Unit Test (Solutions) : Microorganisms: Friend and Foe | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
Maximum Marks: 30
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: Who discovered the vaccine for smallpox in 1798.(1 Mark)
Ans: Edward Jenner
Q2: Fill in the blank: ___________ is the process of converting sugar into alcohol by yeast.(1 Mark)
Ans: Fermentation
Fermentation is the process carried out by yeast to convert sugars into alcohol, commonly used in brewing and baking. Fermentation in Dough
Fermentation in Dough
Q3: Which of the following diseases is caused by a virus? (1 Mark)
(i) Tuberculosis
(ii) Malaria
(iii) Cholera
(iv) Influenza
Ans: (iv)
Influenza is a viral infection, unlike tuberculosis (bacteria), malaria (protozoa), and cholera (bacteria).
Q4: The bacterium involved in the setting of curd is ___________. (1 Mark)
Ans: Lactobacillus
Lactobacillus bacteria help in converting milk into curd by fermenting the lactose present in milk.
Q5: Which microorganism is commonly used in the baking industry to make bread rise? (1 Mark)
(i) Rhizobium
(ii) Penicillium
(iii) Yeast
(iv) Amoeba
Ans: (iii)
Yeast is used in baking because it produces carbon dioxide during respiration, which helps the dough to rise.
Q6: What are antibiotics? Give two examples. (2 Marks)
Ans: Antibiotics are powerful medicines derived from certain bacteria and fungi that are used to treat bacterial infections. These medicines work by either killing bacteria or inhibiting their growth, thus helping to combat diseases. Two examples of antibiotics include Penicillin, the first antibiotic ever discovered, and Streptomycin, which is used to treat tuberculosis.
Q7: How do microorganisms help in the process of decomposition, and why is this process important for the environment? (2 Marks)
Ans: Microorganisms also play a vital role in the process of decomposition, where they break down dead plants and animals into simpler substances. This decomposition is crucial for the environment as it recycles nutrients back into the soil, making them available for plants. Without microorganisms, dead matter would accumulate, and nutrients would not be recycled, disrupting the balance of the ecosystem.
Q8: Describe how food poisoning occurs and mention one preventive measure. (2 Marks)
Ans: Food poisoning is an illness caused by consuming contaminated food, which can contain harmful bacteria, viruses, or toxins. Common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and abdominal pain. To prevent food poisoning, it is crucial to store food properly, cook it thoroughly, and avoid consuming food that looks or smells spoiled. Ensuring good hygiene practices during food handling and preparation also plays a vital role in prevention.
Q9: Fill in the blanks in the table below regarding common plant diseases, the microorganisms causing them, and their modes of transmission.(3 Marks)
| Plant Diseases | Micro-organism | Mode of Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| Citrus canker | ______________ | Air |
| Rust of wheat | Fungi | ______________ |
| Yellow vein mosaic of bhindi | Virus | ______________ |
Ans:
Micro-organism for Citrus canker: Bacteria
Mode of Transmission for Rust of wheat: Air, seeds
Mode of Transmission for Yellow vein mosaic of bhindi: Insect
Q10: How do vaccines work to protect against diseases? Give one example.(3 Marks)
Ans: Vaccines protect by training the immune system to recognize and fight pathogens without causing the disease. They contain weakened or inactive parts of a pathogen (like viruses or bacteria). When introduced into the body, the immune system responds by producing antibodies and creating memory cells that "remember" the pathogen. If exposed to the real pathogen later, the immune system quickly reacts, preventing illness.
Example:The polio vaccine contains an inactivated poliovirus, which triggers the immune system to produce antibodies. This prepares the body to fight off the actual virus if encountered, effectively preventing polio.
Q11: Explain how microorganisms and vectors like mosquitoes cause diseases in humans, providing examples of diseases caused by each. (3 Marks)
Ans: Microorganisms cause diseases in humans by entering the body through air, water, food, or direct contact. Once inside, they multiply, produce toxins, or damage tissues, leading to illness. For example, the bacterium Vibrio cholerae causes cholera, which spreads through contaminated water and leads to severe dehydration.
Vectors like mosquitoes also contribute to disease spread by carrying pathogens from one host to another. The Anopheles mosquito transmits the protozoan Plasmodium, causing malaria, while the Aedes mosquito spreads the virus responsible for dengue fever.
Q12: Explain the nitrogen cycle in detail, highlighting the role of microorganisms.(5 Marks)
Ans: The nitrogen cycle is a vital process that ensures the availability of nitrogen to living organisms. Although nitrogen gas makes up 78% of the atmosphere, it cannot be directly used by plants and animals. Microorganisms play a crucial role in converting this atmospheric nitrogen into forms that can be absorbed by plants.
Role of Microorganisms:
Nitrogen Fixation: Certain bacteria and blue-green algae present in the soil, such as Rhizobium, fix atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous compounds like nitrates and ammonia. These compounds are absorbed by plants through their root systems.
Usage by Plants and Animals: Plants use these nitrogen compounds to synthesize proteins and other essential compounds. When animals eat these plants, they also obtain these nitrogenous compounds.
Decomposition: When plants and animals die, bacteria and fungi in the soil break down their bodies, converting the nitrogen in them back into nitrogenous compounds.
Release Back to the Atmosphere: Some bacteria convert these nitrogenous compounds back into nitrogen gas, which is released into the atmosphere, maintaining the nitrogen balance.
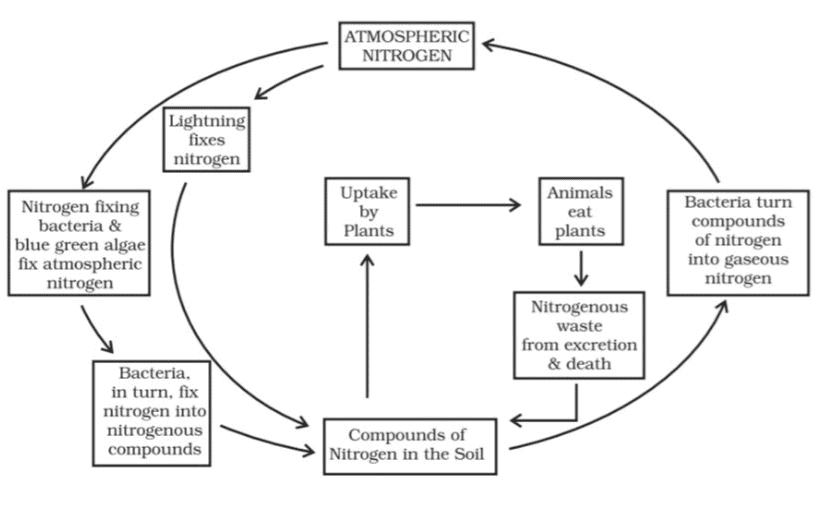
This cycle is essential for replenishing soil nutrients and ensuring that nitrogen remains available to all living organisms in the ecosystem.
Q13: Describe the process of food preservation. Mention different methods used and explain why they are effective. (5 Marks)
Ans: Food preservation involves various techniques used to prevent the growth of microorganisms in food, thereby extending its shelf life and keeping it safe for consumption. Several methods are employed, including chemical methods, temperature control, and proper storage techniques.
Chemical Method:
- Preservatives: Chemicals like salts and edible oils are commonly used to prevent the growth of microorganisms in food. These substances are known as preservatives. For example, sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite are preservatives often added to jams, squashes, and other food items to prevent spoilage.
- Salt or Acid in Pickles: Salt or acidic substances are added to pickles to protect them from microbial attacks. These chemicals create an environment that is inhospitable for the growth of bacteria and fungi.
Preservation by Common Salt: Common salt has been used for ages to preserve food items such as meat and fish. By covering meat or fish with dry salt, the growth of bacteria is inhibited, which helps in preserving the food for longer periods. Salting is also a method used to preserve fruits like amla (Indian gooseberry), raw mangoes, and tamarind.
Preservation by Sugar: Sugar is used to preserve jams, jellies, and squashes. It works by reducing the moisture content in the food, which inhibits the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms that could cause spoilage.
Preservation by Oil and Vinegar: The use of oil and vinegar in pickles helps prevent microbial spoilage. Bacteria cannot survive in environments where oil and vinegar are present. This method is commonly used to preserve vegetables, fruits, fish, and meat.
Heat and Cold Treatments:
- Boiling: Boiling food, such as milk, before storing or using it, kills many microorganisms, making the food safer for consumption.
- Refrigeration: Keeping food in the refrigerator slows down the growth of microorganisms due to the low temperature, thereby extending the freshness of perishable items.
- Pasteurization: Pasteurized milk is treated by heating it to about 70°C for 15 to 30 seconds and then quickly chilling it. This process, discovered by Louis Pasteur, effectively kills harmful microbes while maintaining the quality of the milk.
Storage and Packing: Modern preservation techniques often involve storing dry fruits and vegetables in sealed airtight packets. This packaging prevents the entry and growth of microorganisms, thus protecting the food from spoilage.
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions) : Microorganisms: Friend and Foe - Science Class 8
| 1. What are some common beneficial microorganisms and their uses? |  |
| 2. How do harmful microorganisms affect human health? |  |
| 3. What role do microorganisms play in ecosystems? |  |
| 4. How can we protect ourselves from harmful microorganisms? |  |
| 5. What are the methods used to study microorganisms? |  |






















