increase Public Investment:
- The report highlights the need to increase public spending on food security and nutrition by boosting budgets for programs that reduce hunger and malnutrition.
Mobilize Private Sector Investment:
- Encouraging private sector investment through innovative financing mechanisms can provide additional resources for food security initiatives.
Promote Climate-Resilient Agriculture:
- Developing and implementing climate-resilient agricultural practices is critical to mitigate the impact of climate change on food production.
Improve Agrifood Systems:
- Enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of agrifood systems through better infrastructure, logistics, and market access can help reduce food loss and waste.
Comprehensive Nutrition Programs:
- The report calls for integrated nutrition programs that address both undernutrition and overnutrition.
Focus on Vulnerable Populations:
- Policies should focus on supporting vulnerable groups, like small farmers, women, and children.
Strengthen Data Collection, Monitoring and Reporting:
- Improving data collection and integration with national databases is essential for tracking food security and nutrition.
Mains Question:
Q. Examine the key challenges faced by India in ensuring food security. Discuss the underlying factors contributing to these challenges and suggest effective measures to address them.
GS3/Economy
India's Lithium Mining Challenges
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- India's efforts to secure domestic lithium resources have hit a roadblock as the Ministry of Mines cancelled the auction for a lithium block in Jammu and Kashmir's Reasi district for the second time. The repeated setback has officials weighing the need for further exploration before attempting another auction.
Key Points About the Lithium Block in J&K's Reasi district
Estimated Resources:
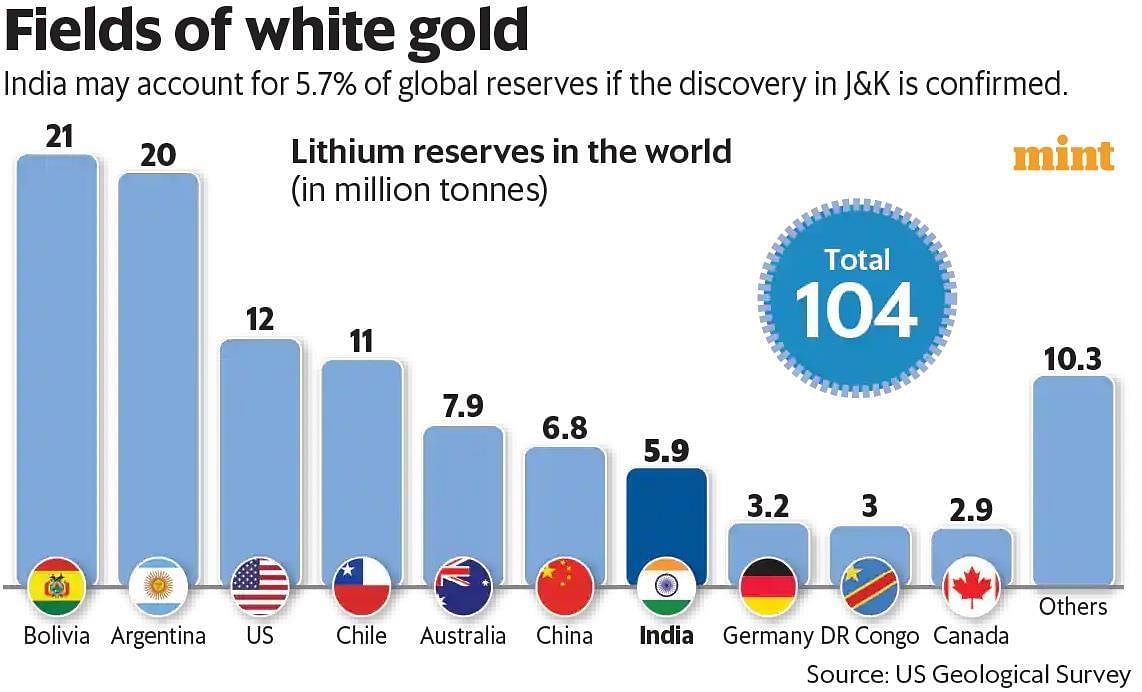
- In February 2023, the Geological Survey of India (GSI) established lithium-inferred resources of 5.9 million tonnes in the Reasi district in Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), which is essential for various applications, particularly in electric vehicle (EV) batteries. This discovery makes India the seventh-largest source of lithium globally.
Auction Attempts:
- The first auction attempt took place in November 2023 but was annulled on March 13 due to fewer than three bidders qualifying. A second auction attempt was made but was again annulled due to no bidders qualifying.
Regulatory Framework:
- According to the Mineral (Auction) Rules, 2015, the auction can proceed to a second round even if fewer than three bidders qualify. However, in this case, no bidders met the qualification criteria. The second auction attempt saw no qualified bidders, which highlights the extent of investor hesitation.
Reasons for Investor Hesitation
Clay Deposits:
- The J&K lithium reserves are primarily clay deposits, which have not yet been commercially proven on a global scale. The path to commercialisation for such deposits is uncertain and may take longer time.
Lack of Beneficiation Study:
- The absence of a beneficiation study to evaluate the feasibility of extracting and processing lithium has raised concerns among potential bidders about the economic viability of the project.
Sub-Par Reporting Standards:
- The auction documents have been criticised for providing limited information about the block. Prospective bidders have expressed concerns about the block's small size and the inadequacy of the data for applying modern mineral systems-based tools.
Exploration Stage Ambiguities
- The primary reason for the low bid interest is the block's exploration status, which is currently at the G3 level according to the United Nations Framework Classification for Resources (UNFC). This level of exploration provides preliminary and less confident estimates of the mineral reserves, which deters investors due to the high risk and uncertainty associated with such investments.
Economic Viability Concerns
- The extraction of lithium is expensive, and with global lithium prices falling, investors are wary of potential financial losses. The current reporting standards do not provide enough clarity on the project's profitability, further deterring investment.
Reserve Price
- The reserve price set for the second auction attempt was based on the highest initial bid offer from the previous round. If this reserve price was deemed too high relative to the perceived value or risk of the block, it could have deterred potential bidders.
Status of Lithium Exploration in India
Successful Auction in Chhattisgarh:
- India’s first successful lithium auction took place in Korba district, Chhattisgarh. The block was auctioned to Maiki South Mining Pvt Ltd in June 2024. The bid included a premium of 76.05%, reflecting strong interest and competitive bidding.
Additional Findings in Korba:
- A private exploration company funded by the National Mineral Exploration Trust (NMET) has identified hard rock lithium deposits in Korba, with concentrations ranging from 168 to 295 parts per million (ppm).
Challenges in Other States:
- Manipur: Lithium exploration efforts in Kamjong district have been stalled due to local resistance. The NMET committee has decided to pause further actions in this area.
- Ladakh: Exploration in the Merak block near the India-China border has yielded disappointing results, leading the NMET committee to suggest dropping the exploration efforts there.
- Assam: Exploration in Dhubri and Kokrajhar districts has not been promising, with the NMET recommending against further upgrades or exploration in these areas.
Challenges in Extraction and Investment of Lithium in India
Extraction Challenges:
- Lithium extraction from hard rock pegmatite deposits is difficult, requiring specialized technology and expertise. Extracting lithium from pegmatite ores involves multiple complex and costly processing stages.
Environmental Concerns:
- Lithium extraction, particularly through open-pit mining, can have substantial environmental impacts, including habitat destruction and pollution. Proper management and mitigation measures are required to minimize these effects.
Transportation:
- In remote areas like J&K's Reasi district, inadequate infrastructure for transportation and logistics can hinder efficient extraction and increase costs.
Nascent Industry:
- India’s lithium sector is still developing, with substantial time required to establish a functional mining and processing infrastructure. Lithium projects, especially from brine assets, typically take 6 to 7 years from discovery to production, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Investment Challenges
- India’s current mineral reporting standards, based on the do not align with the Committee for Mineral Reserves International Reporting Standards (CRIRSCO) used globally. The UNFC standards lack the detail needed to assess economic viability comprehensively.
Local Tensions
- The ethnic and religious tensions could complicate efforts to attract investment and manage resource development. Past conflicts and ongoing violence make the area particularly unstable.
Global Competition and Dependency
- China controls 77% of the global lithium-ion battery manufacturing capacity, creating a strategic challenge for other nations, including India, which seeks to reduce its dependency on Chinese supplies. Investors have multiple opportunities in the global mining market. If other regions offer more attractive or lower-risk opportunities, investors might prioritize those over regions like the J&K lithium block.
Way Forward
Attract Foreign Expertise:
- Attracting foreign companies with expertise in lithium mining and processing will be crucial for accelerating India’s domestic lithium exploration and mining activities.
Lessons from the Lithium Triangle:
- Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina, which house the world's largest lithium reserves, offer valuable lessons. Chile and Bolivia have implemented state-controlled or regulated lithium extraction processes. Recent environmental and social challenges in these countries underscore the importance of robust regulatory frameworks and community engagement.
- Integrate sustainability principles into the entire lifecycle of lithium mining, from extraction to end-of-life battery management.
Local Involvement:
- Plans for lithium exploration include involving local communities and prioritizing them for employment opportunities. However, the broader socio-economic impacts on agriculture, animal husbandry, and tourism need to be addressed.
Government Incentives:
- Government initiatives, including Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes aim to improve the ease of doing business and incentivize investments in the critical minerals sector can draw interest from major players like Ola Electric and Reliance New Energy.
Further Exploration:
- Additional exploration could provide more clarity about the resource and potentially make the block more attractive to investors. However, this approach involves time and additional investment.
Government-Initiated Development:
- Another option is for the government to undertake prospecting or mining operations directly through a government-owned company, as permitted under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) (MMDR) Act. This approach could ensure the development of the block despite the lack of private investor interest.
Easing Business Conditions:
- Amendments to mining regulations and improved ease of doing business are expected to support the development of India’s lithium industry. Negotiate trade agreements that ensure fair access to global markets and protect India’s interests in the lithium supply chain.
Mains Question:
Q. Evaluate the challenges and opportunities in the management and exploitation of lithium resources in India, considering recent developments and setbacks. How does India's dependency on lithium imports from China impact its strategic and economic interests? Suggest measures to reduce this dependency.
GS3/Economy
9th Governing Council Meeting of NITI Aayog
 Why in news?
Why in news?
- Recently, the 9th Governing Council Meeting of NITI Aayog, chaired by the Prime Minister, convened leaders from 20 states and 6 union territories to discuss the "Viksit Bharat @2047" theme, aiming to establish a framework for India's development as a developed nation by 2047.
What are the Key Outcomes of the Meeting?
- Vision of a USD 30 Trillion Economy: India aims to become the world's third-largest economy by 2047, with a GDP target of USD 30 trillion. This ambition highlights the country's focus on sustained economic growth, innovation, global competitiveness.
- State Visions for 2047: The meeting encouraged each state and district to formulate its vision for 2047, aligning with the national vision of a developed India. Emphasising the importance of states in achieving national goals, the Prime Minister reiterated that developed states are crucial for a developed India.
- Zero Poverty Objective: A significant takeaway from the meeting was the emphasis on eradicating poverty at an individual level. The concept of 'zero' villages was discussed, aiming for holistic development starting at the grassroots.
- Infrastructure and Investment: The Prime Minister stressed the importance of infrastructure, law and order, and good governance as key factors in attracting investments. An 'Investment-friendly Charter' was proposed to encourage states to create an investor-friendly environment, monitored through parameters fostering healthy competition among states.
- Education and Skill Development: There was a strong emphasis on skilling the youth to make them employment-ready, leveraging India's demographic dividend as a global skilled resource hub.
- Agricultural Productivity and Natural Farming: Enhancing productivity, diversifying agriculture, and promoting natural farming practices were discussed as means to improve soil fertility, reduce costs, and access global markets.
- Ease of Living: Recommendations from the National Conference of Chief Secretaries were considered, focusing on 5 key themes such as drinking water, electricity, health, schooling, and land/property management. The Prime Minister encouraged States to initiate Demographic Management Plans to address the issues of population ageing in the future.
- The Prime Minister asked the States to take up capacity building of government officials at all levels and encouraged them to collaborate with the Capacity Building Commission for the same.
- The Prime Minister encouraged the creation of River Grids at the State level for the effective utilization of water resources.
- Cybersecurity and AI in Governance: The integration of technology in governance, addressing cybersecurity challenges, and leveraging AI for efficient governance were highlighted as critical areas for future readiness.
What is the Governing Council of NITI Aayog?
- About: NITI Aayog is the premier body tasked with evolving a shared vision of national priorities and strategies, with the active involvement of States, in shaping the development narrative. The Governing Council, which embodies the objectives of cooperative federalism presents a platform to discuss inter-sectoral, inter-departmental, and federal issues to accelerate the implementation of the national development agenda.
- Members: Prime Minister of India (Chairperson), Chief Ministers (States and Union Territories with legislature), Lt Governors of other UTs, Ex-Officio Members, Vice Chairman, NITI Aayog, Full-Time Members, NITI Aayog, Special Invitees.
- Functions: Governing Council Secretariat (GCS) coordinates the meetings of the Governing Council. It also coordinates the activities of all the Verticals, Divisions, and Units of NITI Aayog. GCS acts as the nodal division for coordinating matters related to the Annual Report of NITI Aayog for circulation in the Parliament. The Division also handles Parliament Questions, Standing Committee matters, RTI queries, CPGRAMS grievances, pertaining to GCS.
Mains Question:
- Q. Discuss the role of NITI Aayog in fostering cooperative federalism in India. How has it contributed to enhancing the quality of governance at both the central and state levels?
GS3/Economy
Report on Currency and Finance (RCF) 2023-24
 Why in news?
Why in news?
As per the 'for the year 2023-24' released by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), India's digital economy is set to constitute 20% of the country's GDP by 2026, doubling its current contribution of 10%. This significant growth projection underscores the transformative potential of digitalization in finance and its far-reaching impact on India's economy.
What is the Report on Currency and Finance?
About:
- It is an annual publication of the RBI.
- The report covers various aspects of the Indian economy and financial system.
Theme:
- The theme of the "Report is "India’s Digital Revolution."
- It focuses on the transformative impact of digitalization across various sectors in India, particularly in the financial sector.
Dimensions:
It highlights how digital technologies are reshaping economic growth, financial inclusion, public infrastructure, and the regulatory landscape, while also addressing the associated opportunities and challenges.
What are the Key Highlights from the Report on Currency and Finance 2023-24?
Expansion of Financial Services:
- The evolution and adoption of technological advancements have led to massive improvement in deepening of digital financial services.
- The potential for expanding financial inclusion in India by application of digital technologies is high in view of existing conditions.
- First, the progress of financial inclusion in India is evident in the Reserve Bank’s Financial Inclusion Index and narrowing account access gap between income groups.
- Second, in rural India, 46% of the population consists of wireless phone subscribers and 54% are active internet users.
- Third, given that more than half of FinTech consumers are from semi-urban and rural India and more than a third of digital payment users are from rural areas there is potential for furthering digital penetration and closing the rural-urban gap.
- Over two lakh gram panchayats have been connected through BharatNet in the last decade, enabling provision of services like e-health, e-education and e-governance in rural areas.
Mobile Penetration:
- Although internet penetration in India was at 55% in 2023, the internet user base has grown by 199 million in the recent three years.
- India’s cost per gigabyte (GB) of data consumed is the lowest globally at an average of Rs. 13.32 per GB.
- India also has one of the highest mobile data consumption in the world, with an average per-user per-month consumption of 24.1 GB in 2023.
- There are about 750 million smartphone users, which is expected to reach about one billion by 2026.
- India is expected to be the second largest smartphone manufacturer in the next five years.
Digital Economy:
- The digital economy currently accounts for 10% of India's GDP.
- By 2026, this figure is expected to double, contributing to 20% of GDP, driven by rapid advancements in digital infrastructure and financial technology.
India Stack:
- Key components such as Aadhaar, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), DigiLocker have revolutionised service delivery. UPI has seen a tenfold increase in transactions over four years.
- The world's largest biometric-based identification system, covering 1.38 billion ID holders.
- A real-time, low-cost transaction platform contributing significantly to financial inclusion.
- Cloud-based storage providing secure document access.
Internationalisation of Digital Public Infrastructure:
- India’s DPI is going global by collaborating with other nations to develop digital identity solutions under the Modular Open Source Identity Platform (MOSIP) programme.
- Interlinkage of the UPI with fast payment systems of other nations like Singapore’s PayNow, the United Arab Emirates’ (UAE) Instant Pay Platform (IPP) and Nepal’s National Payments Interface (NPI) for cost-effective and fast remittances.
- Partnering with other central banks and foreign payment service providers to broaden RuPay acceptance beyond geographical borders, such as in countries like Bhutan, Mauritius, Singapore and the UAE.
- Sharing the Beckn protocol with nations to provide their public and private services through open, lightweight and decentralised specifications. Beckn Protocol enables the creation of open, peer-to-peer decentralized networks for pan-sector economic transactions.
Vibrant Initiatives:
- Open Credit Enablement Network, Open Network for Digital Commerce, and the Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit are driving the digital lending ecosystem.
- Fintech companies are partnering with non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) to offer digital credit solutions and enhance financial inclusion.
What are the Challenges Posed by Digitalisation?
Impact on Financial Markets:
- Digitalisation has led to the introduction of complex financial products and services, significantly impacting market structure and financial stability.
- The emergence of digital players with unreliable funding models increases system vulnerabilities and poses challenges to financial stability.
- Hyper-diversification of financial services may result in a "barbell" financial structure, where a few dominant multi-product players coexist with numerous niche service providers.
Fear of Monopolisation:
- In India's digital payment ecosystem proliferation of Unified Payments Interface (UPI) applications has expanded customer choices and increased transaction volumes. However, a significant share of transactions is dominated by a few applications, as indicated by the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) (a common measure of market concentration of an industry used to determine market competitiveness).
- To address concentration risks, the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has capped the market share of a single third-party application provider to 30% by December 2024.
Cyber Security Challenges:
- Cybersecurity is a major concern due to the diverse nature of cyber threats targeting digital financial infrastructure.
- In India, security incidents handled by the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) have skyrocketed from 53,117 in 2017 to over 1.32 million between January and October 2023.
- The majority of these incidents involve unauthorized network scanning, probing, and exploitation of vulnerable services.
- In India, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was USD 2.18 million, which is less than the global average but still represents a significant increase.
Consumer Protection Issues:
- Digitalisation has also led to dark patterns, where consumers are tricked into making decisions against their interests. Additionally, extensive use of customer data by companies raises concerns about data protection and privacy, potentially compromising customer trust.
Reshaping Labour Markets:
- Digital technologies are transforming workforce composition, job quality, skill requirements, and labour policies. The implementation of AI in financial services shifts roles towards higher-skilled tasks, automating routine functions and aiding decision-making.
- Between 2013 and 2019, support roles in the financial sector declined, while the number of professionals and technicians increased.
- Private sector banks reported high turnover rates in 2022-23, leading to significant risks such as loss of institutional knowledge and higher recruitment costs.
What Steps Have Been Taken to Deal With the Challenges?
Financial and Digital Inclusion:
- India has established Digital Banking Units (DBUs) and improved UPI with offline and conversational payments in local languages.
- Payment Infrastructure Development Fund (PIDF) has been launched to broaden payment infrastructure, and digitalisation of agricultural finance is underway.
Customer Protection:
- To address regulatory and customer protection challenges in the digital lending ecosystem, the RBI issued the Guidelines on Digital Lending, focusing on loan servicing, disclosures, grievance redressal, credit assessment standards, and data privacy.
- Reserve Bank-Integrated Ombudsman Scheme (RB-IOS) has improved grievance redress mechanisms, and public awareness campaigns like ‘RBI Kehta Hai’ e-BAAT programme educate the public on digital payment products and fraud prevention.
Data Protection:
- The RBI has implemented data localisation for payments data and guidelines preventing digital lending applications from accessing private information without explicit user consent.
- Card-on-file tokenisation (CoFT) through card-issuing banks has been enabled to enhance the security of digital payments.
Cyber Security:
- To promote the security of digital transactions, measures such as two-factor authentication, increased customer control over card usage, faster turnaround times for transaction failures, and augmented supervisory oversight have been implemented.
- The RBI has issued comprehensive guidelines for IT and Cyber Risk management.
FinTech Regulation:
- The RBI has launched the Regulatory Sandbox scheme, the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub, and FinTech Hackathons to encourage FinTech innovations.
Digital Technologies in Regulation and Supervision:
- Digital tools are being leveraged to enhance supervisory and monitoring frameworks. The DAKSH system helps digitalise supervisory processes.
- Integrated Compliance Management and Tracking System (ICMTS) and Centralised Information Management System (CIMS) are also being implemented to enhance data management and analytics capabilities.
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the major challenges associated with the digitalisation of the Indian economy. How can these challenges be effectively addressed to ensure inclusive and sustainable growth?
|
164 videos|800 docs|1160 tests
|
















