Unit Test (Solutions): How Do Organisms Reproduce? | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: Which part of a flower develops into a fruit after fertilization? (1 Mark)
a) Stamen
b) Stigma
c) Ovary
d) Ovule
Ans: (c)
Fruits are formed from the ovary of a flower after fertilization. The ovary develops into the fruit, while the ovules inside it become seeds.
Q2: Which of the following is NOT a function of the testes in humans at puberty? (1 Mark)
(i) Formation of germ cells
(ii) Secretion of testosterone
(iii) Development of placenta
(iv) Secretion of estrogen
a) (i) and(ii)
b) (ii) and(iii)
c) (iii) and(iv)
d) (i) and(iv)
Ans: (c)
The testes have two primary functions at puberty: the formation of germ cells (sperm) and the secretion of the hormone testosterone. They do not play any role in the development of the placenta, which is a function related to female reproduction, nor do they secrete estrogen, which is primarily produced in the ovaries.
Q3: How does Plasmodium reproduce asexually? (1 Mark)
a) The cyst repeatedly divides to form many daughter cells.
b) The cell divides multiple times giving rise to many daughter cells.
c) The nucleus repeatedly divides inside the cell to form new daughter cells.
d) The cyst enlarges in size and then bursts, producing many new daughter cells.
Ans: (b)
Plasmodium reproduces through multiple fission, where the cell divides many times to produce numerous daughter cells.
Q4: In which part of the human female reproductive system does fertilization typically occur? (1 Mark)
Ans: Oviduct.
Q5: Name the part of Bryophyllum where the buds are produced for vegetative propagation. (1 Mark)
Ans: Bryophyllum propagates vegetatively by the buds produced at the margins of leaves.
Q6: Define binary fission and give one example of an organism that reproduces by this method. (2 Marks)
Ans: Multiple fission is an asexual mode of reproduction in which the parent organism splits to form many new organisms at the same time. Multiple fission occurs in Plasmodium.
Q7: Name an organism which reproduces by spore formation. List three conditions favourable for spores to germinate and grow. (2 Marks)
Ans: Rhizopus reproduce by the method of spore formation. The three conditions favourable for spores to germinate and grow are moisture, suitable temperature and food (nutrition).
Q8: Name the mode of reproduction of the following organisms and state the important feature of each mode: (2 Marks)
(i) Planaria
(ii) Hydra
Ans:
(a) (i) Planaria – Regeneration
Regeneration of organism from its cut body parts occurs by the process of growth and development.
Regeneration is an asexual mode of reproduction common in lower plants and animals.
(ii) Hydra – Budding
In budding, a small part of the body of the parent organism grows out as a bud which on detaching forms a new organism.
Budding occurs in yeast, some protozoans and certain lower animals.
Q9: “The chromosomal number of the sexually producing parents and their offspring is the same”. Justify this statement. (3 Marks)
Ans: In sexual reproduction, two gametes, male and female, combines together to form a new cell ‘zygote’. The reproductive cells or gametes contain only half the amount of DNA as compared to the non-reproductive cells of an organism. So, when a male gamete combines with a female gamete during sexual reproduction, then the new cell ‘zygote’ will have the normal amount of DNA. For example, the human sperm has 23 chromosomes and the human egg has also 23 chromosomes. So when a sperm and an egg fuse together during fertilisation, then the zygote formed will have 23 + 23 = 46 chromosomes, which is the normal number of chromosomes in humans.
Q10: State one genetically different feature between sperms and eggs of humans. What is its consequence? (3 Marks)
Ans: A sperm may have X or Y chromosomes whereas egg have X chromosomes. The consequence of this is that sperm decides the sex of the child because eggs contribute only X chromosome while sperms contribute either X or Y chromosomes to the offspring. Therefore, if a child inherits X chromosome from her father, will be a girl and the one that inherit Y chromosome will be a boy.
Q11: State the changes that take place in the uterus when: (3 Marks)
(a) Implantation of embryo has occurred.
(b) Female gamete/egg is not fertilised.
Ans:
(a) Implantation is the close attachment of the blastocyst (young multicellular embryo) to the uterine wall. It is fullowed by a number of developmental changes in the thickened wall of uterus. An intimate connection between the fetal membrane and the uterine wall called placenta is formed. This is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall. The placenta serves as the nutritive, respiratory and excretory organ of the fetus.
(b) When the female gamete/egg is not fertilised, this lining is not needed any longer. So, the lining slowly breaks and comes out through vagina as blood and mucus. This cycle takes place every month and is known as menstrual cycle.
Q12: How do organisms, whether reproduced asexually or sexually maintain a constant chromosome number through several generations? Explain with the help of suitable example. (5 Marks)
Ans: In organisms reproducing asexually, only single parent is involved in reproduction. Therefore, amount of DNA remains same from parent to offspring. For example in Amoeba, whole organism divides into two daughter individuals by binary fission. Therefore, amount of DNA remain constant.
In organisms reproducing sexually, reproduction take place with the help of formation of haploid gametes. Gametes are special type of cells called reproductive cells which contain only half the amount of DNA as compared to the normal body cells of an organism. So, when a male gamete combines with a female gamete during sexual reproduction, then the new cell ‘zygote’ will have the normal amount of DNA. For example, the human sperm has 23 chromosomes and the human egg (or ovum) has also 23 chromosomes. So, when a sperm and an egg fuse together during fertilisation, then the zygote formed will have 23 + 23 = 46 chromosomes, which is the normal number of chromosomes.
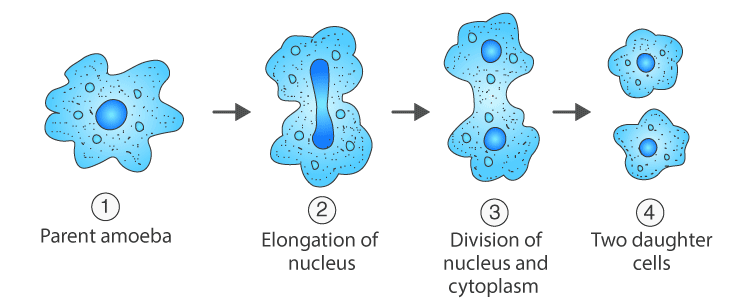
Q13: What is binary fission in organisms? With the help of suitable diagrams, describe the mode of reproduction in Amoeba. (5 Marks)
Ans: Binary fission is the division of adult parental body into two nearly equal daughter cells. It is the simplest and most common method of asexual reproduction found in protistan protozoans, i.e., Amoeba, Paramecium, etc.
Amoeba reproduces by binary fission by dividing its body into two parts. When the Amoeba cell has reached its maximum size of growth, then first the nucleus of Amoeba lengthens and divides into two parts. After that the cytoplasm of Amoeba divides to form two smaller Amoeba (called daughter amoebae).
Diagrammatic representation of binary fission in Amoeba is as follows :
|
82 videos|677 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): How Do Organisms Reproduce? - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the two main types of reproduction in organisms? |  |
| 2. How does asexual reproduction occur in organisms? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of sexual reproduction in evolution? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the process of fertilization in sexual reproduction? |  |
| 5. What role do external factors play in the reproduction of organisms? |  |
















