Inflation Accounting | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
What is Inflation Accounting?
Inflation accounting involves adjusting financial statements to reflect changes in price levels. It is a method used in financial reporting to present a more accurate view of a company's financial health during times of significant inflation or deflation. Unlike traditional historical cost accounting, which records transactions at their original purchase prices, inflation accounting updates these values to reflect current market prices. This adjustment helps counter the distortions caused by inflation, such as understating asset values and overstating profits.
Methods of Inflation Accounting
Inflation accounting involves methods that help adjust financial statements to account for changes in purchasing power due to inflation. One such method is the Current Purchasing Power (CPP) Method.
Current Purchasing Power (CPP) Method
The CPP method adjusts historical costs by using a general price index, like the Consumer Price Index (CPI), to show what these costs would be in terms of current purchasing power.
Key Features and Steps:
The current purchasing power method has specific features and steps that are crucial to understanding how it works effectively. These include:
- Use of Price Index: The CPP method employs a general price index, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI), to adjust historical costs of assets, liabilities, equity, and income statement items.
- Uniform Adjustment: All items in the financial statements are adjusted uniformly using the same index, ensuring consistency across the board.
- Monetary vs. Non-Monetary Items: Monetary items like cash and receivables are not adjusted since their value is already in current terms. Non-cash items such as inventory and fixed assets are adjusted to reflect their current purchasing power.
- Equity Adjustment: The equity section in the balance sheet is also adjusted to reflect changes in purchasing power over time.
Calculation Steps:
- Determine the General Price Index: Find the price index for both the base period and the current period.
- Calculate the Index Adjustment Factor: Determine the adjustment factor for the index.
- Adjust Historical Costs: Multiply the historical cost of non-monetary items by the index adjustment factor.
 |
Test: Inflation Accounting
|
Start Test |
Current Cost Accounting (CCA) Method
The Current Cost Accounting method involves adjusting assets and liabilities to their current replacement costs rather than considering general price level changes.
Key Features and Steps:
- Replacement Cost: This involves valuing assets and liabilities at their current replacement costs, which means determining the amount it would currently cost to replace them at present prices.
- Depreciation Adjustment: In this step, the depreciation of fixed assets is recalculated based on replacement cost. This ensures that the depreciation reflects the current economic value of the asset's consumption.
- Cost of Sales Adjustment: Here, adjustments are made to inventory values and cost of sales to reflect current costs accurately. This helps in preventing the understatement of costs and overstatement of profits.
- Monetary Working Capital Adjustment: This involves making adjustments to the working capital to reflect the current cost of maintaining operational liquidity.
Calculation Steps:
The calculation steps of the current cost accounting method are outlined below for better comprehension:
- Identify Replacement Costs: This step involves determining the current replacement cost of assets and liabilities accurately.
- Depreciation Adjustment: Calculate the depreciation based on the replacement cost of fixed assets to ensure accuracy in reflecting the asset's current economic value.
- Adjust Inventory and COGS: Update inventory values and cost of goods sold to reflect current costs precisely, thereby ensuring the financial statements are more representative of the current economic reality.
Objectives of Inflation Accounting
 Inflation accounting serves several purposes to ensure financial statements remain accurate and relevant amidst significant changes in price levels:
Inflation accounting serves several purposes to ensure financial statements remain accurate and relevant amidst significant changes in price levels:
- Reflect True Economic Value: Estimating asset values accurately is crucial. Adjusting asset values to match current market conditions prevents undervaluation or overvaluation due to historical cost distortions. It also enhances the representation of liabilities, reflecting their true economic impact at current price levels.
- Improve Decision-Making: Inflation accounting aids informed management decisions. It offers a clearer financial overview to management, assisting in strategic and operational decision-making. Additionally, it fosters investor confidence, enabling them to make better-informed choices based on financial statements reflecting actual economic conditions.
- Enhance Comparability Over Time: Ensuring consistent financial reporting is important. Inflation adjustments enable comparability of financial performance and position across different periods, even amidst significant price fluctuations. Longitudinal analysis becomes more accurate, allowing for precise trend analysis over the years by eliminating inflation-induced distortions.
- Accurate Profit Measurement: Inflation accounting aids in calculating sustainable profits. By preventing profit overstatements resulting from ignoring inflation, it provides a more reliable measure of true profitability. Real income determination is also facilitated, as it adjusts revenues and expenses to current price levels, ensuring that income statements reflect the actual earning capacity of a company.
- Protect Capital Maintenance: Inflation accounting helps companies safeguard their physical capital by adjusting for inflation, ensuring the value of their capital investments is preserved. This process also plays a crucial role in maintaining the purchasing power of shareholders' equity, hence safeguarding the real value of investors' investments.
- Regulatory and Compliance Benefits: Inflation accounting aligns with accounting standards and regulations that mandate or recommend adjustments for inflation. By complying with legal and regulatory frameworks, it enhances transparency in financial reporting, meeting stakeholder expectations and regulatory requirements effectively.
- Fair Performance Evaluation: One significant advantage of inflation accounting is its ability to provide a more equitable assessment of management's performance. By eliminating the distortions triggered by inflation, it ensures that performance evaluations are based on genuine financial data. This approach also enables more accurate benchmarking against competitors and industry standards by nullifying the impact of inflation.
- Improved Financial Analysis: Inflation accounting leads to more insightful financial ratios by basing these metrics on values adjusted for inflation. This approach offers better insights into liquidity, solvency, and profitability, ensuring that financial analysis accurately mirrors the true economic conditions. Consequently, stakeholders can make more informed evaluations of the company's financial health.
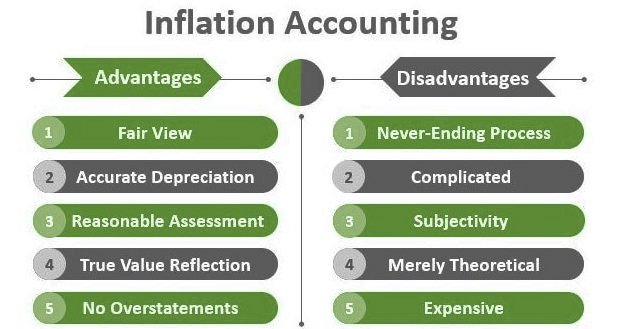
Advantage and Disadvantage of Inflation Accounting
Advantages of Inflation Accounting:
- Inflation accounting enhances the accuracy and relevance of financial statements during inflationary periods.
- Adjusting historical costs to reflect current market values provides a true economic valuation of assets and liabilities.
- Prevents overstatement of profits that can occur with non-adjusted accounting methods.
- Leads to more accurate profit measurement and a better understanding of a company's financial performance.
- Promotes better decision-making by management and investors.
- Improves comparability over different periods for more consistent and accurate trend analysis.
- Preserves the real value of capital and equity, protecting investments from inflation's eroding effects.
- Enhances transparency and compliance with accounting standards, fostering confidence among stakeholders.
Disadvantages of Inflation Accounting:
- Implementing and maintaining inflation accounting systems involve complexity and additional costs.
- Updating data using current price indices or replacement cost measures requires extensive resources and time.
- Complexity can introduce a greater risk of errors in financial reporting.
- Subjective judgments in determining indices or replacement costs can lead to inconsistencies.
- Reduced comparability among companies due to varying judgment criteria.
- Users unfamiliar with inflation-adjusted figures may face difficulties in interpreting financial statements correctly.
- Challenges in regulatory compliance and potential legal implications due to differing methods and indices.
 |
Download the notes
Inflation Accounting
|
Download as PDF |
Conclusion
Inflation accounting is a crucial method that helps companies show a more realistic financial picture during times of changing prices. By adjusting historical costs to current values, this approach removes distortions caused by inflation or deflation. This adjustment ensures that financial statements accurately reflect the true economic value of a company's assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses.
Implementing inflation accounting can result in better decision-making, enhanced financial analysis, and improved alignment of financial reporting with the actual economic conditions. Despite the added complexity and potential adjustments needed, the benefits of presenting a clearer and more accurate financial picture far outweigh the challenges. Organizations, investors, and other stakeholders rely on precise financial information to make crucial decisions, and inflation accounting plays a vital role in enhancing the reliability and relevance of financial reporting in times of inflation.
|
190 videos|1 docs
|
FAQs on Inflation Accounting - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is Inflation Accounting? |  |
| 2. What are the methods of Inflation Accounting? |  |
| 3. What are the objectives of Inflation Accounting? |  |
| 4. How does Inflation Accounting help in providing accurate financial information? |  |
| 5. Why is Inflation Accounting important for investors? |  |
























