Unit Test (Solutions): Control and Coordination | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each
Q1: Which is the largest and most prominent part of the human brain? (1 Mark)
(a) Cerebellum
(b) Medulla
(c) Cerebrum
(d) Hypothalamus
Ans: (c)
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, covering most of the cranial cavity. It is responsible for intelligence, memory, voluntary actions, reasoning, and senses.
Q2: A female is suffering from an irregular menstrual cycle. The doctor prescribed her some hormonal tablets. Which option shows that the hormone she lacks in her body is from the endocrine gland? (1 Mark)
(a) Oestrogen
(b) Testosterone
(c) Adrenalin
(d) Thyroxin
Ans: (a)
Oestrogen is a hormone produced by the ovaries, an endocrine gland, and is crucial for regulating the menstrual cycle in females.
Q3: Which two tissues provide control and coordination in animals? (1 Mark)
(a) Epithelial and connective tissues
(b) Muscular and connective tissues
(c) Nervous and muscular tissues
(d) Nervous and epithelial tissues
Ans: (c)
Nervous tissue controls coordination by transmitting signals throughout the body. Muscular tissue helps in responding to these signals by causing movement. Together, they maintain control and coordination in animals.
Q4: Which plant hormone inhibits growth and helps in the wilting of leaves?(1 Mark)
(a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellin
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Abscisic acid
Ans: (d)
Abscisic acid is known as a growth-inhibiting hormone. It helps plants to conserve water during stress by promoting leaf wilting and stomatal closure. Hence, it is also called the stress hormone in plants.
Q5: What is the function of the pituitary gland? (1 Mark)
(a) To develop sex organs in males
b) To stimulate growth in all organs
(c) To regulate sugar and salt levels in the body
(d) To initiate metabolism in the body
Ans: (b)
The pituitary gland releases growth hormone (GH), which promotes growth in bones and tissues throughout the body. It also controls other endocrine glands, making it essential for overall growth and development.
Q6: How is the movement in sensitive plants different from the movement in our legs (2 Marks)
Ans: The sensitive movement in plants occurs in response to a touch stimulus. The information is transmitted from cell to cell by electrochemical signals as the plant lacks specialised tissue for the conduction of impulses. There is a change in the shape of plant cells by changing the amount of water.
Movement in the legs is due to voluntary action. The signals are passed to the brain and hence they are controlled consciously. There are proteins present in animals which allow movement to take place.
Q7: What is the nervous mechanism and hormonal mechanism? (2 Marks)
Ans: The nervous mechanism is carried out by the nervous system in which electrical impulses are transmitted instantaneously and the effects are short-lived.
The hormonal mechanism is performed by the chemical substances which are secreted by the endocrine glands. The rate of information transmission is slow and the effect is prolonged.
Q8: Define phototropism. Name the plant hormone which is responsible for phototropism. (2 Marks)
Ans: Phototropism is the movement of a part of the plant in response to light. Shoots generally grow towards light and are said to be positively phototropic, while roots grow away from light and are said to be negatively phototropic.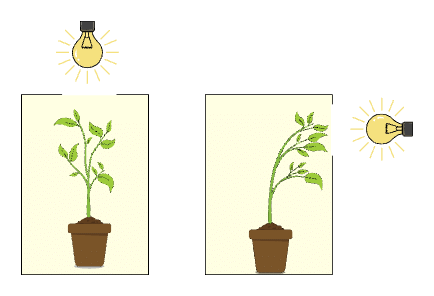 The growth movement of the plant part (stem) is caused by the action of auxin hormone. Auxin causes cell elongation. Thus, causing growth of stem towards the light stimulus.
The growth movement of the plant part (stem) is caused by the action of auxin hormone. Auxin causes cell elongation. Thus, causing growth of stem towards the light stimulus.
Q9: Mention three major regions of brain. Write one function of each. (3 Marks)
Ans: Brain is divided into three main regions forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain.
(i) Forebrain: This region includes the cerebrum, olfactory lobes, and diencephalon. Its primary function is thinking and controlling various activities such as touch, smell, hearing, speech, and sight.
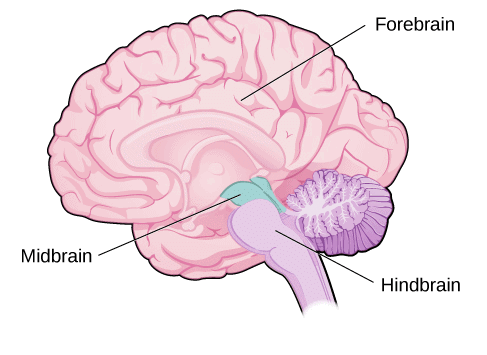 (ii)Midbrain: The midbrain is responsible for controlling reflex movements of the head, neck, and trunk in response to visual and auditory stimuli.
(ii)Midbrain: The midbrain is responsible for controlling reflex movements of the head, neck, and trunk in response to visual and auditory stimuli.
(iii) Hindbrain: Comprising the pons, cerebellum, and medulla. This part is responsible for regulating respiration, maintaining posture and balance of body and controlling involuntary actions such as heartbeat, breathing, swallowing, coughing, sneezing, vomiting, etc.
Q10: A squirrel is in a scary situation. Its body has to prepare for either fighting or running away. State the immediate changes that take place in its body so that the squirrel is able to either fight or run. (3 Marks)
Ans:When a squirrel finds itself in a scary situation, its body undergoes several immediate changes to prepare for either fighting or running away:
- The nervous system activates the adrenal glands.
- These glands release more adrenaline into the bloodstream.
- This hormone causes the following changes:
- Increased heartbeat to pump more blood.
- Faster breathing rate to supply more oxygen.
- Enhanced blood flow to muscles for energy.
- Release of stored glucose from the liver into the blood.
These changes provide the energy needed for the squirrel to either fight or flee effectively.
Q11: Name any three endocrine glands in human body and briefly write the function of each of them. (3 Marks)
Ans: Three endocrine glands with their function in human body are as follows:
- Thyroid gland: It produces the hormone thyroxine, which helps regulate the body's metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. This ensures a proper balance of nutrients and supports mental function.
- Adrenal gland: This gland releases hormone adrenalin, which play a crucial role in controlling blood pressure, heartbeat, breathing rate, and carbohydrate metabolism. This hormone is also called fight or flight hormone.
- Pancreas: The pancreas secretes two important hormones: insulin and glucagon. Insulin lowers blood glucose levels, while glucagon raises them.
Q12: Why is chemical communication better than electrical impulses as a means of communication between cells in a multicellular organisms? (5 Marks)
Ans: Chemical communication is often preferred over electrical impulses for several reasons:
- Speed and Range: Electrical impulses are quick but only reach cells connected by nervous tissue.
- Reset Time: After transmitting an impulse, cells need time to reset before sending another, limiting continuous communication.
- Wider Reach: Chemical communication can spread information throughout the body via the blood, reaching all cells regardless of their connection to the nervous system.
- Longevity of Effects: While slower, the effects of chemical signals last longer, allowing for sustained responses.
- Diversity of Signals: Chemicals, such as hormones, can coordinate various functions, adapting to different needs in multicellular organisms.
Q13:
(a) Name the hormone which is released into the blood when its sugar level rises. Explain the need of Chemical communication in multicellular organisms the organ which produces this hormone and its effect on blood sugar level. Also mention the digestive enzymes secreted by this organ with one function of each.
(b) Explain how chemical coordination occurs in plants. Mention the role of auxin and Abscisic acid. (5 Marks)
Ans:
(a) Insulin is the hormone released into the blood when sugar levels rise. It is produced by the pancreas and plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. Here’s a breakdown of its functions:
- Glucose is essential for cells to perform respiration.
- Insulin helps maintain a constant level of glucose in the blood.
- When blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas detects this and releases more insulin.
- As blood sugar levels fall, insulin secretion decreases.
The pancreas also secretes digestive enzymes:
- Pancreatic amylase - breaks down carbohydrates into sugars.
- Trypsin - aids in protein digestion.
- Lipase - helps digest fats.
(b) In plants, the cells which are stimulated release the chemical compounds. These chemicals are plant hormones. They play an important role in growth, development and responses to the environment. They are synthesised at other places from the place of action and they get diffused.
The function of auxin is:
- Auxin is a phytohormone and a growth promoter.
- It promotes cell enlargement
- It is responsible for cell differentiation
- Induces tropism
The functions of abscisic acid are:
- This is a phytohormone and a growth inhibitor.
- The production of abscisic acid is promoted by drought, water logging and other adverse conditions where stress is induced. So it is a type of stress hormone.
- It promotes the abscission of flowers and fruits
- It promotes falling and senescence in leaves.
|
82 videos|677 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Control and Coordination - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the main components of the control and coordination system in humans? |  |
| 2. How do hormones function in the control and coordination system? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the nervous system in control and coordination? |  |
| 4. What are reflex actions and how do they relate to control and coordination? |  |
| 5. How do plants exhibit control and coordination? |  |






















