Unit Test: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: What is meant by magnetic field? (1 Mark)
Q2: The strength of magnetic field inside a long current carrying straight solenoid is (1 Mark)
(a) minimum in the middle
(b) found to increase from one end to the other
(c) same at all points
(d) more at the ends than at the centre
Q3: The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is (1 Mark)
(a) the process of generating a magnetic field due to current passing through a coil.
(b) the process of charging a body.
(c) producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
(d) the process of rotating a coil of an electric motor.
Q4: Choose the wrong statement from the following regarding magnetic lines of the field (1 Mark)
(a) Magnetic field lines are closed curves.
(b) The north pole of a magnetic compass is used to determine the direction of the magnetic field at a particular location.
(c) If magnetic field lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent zero-field strength.
(d) The degree of closeness of the field lines indicates the relative strength of the magnetic field.
Q5: A circular loop, when placed in a plane perpendicular to the plane of the paper, may carry a current when the key is ON. The current, as seen from points A and B (in the plane of the paper and on the axis of the coil), is anticlockwise and clockwise, respectively. The magnetic field lines point from B to A. The North pole of the resultant magnet is on the face close to (1 Mark)
(a) A
(b) B
(c) B when the current is small and A if the current is large
(d) A if the current is small, and B if the current is large.
Q6: (a) If field lines of a magnetic field are crossed at a point, what does it indicate?
(b) Mention two parameters that are necessary to describe a magnetic field completely. (2 Marks)
Q7: A straight conductor that is carrying current is put close to a compass needle. Give your opinion in each of the following situations, along with your justifications. (2 Marks)
(a) The magnitude of electric current is increased.
(b) The compass needle is displaced away from the conductor.
Q8: List the properties of magnetic field lines. (2 Marks)
Q9: Diagram shows the lengthwise section of a current carrying solenoid. ⦻ indicates current entering into the page, ⨀ indicates current emerging out of the page. Decide which end of the solenoid A or B, will behave as north pole. Give reason for your answer. Also draw field lines inside the solenoid. (3 Marks)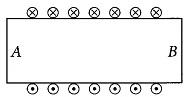
Q10: Give a reason for the following. (3 Marks)
(i) There is either a convergence or a divergence of magnetic field lines near the ends of a current carrying a straight solenoid.
(ii) The current-carrying solenoid, when suspended, freely rests along a particular direction.
Q11: Two circular coils P and Q are kept close to each other, of which coil P carries a current. What will you observe in the galvanometer connected across the coil Q
(a) if current in the coil P is changed?
(b) if both the coils are moved in the same direction with the same speed?
Give reason to justify your answer in each. (3 Marks)
Q12:
(a) Draw a schematic diagram of a common domestic circuit showing provision of
(i) Earth wire
(ii) Main fuse
(iii) Electricity meter and
(iv) Distribution box.
(b) Distinguish between short circuiting and overloading. (5 Marks)
Q13: A current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field. Now answer the following. (5 Marks)
(i) List the factors on which the magnitude of force experienced by conductor depends.
(ii) When is the magnitude of this force maximum?
(iii) State the rule which helps, in finding the direction of motion of conductor.
(iv) If initially this force was acting from right to left, how will the direction of force change if:
(a) direction of magnetic field is reversed?
(b) direction of current is reversed?
You can find the solutions of this Unit Test here: Unit Test (Solutions): Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the basic principles of the magnetic effects of electric current? |  |
| 2. How does a solenoid work and what are its applications? |  |
| 3. What is the right-hand rule and how is it applied in determining the direction of magnetic fields? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of electromagnetic induction and its significance? |  |
| 5. What safety precautions should be taken when working with electric currents and magnetic fields? |  |

















