Finacial Statements Audit | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
Audit of Financial Statements and Audit Report
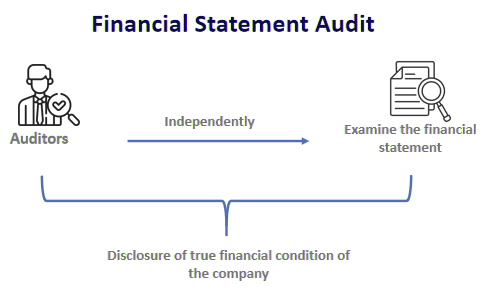
An audit of financial statements is a vital evaluation conducted by an external auditor to ensure that a company's financial statements accurately represent its financial standing and performance. The audit adheres to specific standards and involves reviewing financial records, transactions, and internal controls to identify any significant errors or fraud.
Key Stages of the Audit Process
Here are the key stages of the audit process that aid in better comprehension:
- Planning and Risk Assessment: The auditor delves deeply into understanding the business, its surroundings, and its internal controls. This involves pinpointing areas that could pose risks leading to significant errors in financial statements. A comprehensive plan is then crafted detailing the nature, timing, and extent of audit procedures.
- Evaluation of Internal Controls: This phase entails scrutinizing the design and efficiency of the organization's internal control mechanisms. It aims to determine to what extent the auditor can depend on these controls to lessen the need for substantive testing.
- Substantive Testing: Substantive testing involves conducting thorough examinations of transactions and account balances to gather evidence that validates the figures and disclosures in the financial statements. Various types of substantive testing are employed, such as analytical procedures, detailed tests, and confirmation from external parties.
- Reviewing Financial Statement Presentation: This step ensures that the financial statements and accompanying disclosures are not only comprehensive but also compliant with the pertinent accounting standards and regulations.
- Forming an Audit Opinion: The final stage involves assessing the adequacy and relevance of the evidence accumulated throughout the audit process. It culminates in a determination as to whether the financial statements are devoid of significant errors.
Audit Report
An audit report serves as the formal conclusion of an audit, offering an unbiased evaluation of an organization's financial statements. It conveys the audit findings to various stakeholders, such as shareholders, management, creditors, regulators, and other parties interested in the entity's financial well-being. The report assesses whether the financial statements accurately represent the entity's financial performance and position, ensuring they are devoid of significant errors.
Components of Audit Reports
The key elements of an audit report are detailed below:
Title:
- The title clearly indicates that it is an independent auditor's report.
Addressee:
- Specifies the recipients of the report, commonly the shareholders or the board of directors.
Opinion Section:
- Opinion on the Financial Statements: This section states the auditor's opinion on whether the financial statements present a true and fair view in accordance with the applicable financial reporting framework (e.g., IFRS, GAAP).
- Unqualified (Clean) Opinion: Indicates no material misstatements.
- Qualified Opinion: Indicates that with some exceptions, the financial statements are fairly presented.
- Adverse Opinion: Indicates that the financial statements are materially misstated and do not present a true and fair view.
- Disclaimer of Opinion: Indicates that the auditor was unable to obtain sufficient evidence to form an opinion.
Basis for Opinion:
- Describes the basis for forming the opinion, stating that the audit was conducted in accordance with applicable auditing standards.
- Includes a statement of compliance with ethical requirements and an assertion about the auditor's independence.
Key Audit Matters (KAMs):
- Highlights the most significant matters encountered during the audit.
- Describes why each matter was considered significant and how it was addressed in the audit.
Responsibilities of Management and Those Charged with Governance:
- Outlines management's responsibilities for the preparation and fair presentation of the financial statements.
- Describes the role of management in maintaining internal controls and ensuring that the financial statements are free from material misstatement due to fraud or error.
- Includes responsibilities of those charged with governance (like the board of directors) in overseeing the financial reporting process.
Auditor's Responsibilities for the Audit of the Financial Statements:
- Explains the scope of the audit and the auditor's responsibilities.
- Describes what an audit involves, including risk assessment procedures, understanding of internal controls, and evaluation of accounting policies and estimates.
- States that the auditor believes the audit evidence obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for the opinion.
Other Reporting Responsibilities:
- May include additional reporting responsibilities, such as reporting on other legal and regulatory requirements.
Signature:
- The report is signed by the audit engagement partner or the auditing firm.
Date:
- Indicates the date on which the audit report is signed, marking the completion of the audit.
Auditor's Address:
- The name, city, and country of the audit firm.
Conclusion
An audit report is a document where the auditor gives their final evaluation and viewpoint on the financial statements after completing a comprehensive audit. This section condenses the discoveries and decisions made during the audit procedure and conveys the auditor's judgment on the fairness and accuracy of the financial statements. It condenses the auditor's discoveries in a straightforward and brief way, ensuring openness and responsibility in financial reporting practices.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
















