Unit Test (Solutions): Our Environment | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: In a food chain, the third trophic level is always occupied by (1 Mark)
(a) carnivores
(b) herbivores
(c) decomposers
(d) producers
Ans: (a)
In a food chain, the third trophic level is occupied by carnivores (primary carnivores or secondary consumers) that feed on herbivores.
Q2: In the given food chain, if the amount of energy at the fourth trophic level (Hawk) is 5 kJ, what will be the energy available at the producer level (Plant)? (1 Mark)
Plant→ Insect (Grasshopper) → Frog → Snake → Hawk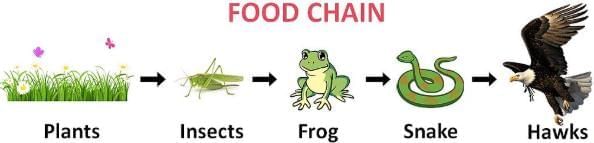
(a) 5 kJ
(b) 50 kJ
(c) 500 kJ
(d) 5000 kJ
Ans: (d)
According to the 10% law of energy transfer, only 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next.
Given that the energy at the fourth trophic level (Hawk) is 5 kJ:
Energy at the third trophic level (Snake) = 5 × 10 = 50
5×10=50 kJ
Energy at the second trophic level (Frog) = 50 × 10 = 500
50×10=500 kJ
Energy at the first trophic level (Grasshopper) = 500 × 10 = 5000
500×10=5000 kJ
Thus, the energy available at the producer level (Grass) is 5000 kJ.
Q3: Depletion of ozone is mainly due to: (1 Mark)
(a) chlorofluorocarbon compounds
(b) carbon monoxide
(c) methane
(d) pesticides
Ans: (a)
 Ozone depletion in the stratosphere is primarily caused by chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). CFCs release chlorine atoms when they are broken down by ultraviolet (UV) radiation. These chlorine atoms then react with ozone (O₃) molecules, leading to the destruction of the ozone layer.
Ozone depletion in the stratosphere is primarily caused by chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). CFCs release chlorine atoms when they are broken down by ultraviolet (UV) radiation. These chlorine atoms then react with ozone (O₃) molecules, leading to the destruction of the ozone layer.
Q4: Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several types of organisms belonging to a lower trophic level constitute the (1 Mark)
(a) food web
(b) ecological pyramid
(c) ecosystem
(d) food chain
Ans: (a)
A food chain is an interaction between different group of organisms through which food and energy move through an ecosystem. All of the local wildlife and the non-living elements of its habitat make up an ecosystem. 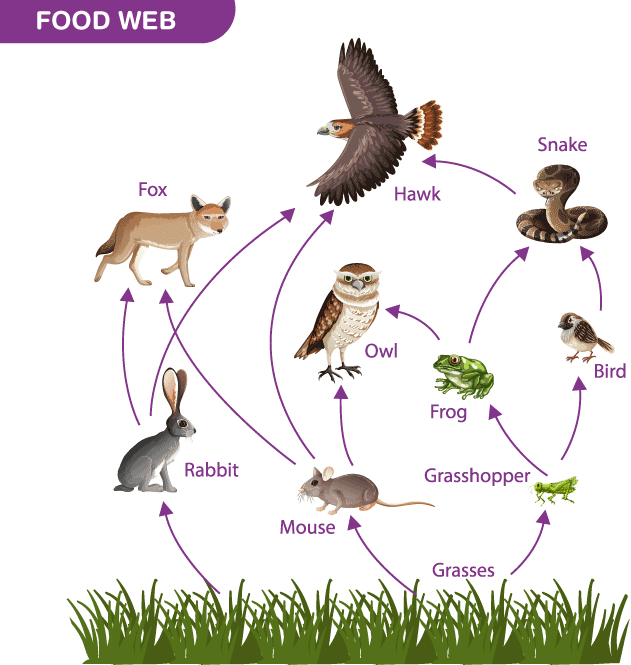 Ecological pyramids visually represent the trophic organisation and energy flow in an ecosystem. The food web comprises higher trophic level species that consume various lower trophic level organisms.
Ecological pyramids visually represent the trophic organisation and energy flow in an ecosystem. The food web comprises higher trophic level species that consume various lower trophic level organisms.
Q5: Why are green plants called producers? (1 Mark)
Ans: Green plants are called producers because they manufacture their own food with the help of CO2 and H2O in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
Q6: List two biotic components of a biosphere. (2 Marks)
Ans: Two biotic components of a biosphere are:
(i) Producers – Include organisms which can produce their food using simple inorganic compounds, e.g., all green plants, blue green algae (cyanobacteria).
(ii) Consumers – Include organisms which are unable to synthesise their food, therefore, utilise materials and energy stored by the producers or eat other organisms, e.g., all the animals.
Q7: What is meant by biological magnification? (2 Marks)
Ans: 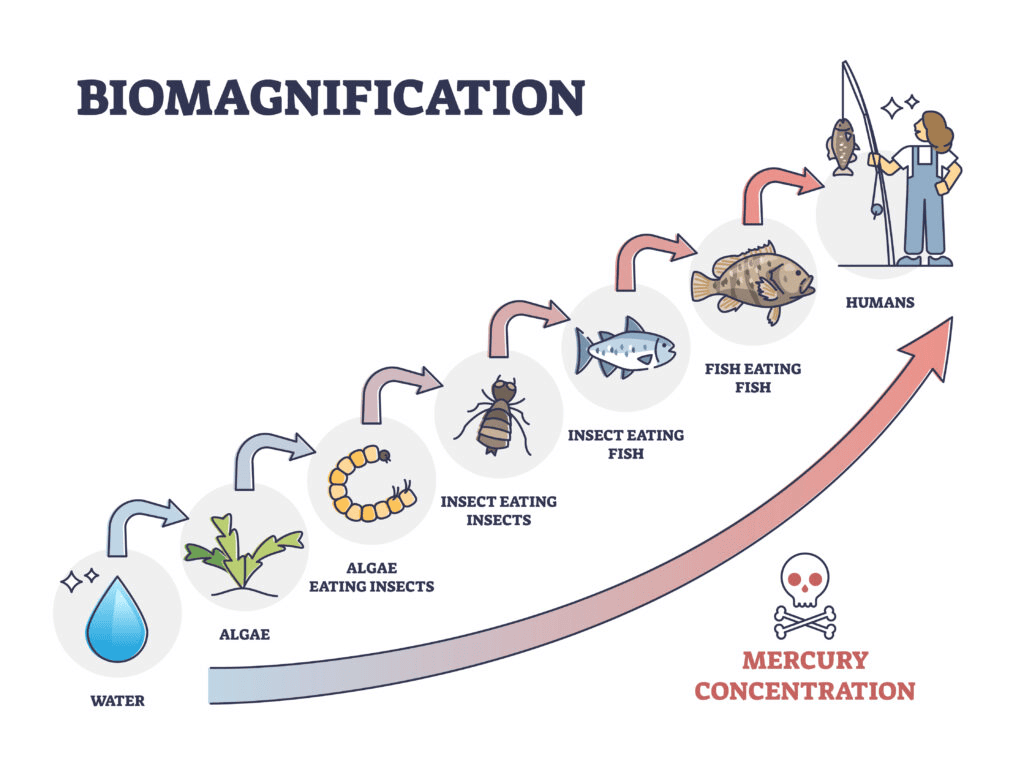 Biological magnification or biomagnification refers to the process of accumulation of non- biodegradable chemicals (pesticides, etc.) into the body of organisms through the food chain which go on increasing in its concentration at each trophic level.
Biological magnification or biomagnification refers to the process of accumulation of non- biodegradable chemicals (pesticides, etc.) into the body of organisms through the food chain which go on increasing in its concentration at each trophic level.
Q8: What are decomposers? List two important roles they play in the environment. (2 Marks)
Ans: Decomposers are microorganisms including bacteria and fungi which decompose or break-down the complex organic compound present in dead plants and animals into simpler substances.
Role of decomposers in environment are-
- They help in decomposing dead bodies of plants and animals and hence act as cleansing agents of environment.
- They help in recycling of materials in the ecosystem to maintain its stability.
Q9: In the following food chain, 100 J of energy is available to the lion. How much energy was available to the producers?
Plants → Deer → Lion (3 Marks)
Ans:
As per 10% law of flow of energy in an ecosystem only 10% of energy is received by the next trophic level.
Hence, in the given food chain : If 100 J of energy is available to lion, the plants or producers have 10,000 J of energy available to them.
Q10: What does a trophic level represent in a food chain? State the position of autotrophs and herbivores in a food chain. (3 Marks)
Ans: Trophic level represents each of several hierarchical levels of a food chain operating in an ecosystem, consisting of organism sharing the same function in the food chain and the same nutritional relationship to the primary sources of energy.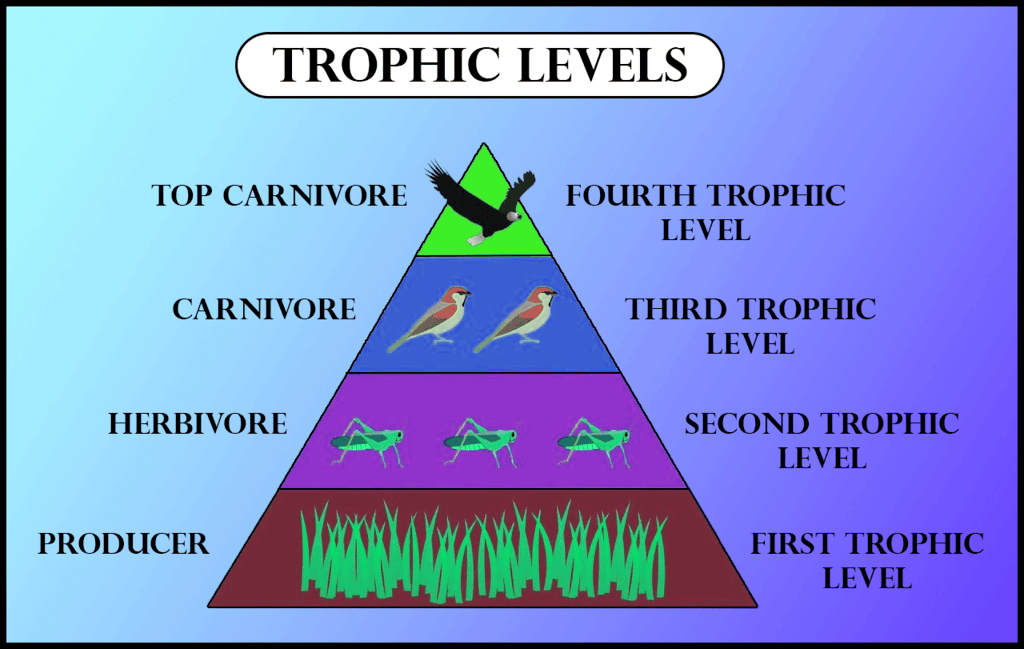 The position of producers (or autotrophs) in a food chain constitute the first trophic level. They fix up sun’s energy and make it available for consumers. The herbivores or primary consumers (which feed upon plants) constitute the second trophic level in a food chain.
The position of producers (or autotrophs) in a food chain constitute the first trophic level. They fix up sun’s energy and make it available for consumers. The herbivores or primary consumers (which feed upon plants) constitute the second trophic level in a food chain.
Q11: “Our food grains such as wheat and rice, the vegetables and fruits and even meat are found to contain varying amounts of pesticide residues.” State the reason to explain how and why it happens. (3 Marks)
Ans: Pesticides are poisonous chemical substances which are sprayed over crop plants to protect them from pests and diseases. These chemical pesticides mix up with soil and water. From soil and water, these pesticides are absorbed by the growing plants along with water and other minerals. When herbivorous animals feed on these plants the poisonous pesticides enter their bodies through the food chain. Similarly, when the carnivorous animals eat these herbivores, the pesticides get transferred to their bodies. Therefore, the plant products such as food grains, vegetables and fruits as well as meat of animals contain varying amounts of pesticide residues in them depending upon the trophic level they occupy in a food chain.
Q12: “Industrialisation has adversely deteriorated the environment.” Give four reasons in support of this statement. (5 Marks)
Ans: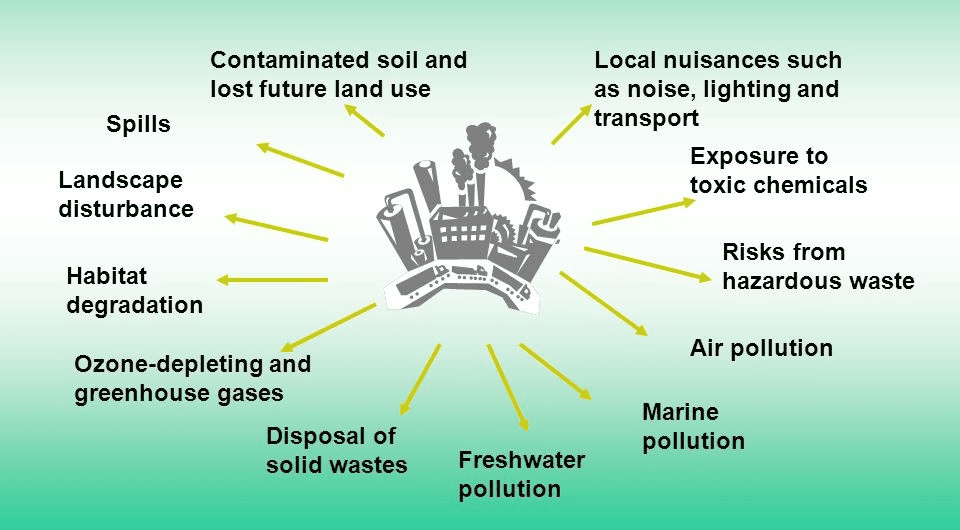 Industrialisation has deteriorated our environment in the following ways :
Industrialisation has deteriorated our environment in the following ways :
- Rapid industrialisation has increased the demand of more land area for setting up of new factories. This demand is being fulfilled by clearing up of forest area. Deforestation is one of the major causes of ecological imbalance, biodiversity loss and ecosystem unstability.
- Industries release various harmful gases in the environment which pollute the air. These gases when inhaled by people around, cause various respiratory diseases in them.
- A lot ol effluent and liquid waste is discharged from various industries which is mostly dumped into nearby water bodies. This causes water pollution. Polluted water causes death of various aquatic organisms and consumption of this polluted water causes various diseases in humans.
- The solid waste released from factories is dumped on open land and not treated properly to ensure their proper decomposition. This leads to land pollution that degrades quality of soil and also causes various kinds of diseases in humans and animals.
Q13: Define an ecosystem. Draw a block diagram to show the flow of energy in an ecosystem. (5 Marks)
Ans:
An ecosystem is defined as a structural and functional unit of the biosphere. It comprises of living organisms and their non-living environment that interact by means of food chains and biogeo-chemical cycles resulting in energy-flow, biotic diversity and material cycling to form stable self-supporting system.
Green plants capture about 1% of the solar energy incident on the earth to carry out the process of photosynthesis. A part of this trapped energy is used by plants in performing their metabolic activities and some energy is released as heat into the atmosphere. The remaining energy is chemical energy stored in the plants as photosynthetic products. When these green plants are eaten up by herbivores, the chemical energy stored in the plants is transferred to these animals. These animals (herbivores) utilise some of this energy for metabolic activities and some energy is released as heat while the remaining energy is stored in their body. This process of energy transfer is repeated till top carnivores. In an ecosystem, transfer of energy follows 10 percent law, i.e,, only 10 percent of the energy is transferred to each trophic level from the lower trophic level. Nearly 90 percent of energy is lost when it moves from one trophic level to the next.
The given block diagram shows unidirectional flow of energy at different trophic levels in a freshwater ecosystem: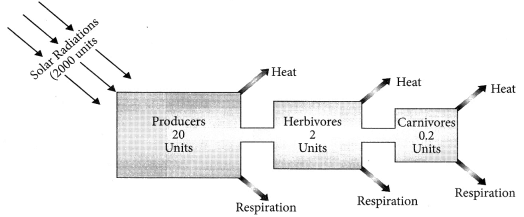
|
80 videos|567 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Our Environment - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the main components of our environment? |  |
| 2. How does pollution affect our environment? |  |
| 3. Why is biodiversity important for our environment? |  |
| 4. What steps can individuals take to protect the environment? |  |
| 5. What role do forests play in our environment? |  |

















