Collective Bargaining | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
What is Collective Bargaining?
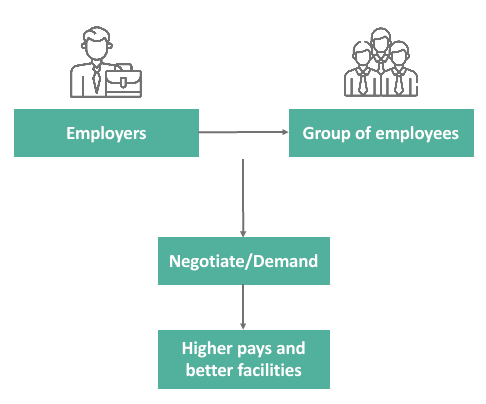
Collective bargaining is the process through which an employer and a group of employees negotiate employment terms. Typically, employees are represented by a labor union during these negotiations.
Negotiations can cover various aspects such as working conditions, salaries, compensation, working hours, and benefits. The aim is to establish a collective bargaining agreement, which is a written contract outlining these terms. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), collective bargaining is a fundamental right for all workers.
Key Points:
- Collective bargaining involves negotiating employment terms between an employer and a group of workers, usually represented by a labor union.
- Issues addressed in these negotiations include working conditions, salaries, compensation, working hours, and benefits.
- The objective is to create a collective bargaining agreement or contract.
- Different types of collective bargaining include composite, concessionary, distributive, integrative, and productivity bargaining.
- In the 2022 midterm elections, Illinois and Tennessee voters took opposing stances: either securing collective bargaining rights in their state constitution or limiting union powers.
How Collective Bargaining Works
The ILO asserts that collective bargaining is a fundamental right for all workers, allowing them to present grievances and negotiate employment terms. This process helps to reduce workplace inequalities and provides labor protection.
Typically, collective bargaining occurs between company management and labor union leaders, who represent the employees' interests. It is initiated when employee contracts need renewal or when changes are proposed in the workplace. These changes might involve:
- Employment conditions
- Working conditions and workplace rules
- Base pay, wages, and overtime
- Work hours and shift lengths
- Holidays, sick leave, and vacation time
- Benefits such as retirement and healthcare
Issues in collective bargaining fall into three categories:
- Mandatory Subjects: Legally required topics, like salary and workplace safety.
- Voluntary Subjects: Negotiable topics not legally mandated, such as union issues and employer board member decisions.
- Illegal Subjects: Topics that violate laws, such as workplace discrimination.
The goal is to achieve a collective bargaining agreement that defines employment rules for a specified period. Union members contribute to the cost of this representation through union dues. The process may sometimes involve strikes or lockouts if an agreement is not reached.
Steps in Collective Bargaining
Collective bargaining is a complex and sometimes contentious process, involving various stages to reach an agreement. Here’s a breakdown of the typical steps:
Identifying Issues and Preparing Demands: This initial step involves listing grievances, such as poor management practices or insufficient salaries.
Negotiating: The union assembles a team of professional negotiators to engage with the employer’s negotiating team. Both sides meet repeatedly to work toward a satisfactory agreement.
Reaching a Tentative Agreement: Once an agreement is reached, both negotiating teams present it to their respective groups. This stage may involve resolving any last-minute issues and finalizing details.
Accepting and Ratifying the Agreement: The proposed agreement is then put to a vote among union members, who decide whether to accept or reject the contract.
Administering the Agreement: After ratification, the agreement is put into practice. Workers and shop stewards monitor compliance to ensure the employer adheres to the terms.
In cases where an agreement isn’t reached by the deadline, unions may call for a strike, while employers might impose a lockout. These measures are considered last resorts and are usually avoided if possible.
Collective Bargaining Laws
In many industrialized nations, laws protect workers' rights to collective bargaining and union formation, though restrictions may apply in certain sectors. In the United States, the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA) safeguards most workers’ rights to engage in collective bargaining, form unions, discuss grievances, and strike. However, certain workers, such as federal, state, and local government employees and agricultural workers, are excluded from these protections.
The National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) oversees labor practices and collective bargaining under the NLRA, including supervising union elections and ensuring fair voting.
States also have their own collective bargaining laws. For example, in the 2022 midterm elections, Illinois voters enshrined collective bargaining rights in the state constitution, while Tennessee voters approved a right-to-work law limiting union power.
Types of Collective Bargaining
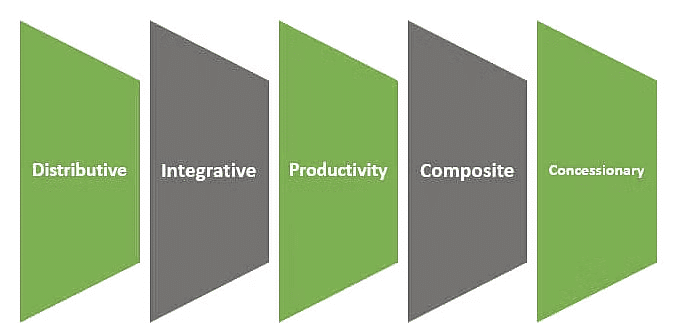
Collective bargaining can take various forms:
- Composite Bargaining: Focuses on issues beyond compensation, such as working conditions and job security, aiming for a harmonious employer-employee relationship.
- Concessionary Bargaining: Involves unions making concessions, such as giving up benefits, often during economic downturns, to secure job security.
- Distributive Bargaining: Aims to benefit one party financially at the expense of the other, typically involving wage increases or other financial gains for workers.
- Integrative Bargaining: Seeks to find win-win solutions where both parties gain. It involves addressing each side’s interests to create mutual benefits.
- Productivity Bargaining: Focuses on linking compensation to productivity. Higher wages are negotiated to boost employee output and, consequently, company profits.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Collective Bargaining
Advantages:
- Increased Employee Voice: Collective bargaining amplifies workers' voices. When employees unite with a common goal, they gain greater negotiating power compared to individual negotiations. Companies find it challenging to ignore the demands of a unified group.
- Enhanced Workplace Conditions: Collective bargaining can lead to significant improvements in working conditions. It ensures that health and safety standards are enforced and provides fair wages, overtime pay, and vacation time for all workers.
- Clear Rights and Responsibilities: The process results in a clear collective bargaining agreement that outlines the rights and responsibilities of both employers and employees. This agreement helps both parties understand their obligations and expectations.
Disadvantages:
- Time-Consuming: Collective bargaining can be a lengthy process, sometimes taking weeks or even months. Negotiations involve multiple rounds of discussions, revisions, and votes, which can prolong the finalization of terms.
- High Costs: The negotiation process can incur significant costs. Time spent away from work for negotiations can reduce productivity and impact the company’s financial performance.
- Potential Bias: The process may be perceived as biased because unions, representing a collective group, can sometimes pressure employers into accepting terms that may not be favorable for the company. This can lead to agreements that might be disadvantageous to the employer.
Summary of Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Amplifies employee voice and bargaining power.
- Improves working conditions and ensures protections.
- Clearly defines rights and responsibilities for both parties.
Cons:
- Can be a lengthy and complex process.
- Involves significant costs and potential productivity loss.
- Employers may face pressure to accept terms that may not be ideal.
Criticisms of Collective Bargaining
Collective bargaining, especially in the public sector, faces criticism for potentially leading to excessive pay and burdening taxpayers. Critics argue that it can lead to unsustainable wages for public employees. Supporters contend that concerns about excessive pay are often overstated, with public sector workers typically earning only slightly more than their nonunion counterparts.
Notable examples include former Governors Chris Christie and Scott Walker, who faced backlash for their actions against public sector unions. Christie’s pension reforms and Walker’s limits on teachers' bargaining rights were particularly controversial.
Example of Collective Bargaining
In 2021, John Deere employees sought improved wages and benefits during a period of high company profits. After rejecting the initial proposal, workers went on strike, which caused significant disruption. The strike ended after a month when John Deere agreed to a new contract meeting most of the workers’ demands.
Objectives of Collective Bargaining
The primary goal of collective bargaining is to negotiate and finalize a collective bargaining agreement that establishes fair employment terms and conditions, benefiting both employees and employers.
Scope of Collective Bargaining
Collective bargaining addresses various workplace issues, including compensation, working conditions, benefits, and company policies, and provides a framework for resolving disputes between employers and employees.
Conclusion
Collective bargaining empowers workers to negotiate for better wages, benefits, and working conditions collectively. It enhances their leverage compared to individual negotiations and has been crucial in developing an industrial middle class in modern economies.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Collective Bargaining - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is collective bargaining? |  |
| 2. What are the key elements of collective bargaining? |  |
| 3. Why is collective bargaining important? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of collective bargaining for employees? |  |
| 5. How does collective bargaining impact the relationship between employers and employees? |  |





















