Unit Test (Solutions): Carbon and its Compounds | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 Hour
M.M. 30 Marks
Attempt all Questions
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1. How many double bonds are there in a saturated hydrocarbon? (1 Mark)
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Zero
Ans: (d)
A saturated hydrocarbon has zero double bonds, as all carbon atoms are bonded to the maximum number of hydrogen atoms.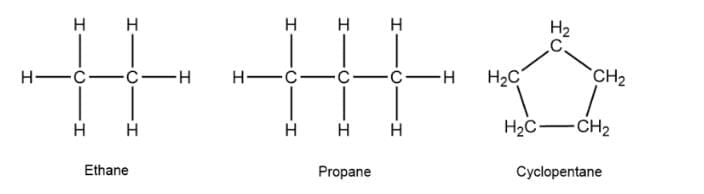 Saturated Hydrocarbons
Saturated Hydrocarbons
Q2. The allotrope of carbon which is a good conductor of heat and electricity is (1 Mark)
(a) Diamond
(b) Graphite
(c) Charcoal
(d) None of these
Ans: (b)
The allotrope of carbon which is a good conductor of heat and electricity is graphite, due to its layered structure allowing electron mobility.
Q3. Which of the following will undergo an addition reaction? (1 Mark)
(a) CH4
(b) C3H8
(c) C2H6
(d) C2H4
Ans: (d)
C2H4 is an alkene, which can undergo an addition reaction due to the presence of a double bond.
Q4. In a diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms to form (1 Mark)
(a) A hexagonal array
(b) A rigid three-dimensional structure
(c) A structure in the shape of a football
(d) A structure of a ring
Ans: (b)
In a diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms to form a rigid three-dimensional structure, contributing to its hardness.
Q5. C3H8 belongs to the homologous series of (1 Mark)
(a) Alkynes
(b) Alkenes
(c) Alkanes
(d) Cycloalkanes
Ans: (c)
C3H8 belongs to the homologous series of alkanes.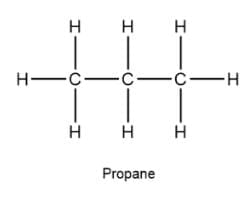
Q6. Gas is evolved when ethanol reacts with sodium. Name the gas evolved and write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved. (2 Marks)
Ans: Hydrogen gas is evolved when ethanol reacts with sodium. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
2Na + 2CH3CH2OH → 2CH3CH2ONa + H2
Q7. How is ethene prepared from ethanol? Give the reaction involved in it. (2 Marks)
Ans: Ethanol is heated at 443 k in excess of concentrated sulphuric acid to obtain ethene. The reaction removes water from ethanol, resulting in the formation of ethene.
CH3CH2OH + Conc. H2SO4 → CH2 = CH2 + H2O
Q8. Carbon, the Group (14) element in the Periodic Table, is known to form compounds with many elements. Write an example of a compound formed with (2 Marks)
(a) Chlorine (Group 17 of the periodic table)
(b) Oxygen (Group 16 of the periodic table)
Ans:
(a) Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
(b) Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Q9. Name the functional groups present in the following compounds (3 Marks)
(a) CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3
(b) CH3CH2CH2COOH
(c) CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO
Ans:
(a) A ketone functional group is present in the compound CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3.
(b) A carboxylic acid functional group is present in the compound CH3CH2CH2COOH.
(c) An aldehyde functional group is present in the compound CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO.
Q10. Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain multiple bonds between the two C-atoms and show addition reactions. Give the test to distinguish ethane from ethene. (3 Marks)
Ans: The bromine water test can be used to distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Saturated compounds don’t give an additional reaction. Hence, there won’t be any change in the reaction mixture. In contrast, if an unsaturated hydrocarbon is added to bromine water, its colour will decolourise.
Saturated hydrocarbon + Br₂ → No Reaction (No Colour Change)
Unsaturated hydrocarbon + Br₂ → Reaction will occur (Decolourise)
Q11. A compound X is formed by the reaction of carboxylic acid C2H4O2 and alcohol in the presence of a few drops of H2SO4. The alcohol on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 followed by acidification gives the same carboxylic acid as used in this reaction. Give the names and structures of (a) carboxylic acid, (b) alcohol and (c) compound X. Also, write the reaction. (3 Marks)
Ans: Here, the carboxylic acid is ethanoic acid, alcohol is ethanol, and compound X is ethyl ethanoate.
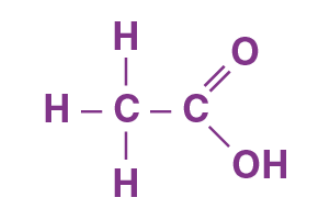 Structure of Ethanoic Acid
Structure of Ethanoic Acid
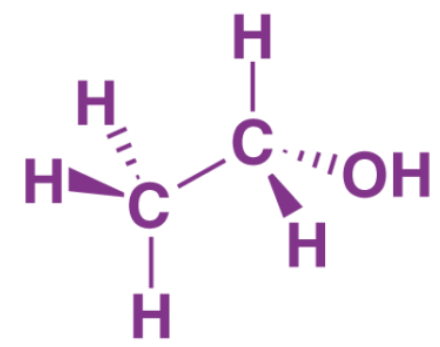 Structure of Ethanol
Structure of Ethanol
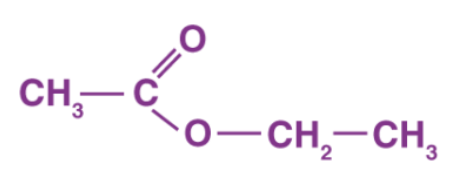 Structure of Ethyl Ethanoate
Structure of Ethyl Ethanoate
Reactions Involved:
CH3COOH + CH3CH2COOH → CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
C2H5OH + Alkaline KMnO4 → CH3COOH
Q12. Write the structural formulae of all the isomers of hexane. (5 Marks)
Ans: There are five isomers of hexane.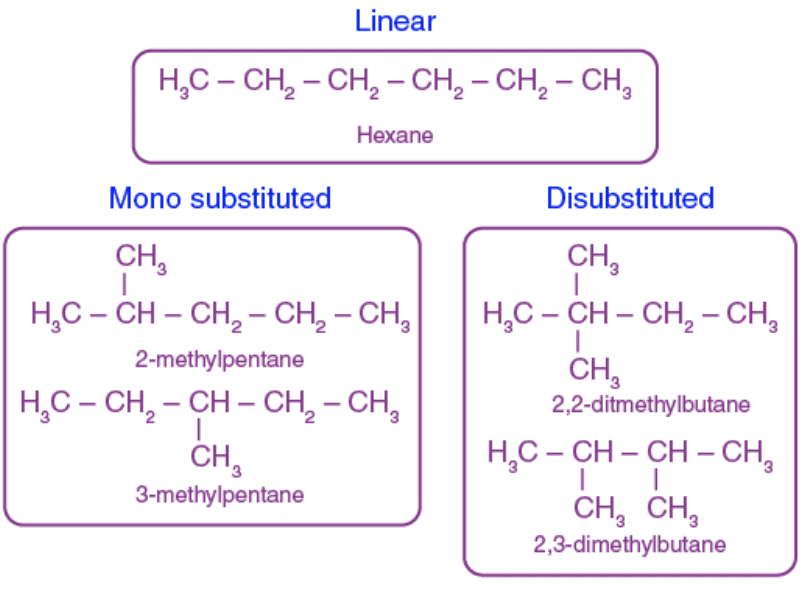
Q13. Look at Figure and answer the following questions: (5 Marks) 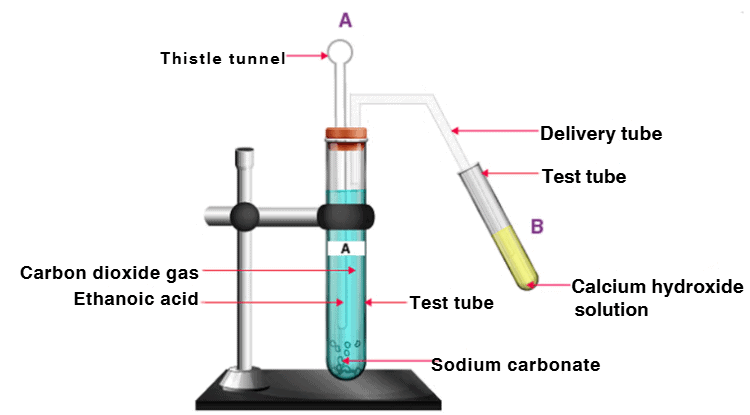
(a) What change would you observe in the calcium hydroxide solution taken in tube B?
(b) Write the reaction involved in test tubes A and B.
(c) Would you expect the same change if ethanol is given instead of ethanoic acid?
(d) How can a solution of lime water be prepared in the laboratory?
Ans:
(a) Calcium hydroxide solution in test tube B will become milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate.
(b) Reaction in test tube A: CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
Reaction in test tube B: Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(c) If ethanol is given instead of ethanoic acid, similar changes won’t be observed because ethanol does not react with sodium hydrogen carbonate.
(d) First, take distilled water in a beaker and mix calcium carbonate powder. After stirring entirely, wait till the mixture settles down. Decant the clear liquid from the beaker. This liquid is lime water.
|
80 videos|567 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Carbon and its Compounds - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the main properties of carbon that make it essential for life? |  |
| 2. How do carbon compounds differ from inorganic compounds? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of carbon compounds and their uses? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of carbon's allotropes, such as graphite and diamond? |  |
| 5. How does the carbon cycle impact the environment? |  |





















