Unit Test(Solutions): Matter in Our Surroundings | Science Class 9 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each
Q1: Which of the following processes involves a direct change from solid to gas without passing through the liquid state? (1 Mark)
(i) Melting
(ii) Boiling
(iii) Sublimation
(iv) Condensation
Ans: (iii)
Sublimation is the process where a solid changes directly into a gas without passing through the liquid state.
Q2: Define the term "latent heat of fusion." (1 Mark)
Ans: The latent heat of fusion is the amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of a solid into a liquid at its melting point without any change in temperature.
Q3: Which of the following statements is true about gases? (1 Mark)
(i) They have a fixed shape.
(ii) They have a fixed volume.
(iii) They are highly compressible.
(iv) They do not occupy space.
Ans: (iii)
Gases are highly compressible because the particles are far apart and move freely, allowing them to be compressed into a smaller volume when pressure is applied. Unlike solids and liquids, gases do not have a fixed shape or volume, and they can expand to fill any container.
Q4: Fill in the blank: The particles in a gas move _________ than in a solid. (1 Mark)
Ans: faster.
In a gas, particles move much faster than in a solid due to the greater kinetic energy they possess. This high speed allows gas particles to spread out and fill the entire volume of their container, unlike the tightly packed and slower-moving particles in a solid.
Q5: Which of the following statements about matter is correct? (1 Mark)
(i) Particles in solids have the highest kinetic energy.
(ii) Gases have a definite shape and volume.
(iii) The density of a substance generally increases as it changes from liquid to solid.
(iv) In a gaseous state, the intermolecular forces are strongest.
Ans: (iii)
As a substance changes from liquid to solid, the particles pack more closely together, increasing the density. The other options are incorrect: solids have the least kinetic energy, gases do not have a definite shape or volume, and intermolecular forces are weakest in the gaseous state.
Q6: Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature? (2 Marks)
Ans: Ice at 273 K absorbs latent heat of fusion from the surroundings to change into water at the same temperature. This extra energy absorption makes ice more effective in cooling than water at 273 K.
Q7: State two differences between evaporation and boiling. (2 Marks)
Ans: 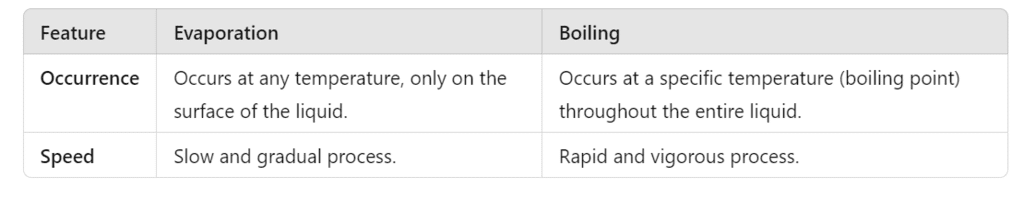
Q8: Why do we feel cool when we apply some acetone or perfume on our palm? (2 Marks)
Ans: When acetone or perfume is applied to the skin, it evaporates quickly. During evaporation, these liquids absorb heat from your skin to transition into a gas, which creates a cooling effect. Since they evaporate easily due to their low boiling points, the cooling sensation is immediate.
Q9: What are the characteristics of the particles of matter? (3 Marks)
Ans:
- Particles of matter are very small: They are small beyond imagination.
- Particles of matter have space between them: This space allows mixing, as seen when sugar dissolves in water.
- Particles of matter are continuously moving: This motion increases with an increase in temperature.
Q10: How does the temperature and pressure affect the state of matter? (3 Marks)
Ans:
(i) Temperature:
- Solids: Increasing temperature gives particles more kinetic energy, causing them to vibrate and eventually melt into liquids (e.g., ice
melts at 0°C). - Liquids: Further heating makes liquid particles move faster, leading to boiling and turning into gas (e.g., water boils at 100°C).
- Gases: Higher temperatures cause gas particles to move faster and expand if the pressure is constant.
(ii) Pressure:
- Gases: Applying pressure compresses gas particles, which can condense into liquids (e.g., CO₂ gas forms dry ice under high pressure).
- Liquids and Solids: Increasing pressure can turn liquids into solids, while decreasing pressure can cause solids to melt or liquids to evaporate.
Q11: Describe the process of sublimation with an example. (3 Marks)
Ans:
Sublimation is a process in which a solid changes directly into a gas without passing through the intermediate liquid state. This occurs when the particles of a solid gain enough energy to overcome the forces holding them in a fixed position and move directly into the gaseous phase.
Example:
- Camphor: Camphor is a substance that, when heated, does not melt into a liquid but instead directly turns into vapour. This can be observed when camphor is heated in a dish—it gradually disappears as it sublimates into the air.
- Dry Ice (Solid CO₂): Another common example is dry ice. When exposed to room temperature, dry ice directly changes from solid carbon dioxide to gaseous carbon dioxide without becoming a liquid. This property makes dry ice useful in various applications, such as creating fog effects or preserving items at low temperatures.
Q12: Explain the effect of change in temperature on the states of matter with suitable examples. (5 Marks)
Ans:
- Solids to Liquids: When a solid is heated, its particles gain kinetic energy, vibrate more, and eventually overcome their fixed positions to turn into a liquid. For example, ice melts into water at 0°C.
- Liquids to Gases: Further heating a liquid increases the kinetic energy of its particles until they can escape into the gas phase. For example, water boils and turns into steam at 100°C.
- Gases to Liquids: Cooling a gas reduces the kinetic energy of particles, causing them to come closer and condense into a liquid, like water vapour condensing into droplets on a cold surface.
- Liquids to Solids: Further cooling a liquid reduces the motion of particles until they form a fixed, solid structure. For example, water freezes into ice at 0°C.
- Sublimation: Some solids like dry ice (solid CO₂) sublimate, turning directly into gas without becoming a liquid, when heated.
Q13: Differentiate between the three states of matter in terms of the arrangement of particles, compressibility, and fluidity. (5 Marks)
Ans:
1. Arrangement of Particles:
- Solids: Particles are tightly packed in a fixed, orderly arrangement.
- Liquids: Particles are close together but not in a fixed position, allowing them to slide over each other.
- Gases: Particles are far apart and move freely in all directions.
2. Compressibility:
- Solids: Almost incompressible due to tightly packed particles.
- Liquids: Slightly compressible but much less than gases.
- Gases: Highly compressible because of large spaces between particles.
3. Fluidity:
- Solids: Do not flow; they maintain a fixed shape.
- Liquids: Flow easily and take the shape of the container.
- Gases: Flow freely and expand to fill the entire volume of the container.
|
84 videos|541 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test(Solutions): Matter in Our Surroundings - Science Class 9
| 1. What are the different states of matter? |  |
| 2. How does temperature affect the state of matter? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical change in matter? |  |
| 4. What are the characteristics of gases in comparison to solids and liquids? |  |
| 5. How do we classify matter based on its composition? |  |

















