Unit Test(Solutions):Nutrition in Animals | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
Maximum Marks: 30
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: Fill in the blank: The process of breaking down complex food substances into simpler forms is called __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: Digestion
Q2: Which of the following is a mode of feeding for a butterfly? (1 Mark)
(i) Scraping
(ii) Chewing
(iii) Siphoning
(iv) Sponging
Ans: (iii)
Butterflies feed on nectar from flowers using a specialized feeding structure called a proboscis, which acts like a long straw. This feeding method is known as siphoning, where the butterfly uses the proboscis to suck nectar from deep within the flower. This mode of feeding allows them to extract liquid food, which is the primary source of nutrition for butterflies.
Q3: Match the following:
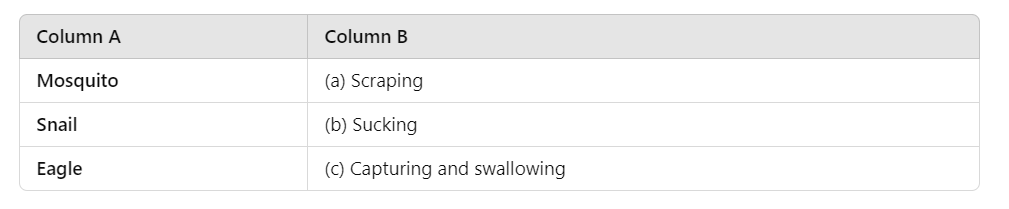
Ans:
Mosquito - (b) Sucking
Snail - (a) Scraping
Eagle - (c) Capturing and swallowing
Q4: True or False: Digestion of proteins starts in the small intestine.(1 Mark)
Ans: False (Digestion of proteins starts in the stomach)
Q5: Why is the villi structure important in the small intestine? (1 Mark)
Ans: Villi increase the surface area of the small intestine for absorption of nutrients. They contain blood vessels that absorb digested food and transport it to different parts of the body for utilization.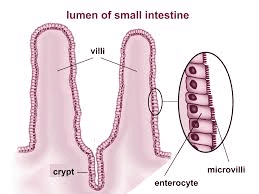
Q6: Diagram-Based Question: (2 Marks)
Label the following parts in and name them:
(a) The largest gland in our body.
(b) The organ where protein digestion starts.
(c) The organ that releases digestive juice into the small intestine.
(d) The organ where bile juice gets stored.
Ans: (a) Liver, (b) Stomach, (c) Pancreas, (d) Gall Bladder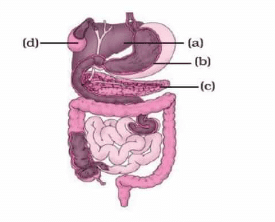
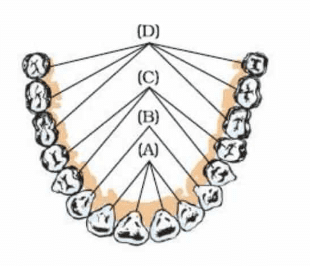
Q7: Label the following parts in and name them:
(i) The cutting and biting teeth as ‘A’
(ii) The piercing and tearing teeth as ‘B’
(iii) The grinding and chewing teeth as ‘C’
(iv) The grinding teeth present only in adult as ‘D'

Ans: A. Incisors, B. Canines, C. Premolars, D. Molars
 Q8: What are ruminants, and how do they digest cellulose? (2 Marks)
Q8: What are ruminants, and how do they digest cellulose? (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Ruminants are grass-eating animals like cows and buffaloes that chew cud.
- They have a special stomach compartment called the rumen, where bacteria help in digesting cellulose from plant material.
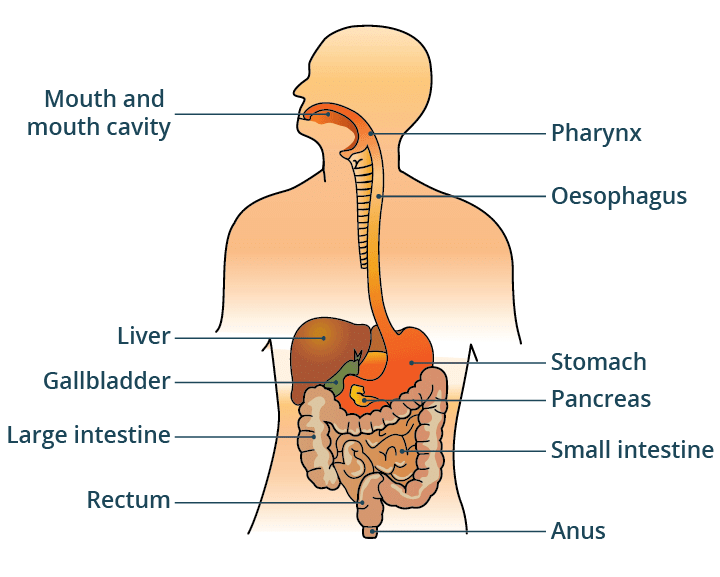
Q9: List six parts of the human digestive system involved in digestion and their functions.(3 Marks)
Ans:
- Mouth: Ingestion and mechanical breakdown of food.
- Oesophagus: Transports food to the stomach through peristalsis.
- Stomach: Secretes acids and digestive juices for protein digestion.
- Small Intestine: Digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats; absorption of nutrients.
- Liver: Secretes bile, which helps in the digestion of fats.
- Large Intestine: Absorbs water and forms feces.
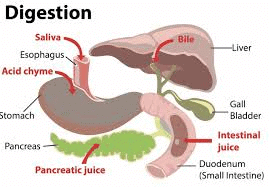
Q10: Explain the role of enzymes in the process of digestion and provide examples. (3 Marks)
Ans:
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up the chemical reactions involved in digestion.
- Salivary amylase in the mouth breaks down starch into simple sugars.
- Pepsin in the stomach helps break down proteins into smaller peptides.
- Pancreatic lipase breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol in the small intestine.
- Trypsin from the pancreas continues the digestion of proteins in the small intestine.
- Maltase in the small intestine breaks down maltose into glucose.
These enzymes work best in specific environments, such as acidic conditions in the stomach and alkaline conditions in the small intestine. Enzymes ensure that complex food substances are converted into simpler forms that can be absorbed by the body. Without enzymes, the digestion process would be too slow to meet the body's needs. Enzymes play a critical role in the efficient and complete digestion of food.
Q11: What happens to food in the stomach during digestion? (3 Marks)
Ans:
- The stomach secretes hydrochloric acid, which kills bacteria and creates an acidic environment.
- Digestive juices secreted by the stomach break down proteins into simpler substances.
- The stomach muscles churn the food, mixing it with digestive juices for better digestion.
- The mucus secreted by the stomach protects its inner lining from acidic damage.
- The partially digested food is then passed on to the small intestine.
- The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of food from the stomach to the small intestine.
Q12: Describe the process of digestion in the small intestine and its importance. (5 Marks)
Ans:
- The small intestine is about 7.5 meters long and is highly coiled to allow maximum digestion and absorption.
- The liver secretes bile into the small intestine, which helps in breaking down fats into smaller droplets.
- The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes that further digest carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- The walls of the small intestine also secrete digestive juices that complete the digestion process.
- The nutrients from the digested food are absorbed through the villi into the bloodstream.
- The small intestine's large surface area allows for efficient nutrient absorption.
- Glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, and glycerol are absorbed and transported to different body parts.
- The absorbed nutrients are used for energy, growth, and repair.
- Any undigested material is passed to the large intestine.
- The small intestine plays a crucial role in ensuring that the body gets the essential nutrients from food.
Q13: Compare the digestion process in amoeba and humans. (5 Marks)
Ans: 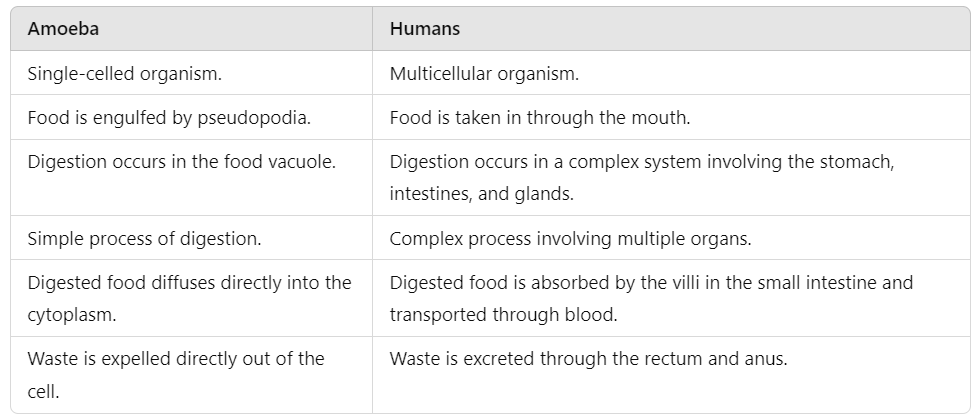
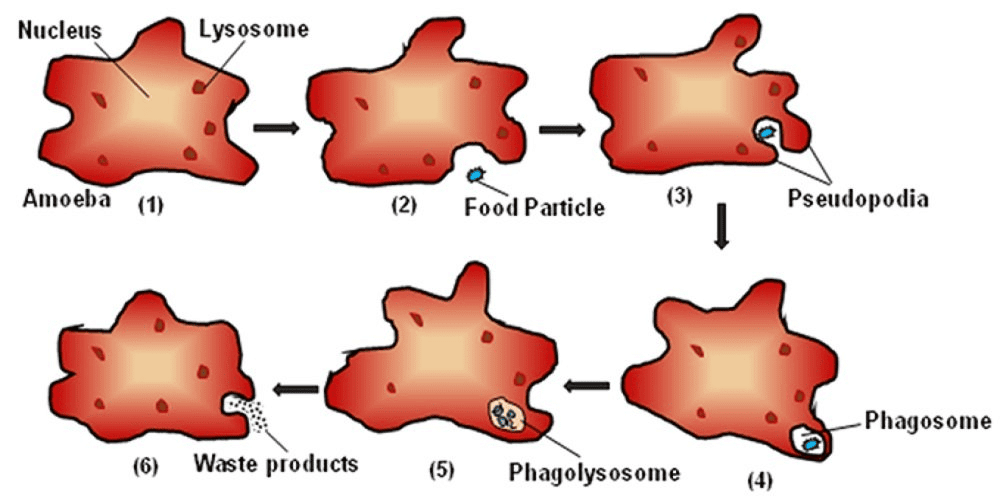 Digestion Process in Amoeba
Digestion Process in Amoeba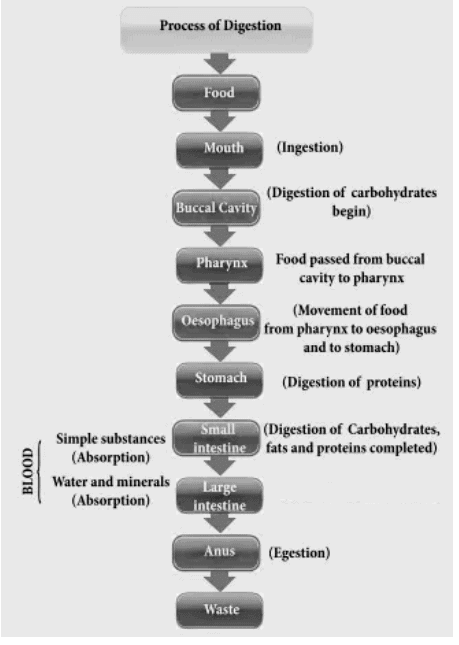 Flowchart of Digestion in Humans
Flowchart of Digestion in Humans
|
111 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|

















