Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 30th September 2024) Part - 1 | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 100 years of Discovery of IVC |

|
| White Revolution 2.0 |

|
| PM Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan |

|
| 6th Quad Summit 2024 |

|
| Strengthening POCSO Act 2012 |

|
| Methane Emissions and Global Warming |

|
GS1/History & Culture
100 years of Discovery of IVC
20th September 2024 marked a century since the discovery of the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC), announced by archaeologist Sir John Marshall in September 1924. This ancient civilization encompasses over 2,000 sites across 1.5 million square kilometers in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, renowned for its sophisticated urban planning and architecture.
What was Harappan Civilization?
The Harappan Civilization, also referred to as the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC), thrived around 2500 BCE along the banks of the Indus River. It was the largest of the four ancient urban civilizations, which included Egypt, Mesopotamia, and China. The IVC is categorized as a Bronze Age civilization due to the numerous artifacts discovered that were crafted from copper-based alloys.
- Daya Ram Sahni initiated excavations at Harappa in 1921-22.
- Rakhal Das Banerji began excavating Mohenjo-daro in 1922.
- Sir John Marshall, the Director General of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), oversaw the excavations that led to the discovery of Mohenjo-daro, a significant site of the IVC.
Phases
- Early Phase (3200 BCE to 2600 BCE): This phase is linked to the Hakra Phase found in the Ghaggar-Hakra River Valley. The earliest known Indus script dates back to 3000 BCE.
- Mature Period (2600 BCE to 1900 BCE): By 2600 BCE, the IVC had reached its peak, with early towns like Harappa and Mohenjo-daro evolving into major urban centers.
- Late Phase (1900 BCE to 1500 BCE): During this period, the Harappan civilization began to decline and eventually collapsed.
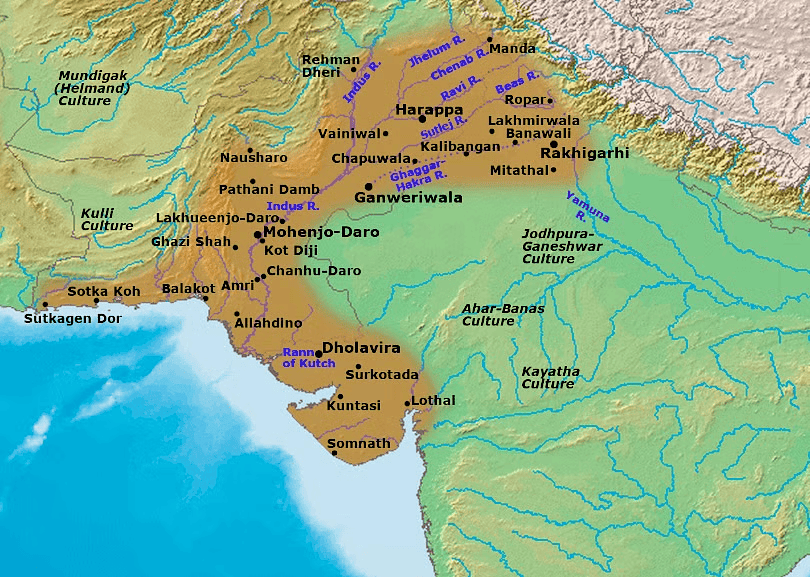
What were the Important Sites of Harappan Civilization?
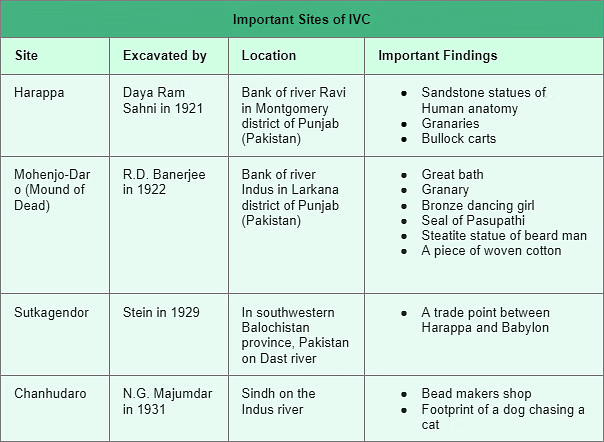
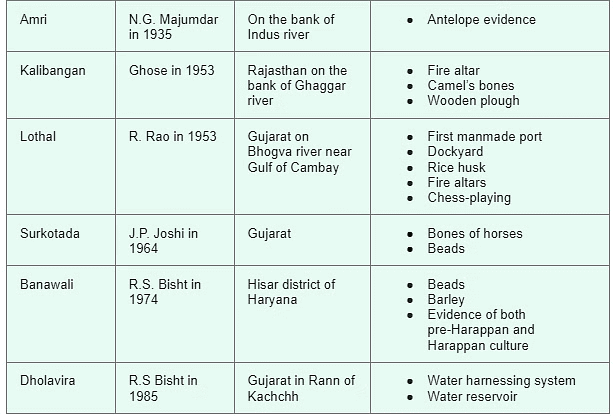
What were the Key Features of Harappan Civilization?
Town Planning
- The Harappan culture is distinguished by its advanced town planning, characterized by cities laid out in a grid-like pattern.
- Both Harappa and Mohenjo-daro had a citadel or acropolis, presumably housing the ruling elite.
- Below these citadels were lower towns, populated by ordinary citizens living in brick houses.
- Large granaries were constructed for grain storage, employing burnt bricks, a technique differing from the sun-dried bricks used in contemporary Egyptian architecture.
- Mohenjo-daro boasted a remarkable drainage system, with most residences featuring courtyards and bathrooms.
- Homes in Kalibangan included private wells.
- At Dholavira in Gujarat, the entire settlement was fortified, with walls dividing internal sections.
Agriculture
- Harappan villages, primarily situated near fertile floodplains, were highly productive, cultivating crops such as wheat, barley, peas, sesame, lentils, chickpeas, and mustard.
- Millets were also grown, particularly in Gujarat, while rice was less common.
- The people of the Indus Valley were pioneers in cotton production, referred to as "Sindon" by the Greeks.
- While evidence of agricultural practices is apparent through grain remains, specific farming techniques remain difficult to reconstruct.
- Alongside agriculture, animal husbandry was widely practiced.
Economy
- Trade was crucial to Harappan society, as indicated by the presence of seals, a standardized script, and uniform weights and measures.
- Key trade goods included stone, metal, and shell items, with a barter system in place, as there was no metal currency.
- Navigation occurred along the Arabian Sea coast, with a trading colony in northern Afghanistan facilitating commerce with Central Asia.
- Harappans traded with Mesopotamia (the Tigris-Euphrates region) and engaged in long-distance trade, including lapis lazuli, which likely conferred social status to the ruling class.
Crafts
- Harappans exhibited exceptional skills in bronze manufacturing, sourcing materials from the Khetri mines in Rajasthan and possibly tin from Afghanistan.
- Textile impressions on artifacts indicate a knowledge of weaving.
- Key crafts included boat-making, bead-making, seal-making, and terracotta production.
- Goldsmiths crafted jewelry from gold, silver, and precious stones.
- The potter's wheel was extensively used, producing shiny and distinctive pottery.
Religion
- A plethora of terracotta figurines of women suggests the worship of a fertility goddess, akin to the Egyptian goddess Isis.
- A male deity, possibly representing Pashupati Mahadeva (in a yogic pose), is depicted on seals with three horned heads, surrounded by diverse animals including elephants, tigers, rhinoceroses, and buffalo.
- Symbols of male and female genitalia indicate a focus on fertility worship.
- Animals and trees were revered, with the unicorn (likely a rhinoceros) and the humped bull being particularly significant.
- Amulets were commonly discovered, possibly used for protection or religious practices.
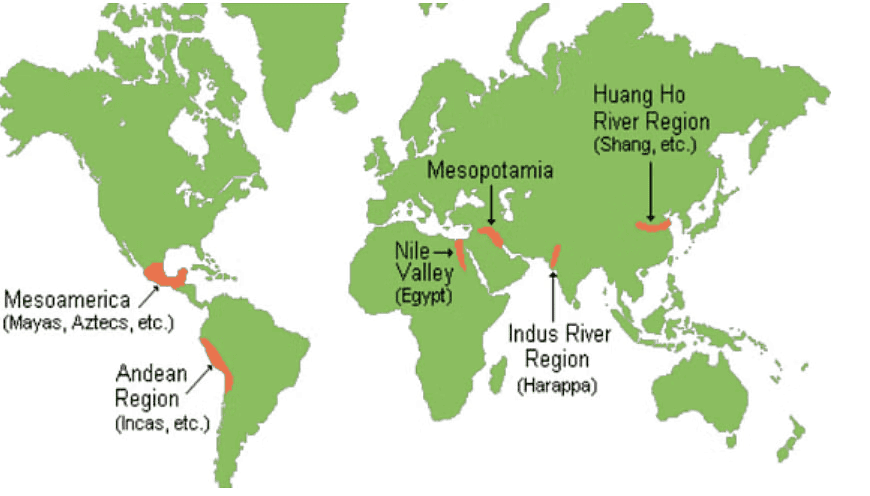
What were the Possible Reasons for Decline of Harappan Civilization?
Invasion Theory
- Some scholars propose that Indo-European tribes, known as Aryans, invaded and toppled the IVC. However, evidence of cultural continuity in succeeding societies challenges the notion of an abrupt invasion.
Natural Environmental Changes
- More widely accepted are the environmental factors impacting the decline.
Tectonic Activity
- Earthquakes may have altered the courses of rivers, resulting in the drying up of vital water sources.
Changes in Rainfall Patterns
- Alterations in monsoon patterns could have reduced agricultural yields, leading to food shortages.
Flooding
- Shifts in river courses may have caused flooding in crucial agricultural regions, further destabilizing the civilization.
GS3/Economy
White Revolution 2.0

Why in News?
- Recently, the Ministry of Cooperation unveiled standard operating procedures (SOPs) aimed at empowering women farmers and creating job opportunities.
About White Revolution 2.0:
- This initiative seeks to enhance milk production while also empowering women and combating malnutrition.
- It aligns with the original White Revolution initiated in 1970 by Dr. Verghese Kurien, which transformed India into a global leader in milk production.
- The original initiative is popularly known as 'Operation Flood.'
Targets under White Revolution 2.0:
- Dairy cooperatives aim to procure 100 million kilograms of milk daily by the end of the five-year initiative.
- The goal is to increase cooperative procurement from the current 660 lakh liters per day to 1,000 lakh liters.
Launch of Margdarshika (SOPs):
- The Margdarshika SOPs will facilitate the formation of 200,000 new multipurpose primary agricultural cooperatives (MPACs).
- This initiative will promote new cooperatives in panchayats lacking agricultural, fisheries, and dairy-related facilities.
- It has been developed by the Ministry of Cooperation in partnership with NABARD and the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB).
Women Empowerment:
- The dairy sector employs a significant number of women, generating a business worth Rs 60,000 crore in Gujarat alone.
- This initiative will formalize women's employment by ensuring direct deposits into their bank accounts.
Tackling Malnutrition:
- By increasing milk availability, the primary beneficiaries will be impoverished and malnourished children.
- This initiative aims to strengthen the fight against malnutrition by providing adequate nutrition for children.
Integration with Existing and Upcoming Schemes:
- The plan will complement existing government programs like the Dairy Processing and Infrastructure Development Fund (DIDF) and the National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD).
- A new phase, NPDD 2.0, is proposed under the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying to further advance the cooperative agenda.
Expansion of 'Cooperation Among Cooperatives' Initiative:
- The government has launched a nationwide expansion of the 'Cooperation among Cooperatives' initiative, which has been piloted successfully in Gujarat.
- This initiative enables dairy farmers to access interest-free cash credit through RuPay Kisan Credit Cards and will distribute micro-ATMs to facilitate financial services in rural areas.
PACS Computerisation:
- Standard operating procedures (SOPs) for the computerization of Primary Agriculture Credit Societies (PACS) have been introduced to modernize PACS, ensuring more efficient and transparent operations.
What is the Need for White Revolution 2.0?
To Increase Milk Productivity:
- The average milk yield is only 8.55 kg per animal per day for exotic/crossbred animals, and 3.44 kg/animal/day for indigenous animals.
- In Punjab, the yield is 13.49 kg/animal/day (exotic/crossbreed), while in West Bengal, it is only 6.30 kg/animal/day.
Reversing the Decline in Milk Production Growth Rate:
- The growth rate of milk production has fallen from 6.47% in 2018-19 to 3.83% in 2022-23, indicating a slowdown in production increase.
Formalisation of Milk Consumption Patterns:
- 63% of total milk production is sold in the market; the remainder is consumed by producers themselves.
- Two-thirds of marketable milk is in the unorganised sector, with cooperatives holding a significant share.
Milk as the Top Food Expenditure in India:
- In rural India, the average monthly expenditure on milk per person was Rs 314, exceeding other food items like vegetables and cereals.
- In urban India, the average expenditure on milk was Rs 466, higher than for fruits, vegetables, cereals, and meat.
Checking Rising Milk Prices:
- The all-India modal price of milk rose from Rs 42 to Rs 60 per litre over the past five years due to increasing input costs, including fodder and feed.
- There is concern that further price hikes may lead to reduced demand, as consumers may find milk unaffordable.
Methane Emissions:
- Livestock emissions from manure and digestive processes account for about 32% of human-caused methane emissions, a significant contributor to global warming.
How can Milk Production be Increased Under White Revolution 2.0?
Genetic Improvement:
- Introducing sex-sorted (SS) semen can increase the likelihood of producing female calves with high milk productivity, raising the probability to 90%.
- This method allows for the selective breeding of desired female calves, which are more productive.
Embryo Transfer (ET) Technology:
- ET technology can enhance the productivity of high-genetic-merit (HGM) cows by allowing multiple embryos to be produced and implanted into various surrogate cows.
- This technique enables a single HGM cow to potentially produce 12 calves per year, significantly increasing milk production capabilities.
In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) Technology:
- In IVF, immature ova are collected, fertilized in a laboratory, and then implanted into surrogate cows.
- This method can yield 33-35 calves per donor cow annually, facilitating rapid scaling of the cow population with high milk yields.
Nutrition and Feed Intervention at Low Cost:
- Alongside genetic improvements, enhancing animal nutrition is essential to lower feed costs for farmers.
- Amul is establishing a Total Mixed Ration (TMR) plant in Gujarat to produce affordable, ready-to-eat fodder mixes that combine various nutrients for cattle.
Improved Diet Quality:
- Offering easily digestible forages such as legumes and grains can decrease fermentation time and reduce methane emissions.
- Specific feed additives may inhibit methane-producing microbes, contributing to more sustainable livestock practices.
What are the Related Schemes for the Livestock Sector?
- Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF)
- National Animal Disease Control Programme
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission
- National Artificial Insemination Programme
- National Livestock Mission
Conclusion:
- White Revolution 2.0 aims to revolutionize India’s dairy sector by boosting milk production, empowering women farmers, and reducing production costs through advanced genetic techniques.
- The focus on lowering feed expenses while increasing milk yield ensures sustainable growth, enhances farmer incomes, and strengthens the rural economy.
Mains Question:
- What role can technology play in enhancing dairy production in India under White Revolution 2.0?
a) Introducing sex-sorted semen for selective breeding of high-yield female calves. b) Implementing Embryo Transfer (ET) technology to increase the productivity of high-genetic-merit cows. c) Utilizing In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) technology to rapidly scale the cow population with high milk yields. d) Developing Total Mixed Ration (TMR) plants to produce affordable, nutrient-rich fodder mixes for cattle.
GS2/Governance
PM Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan

Why in News?
- Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan (PMJUGA) for improving the socio-economic condition of tribal communities.
What are the Key Facts About the PMJUGA?
About PMJUGA:
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme aimed at the welfare of tribal families residing in tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts.
Target Areas and Coverage:
- The program will include 549 districts and 2,740 blocks across all tribal majority villages in 30 States/UTs.
- Approximately 63,000 villages will be covered, benefiting over 5 crore tribal individuals.
- According to the 2011 Census, India has a Scheduled Tribe (ST) population of 10.42 crore (8.6%), comprising over 705 tribal communities.
Objective:
- The initiative aims to address critical gaps in social infrastructure such as health, education, and livelihoods by leveraging various schemes from the Government of India through convergence and outreach.
Goals of the Mission:
- The mission includes 25 interventions to be implemented by 17 ministries, utilizing funds from the Development Action Plan for Scheduled Tribes (DAPST) over the next five years to achieve the following:
Developing Enabling Infrastructure:
- Eligible ST households will have access to pucca housing through PMAY (Rural), along with tapped water from Jal Jeevan Mission and electricity supply.
- Additionally, these households will be entitled to the Ayushman Bharat Card (PMJAY).
Improving Village Infrastructure:
- Ensuring all-weather road connectivity to ST-majority villages through PMGSY.
- Providing mobile connectivity via Bharat Net and improving health, nutrition, and education infrastructure through the National Health Mission, Samagra Shiksha, and Poshan Abhiyan.
Promotion of Economic Empowerment:
- The initiative emphasizes skill development, entrepreneurship, and enhanced livelihood opportunities through access to training via the Skill India Mission.
- Support will also be provided for marketing through the Tribal Multipurpose Marketing Centre (TMMC) and assistance in agriculture, animal husbandry, and fisheries for Forest Rights Act (FRA) patta holders.
Universalisation of Access to Quality Education:
- Efforts will be made to increase the Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER) in schools and higher education for ST students, including setting up tribal hostels at district/block levels under the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan.
Healthy Lives and Dignified Ageing:
- The mission aims to align with national standards for infant mortality rate (IMR), maternal mortality rate (MMR), and immunisation coverage.
- Mobile Medical Units will be deployed in areas where the nearest sub-centre is more than 10 km in plain regions and 5 km in hilly areas.
Mapping and Monitoring:
- Tribal villages under the mission will be mapped on the PM Gati Shakti Portal to identify gaps for scheme-specific requirements, with awards for the best-performing districts.
What are the Innovative Schemes to Promote Livelihood among Tribals under PMJUGA?
Tribal Home Stay:
- To enhance tourism in tribal regions and provide alternative livelihoods, the Ministry of Tourism will promote 1,000 homestays under the Swadesh Darshan scheme.
- Villages with tourism potential will receive funding for 5-10 homestays, with each household eligible for Rs 5 lakh to construct two new rooms, Rs 3 lakh for renovating existing rooms, and Rs 5 lakh for community needs.
Sustainable Livelihood for Forest Right Holders:
- The mission focuses on 22 lakh FRA patta holders in forest areas to expedite the recognition of forest rights and provide sustainable livelihoods through various governmental schemes.
Improving Infrastructure of Government Residential Schools and Hostels:
- The initiative aims to enhance the infrastructure of tribal residential schools, hostels, and ashram schools to improve local educational resources, promote enrollment, and retain students.
Advanced Facilities for Diagnosis of Sickle Cell Disease:
- Centers of Competence (CoC) will be established in AIIMS and other premier institutes in states where sickle cell disease is prevalent, equipped with the latest facilities for prenatal diagnosis at a cost of Rs 6 crore per CoC.
Tribal Multipurpose Marketing Centre (TMMCs):
- 100 TMMCs will be set up to facilitate effective marketing of tribal products and enhance marketing infrastructure, awareness, branding, packaging, and transportation facilities.
What is the Need for PMJUGA?
Poverty:
- Tribal communities often experience high levels of poverty and limited access to resources, with 45.3% of ST individuals living below the poverty line in rural areas and 24.1% in urban areas as per the erstwhile Planning Commission (2011-12).
- Under PMJUGA, Skilling Centers will be established in tribal districts to address poverty and create job opportunities.Land Rights and
Displacement:
- Many tribal communities face displacement due to development projects, mining, and deforestation, often lacking formal land titles that lead to insecure tenure.
- PMJUGA aims to issue 22 lakh FRA pattas under the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006 to acknowledge their land rights.
Low Literacy Rate:
- Literacy rates among tribal populations are significantly lower than the national average, with a literacy rate of 59% for Scheduled Tribes compared to the overall rate of 73% (Census 2011).
- 1,000 hostels will be constructed under the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) to promote affordable education.
Health Issues:
- The National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) 2019-21 reported high levels of stunting, wasting, and underweight among tribal children at 40.9%, 23.2%, and 39.5% respectively, exceeding national averages.
- Additionally, a high incidence of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is prevalent among tribal communities.
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare will implement measures to address these health concerns.
Cultural Erosion and Identity:
- Many tribal communities struggle to preserve their traditional practices amid rapid urbanization and globalization.
- Under the Pradhan Mantri Adi Adarsh Gram Yojana, model villages will be developed while safeguarding cultural identity.
Lack of Awareness about Government Schemes:
- Despite being impoverished, many tribal individuals remain unaware of benefits such as BPL cards, ration cards, and job cards for 100-day employment schemes.
- The Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology will promote various Digital India initiatives to enhance awareness among tribal communities.
What are the Other Government Initiatives for Scheduled Tribes?
- PM-Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN) Scheme
- TRIFED
- Digital Transformation of Tribal Schools
- Development of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups
- Pradhan Mantri Van Dhan Yojana
- Eklavya Model Residential Schools
Conclusion
Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan (PMJUGA) aims to uplift tribal communities through sustainable development, enhancing infrastructure, livelihoods, and access to essential services. By fostering skill development and self-sufficiency, it seeks to improve education, healthcare, and overall quality of life, bridging the development gap and empowering tribal voices in India.
Mains Question:
Q. Examine the key challenges faced by tribal communities in India. What are the various government schemes and policies to address these issues.
GS2/International Relations
6th Quad Summit 2024

- Recently, the 6th in-person Quad Leaders' Summit was held in Delaware, United States. The Quad is leading ambitious projects aimed at assisting partners in addressing pandemics and diseases, tackling climate change, and enhancing cybersecurity, among other goals.
What are the Key Highlights of the 6th Quad Summit?
Health:
- Quad Health Security Partnership (QHSP): Launched in 2023, this initiative aims to improve health security coordination in the Indo-Pacific region.
- A new initiative, the Quad Cancer Moonshot, was announced to address the treatment of cervical cancer.
Pandemic Preparedness:
- The United States has committed over USD 84.5 million to enhance capabilities for infectious disease prevention and response across fourteen Indo-Pacific nations.
Maritime Security:
- MAITRI (Maritime Initiative for Training in the Indo-Pacific) was introduced to bolster regional maritime security capabilities.
- The Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA) was launched in 2022 to improve monitoring of illegal activities.
- A logistics network has been initiated to enhance airlift capacity for rapid disaster response across the Indo-Pacific.
- Plans for a first-ever Quad-at-Sea Ship Observer Mission are set for 2025 to improve interoperability.
Quality Infrastructure Development:
- Digital Infrastructure Principles: The Quad established principles focused on developing secure and inclusive digital public infrastructure.
- Quad Ports of the Future Partnership: This initiative aims to support resilient port infrastructure and enhance connectivity in the Indo-Pacific region, with a Regional Ports and Transportation Conference slated for 2025 in Mumbai.
- Over USD 140 million has been committed to undersea cable projects to ensure primary telecommunication connectivity for Pacific island nations by 2025.
- The Cable Connectivity and Resilience Centre was launched by Australia in July 2024.
- Quad Infrastructure Fellowship: This program aims to enhance capacity and professional networks for managing infrastructure projects.
Critical and Emerging Technology:
- Open Radio Access Network (RAN) and 5G: The Quad initiated its first Open RAN deployment in Palau in 2023, aiming to create a secure telecommunications ecosystem, supported by an investment of approximately USD 20 million.
- The Quad is also backing trials and the Asia Open RAN Academy in the Philippines.
- AI-ENGAGE Initiative (2023): This initiative seeks to leverage AI and robotics for next-generation agriculture.
- BioExplore Initiative: Focused on utilizing AI to study biological ecosystems for advancements in disease diagnosis, crop resilience, and clean energy solutions.
- The Quad leaders finalized a Memorandum of Cooperation to collaborate on semiconductor supply chain risks.
- Quantum Technology: The Quad Investors Network (QUIN) aims to enhance collaboration within the quantum ecosystems of Quad nations.
Climate and Clean Energy:
- Enhanced Early Warning Systems: The US will provide 3D-printed weather stations to support Pacific Island nations, while Australia and Japan are enhancing regional disaster risk reduction efforts.
- The Quad Clean Energy Supply Chain Diversification Program (2023) aims to secure and diversify clean energy supply chains, with India committing USD 2 million to solar projects in Fiji, Comoros, Madagascar, and Seychelles.
Cybersecurity:
- The Quad has developed the Quad Action Plan to safeguard commercial undersea telecommunications cables, aiming to advance shared goals for digital connectivity and global commerce.
- Collaboration to foster a resilient information environment is being pursued through the Countering Disinformation Working Group, which supports media freedom and addresses foreign influence.
Space:
- Quad partners plan to share expertise in space situational awareness (SSA) to ensure long-term sustainability of the space environment.
Countering Terrorism:
- Quad leaders discussed counter-terrorism threats and best practices for mitigating acts of terrorism through information sharing.
- The Quad Counter Terrorism Working Group (CTWG) focuses on countering unmanned aerial systems, CBRN threats, and the use of the internet for terrorist activities.
People-to-People Initiatives:
- India announced a new initiative to offer fifty Quad scholarships worth USD 500,000 to students for a four-year undergraduate engineering program at Government of India-funded technical institutions.
What are Quad Principles for Development and Deployment of Digital Public Infrastructure?
- About the Principles: These principles outline a framework for building and using digital infrastructure that promotes inclusivity, transparency, and respect for democratic values.
- About Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI): DPI includes shared digital systems that are secure, reliable, and interoperable, utilized by both public and private sectors to provide equitable access and improve public service delivery.
- Quad Principles for DPI:
- Inclusivity: Remove barriers to empower end-users and ensure last-mile access while avoiding algorithmic bias.
- Interoperability: Employ open standards, considering legal and technical constraints.
- Scalability: Design systems to flexibly manage unexpected increases in demand.
- Security and Privacy: Incorporate privacy-enhancing technologies to protect individual data.
- Governance for Public Benefit: Ensure systems are safe, trusted, and transparent, promoting competition and data protection.
- Sustainability: Ensure operations continue through adequate financing and technological support.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Safeguard intellectual property rights according to existing legal frameworks.
- Sustainable Development: Align systems with the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
What is Quad?
- About: The Quad, or Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, is a diplomatic partnership involving Australia, India, Japan, and the US, focusing on ensuring stability and prosperity in the Indo-Pacific region, promoting an open, stable, and resilient environment.
- Objectives of Quad: The Quad addresses significant regional challenges, including health security, climate change, infrastructure, technology, cybersecurity, humanitarian assistance, maritime security, countering disinformation, and counter-terrorism.
- Origins of Quad: The Quad was originally formed in response to the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami, where the four nations provided humanitarian assistance. It was formally established in 2007 by Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe but became dormant due to concerns over China's reactions, particularly after Australia's withdrawal in 2008. Revived in 2017 amid changing regional attitudes toward China's influence, it held its first formal summit in 2021.
- Expansion Potential: "Quad-plus" meetings have included nations like South Korea, New Zealand, and Vietnam, indicating potential for future expansion.
Conclusion
The Quad is committed to enhancing health security against pandemics, addressing climate change threats, and strengthening cybersecurity. By fostering collaboration and innovation in these critical areas, the Quad aims to ensure a resilient and prosperous Indo-Pacific, contributing to global stability and sustainable development.
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the significance of the Quad (Quadrilateral Security Dialogue) in addressing contemporary challenges in the Indo-Pacific region.
GS2/Polity
Strengthening POCSO Act 2012

Why in News?
- Recently, the Supreme Court ruled that watching or possessing sexually explicit material involving minors is illegal under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012. This ruling means that simply having such material constitutes a punishable offense, regardless of whether it is shared or transmitted. This decision overturned a previous ruling by the Madras High Court, which stated that viewing child pornography privately did not constitute an offense unless it was distributed.
Key Highlights of the Supreme Court Ruling:
- Redefinition of Terminology: The Supreme Court has recommended that the Union government change the term "child pornography" to "child sexual exploitative and abuse material" (CSEAM). This is important because the term "pornography" can imply consensual adult activities and does not fully capture the nature of abuse and exploitation.
- Expansion of Section 15 of the POCSO Act, 2012:The SC has provided a stricter interpretation of "storage of child pornography," which previously focused on commercial storage. The court's interpretation introduces three critical offenses:
- Possession Without Reporting: Individuals who store or possess such material must delete, destroy, or report it to authorities. Not doing so can lead to punishment under Section 15(1).
- Intent to Transmit or Distribute: Those who possess child pornography with the intention to distribute or display it (except for reporting purposes) may face charges under Section 15(2).
- Commercial Possession: Storing child pornography for commercial purposes falls under Section 15(3), which prescribes the harshest penalties.
- Concept of Inchoate Offences: The ruling categorizes offenses under Section 15 as "inchoate" offences, meaning they are preparatory actions towards committing further crimes.
- Redefinition of Possession: The definition of "possession" in these cases has been broadened. It now includes "constructive possession," where a person may not physically hold the material but has the ability to control it and understands that control. For example, merely watching online without downloading can still lead to accountability if the individual closes a link to child pornography without reporting it.
- Educational Reforms: The court has called on the government to promote comprehensive sex education in schools and society to counter misconceptions and stigmas surrounding discussions about sexual health. This education should cover topics like consent, healthy relationships, gender equality, and respect for diversity.
- Awareness About POCSO Act, 2012: Sections 43 and 44 mandate that central and state governments, along with the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR), promote widespread awareness of the Act.
- Formation of an Expert Committee: An expert committee should be established to create comprehensive programs for health and sex education and to raise awareness among children regarding these issues.
- Victim Support and Awareness: The judgment emphasizes the need for strong support systems for victims of CSEAM, including psychological counseling and educational support. Programs like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can address the cognitive distortions that contribute to such behavior among offenders.
What is the POCSO Act?
- About: The POCSO Act aims to tackle offenses of sexual exploitation and abuse of children, defining a child as anyone under 18. This legislation was enacted following India's ratification of the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child in 1992.
- Features:
- Gender-Neutral Nature: The Act acknowledges that both boys and girls can be victims, asserting that abuse is a crime irrespective of the victim's gender.
- Confidentiality of Victim’s Identity: Section 23 mandates confidentiality for child victims, prohibiting media from revealing any details that could identify them.
- Mandatory Reporting of Child Abuse Cases: Sections 19 to 22 require individuals who suspect child abuse to report it to the authorities.
- Gaps in Implementation of the POCSO Act, 2012:
- Lack of Support Persons: A significant gap is the absence of support persons for victims, as it was found that in 96% of POCSO cases, victims did not receive necessary support during legal proceedings.
- Insufficient Designation of POCSO Courts: Not all districts have POCSO courts; only 408 have been established across 28 states as of 2022.
- Shortage of Special Public Prosecutors: There is a lack of specially trained public prosecutors to handle POCSO cases effectively.
- Conclusion: A coordinated effort among stakeholders—including educators, healthcare providers, and law enforcement—is essential for early intervention in cases of child sexual exploitation. A societal shift in attitudes is necessary to prevent victimization and to support recovery, ensuring that victims can heal and reclaim their dignity and hope.
- Mains Question: Q. Critically analyze the effectiveness of the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012 in addressing child sexual abuse in India.
GS3/Environment
Methane Emissions and Global Warming
Why in News?
- Methane (CH4) emissions are on the rise, posing a risk to the global climate goals established by the Paris Agreement. While carbon dioxide (CO2) has dominated climate discussions, methane, which is a significantly more powerful greenhouse gas (GHG), is receiving increasing attention. Tackling methane's contribution to global warming presents a substantial opportunity for swift climate action.
What is the Climate Impact of Methane Emissions?
- Climate Impact: Methane is roughly 80 times more potent than CO2 as a greenhouse gas and has been responsible for about 30% of global warming since the industrial revolution. However, it only remains in the atmosphere for approximately 7 to 12 years. Thus, reducing methane emissions or enhancing its sinks can lead to significant short-term climate benefits, buying time to address the more challenging task of decreasing reliance on fossil fuels and associated CO2 emissions.
- Reducing methane emissions by 45% by 2030 could aid in achieving the Paris Agreement's objective of limiting global warming to 1.5°C. By mitigating methane emissions and improving its removal from the atmosphere, we can transform this climate adversary into a key ally in maintaining safe global temperatures.
- Air Quality Issues: Controlling methane emissions is vital for enhancing air quality since methane contributes to the formation of ground-level (tropospheric) ozone, a harmful pollutant that adversely impacts respiratory health.
- Emission Sources:Major contributors to methane emissions include:
- Energy sector (particularly oil, gas, and coal)
- Agriculture (mainly livestock and rice cultivation)
- Waste management (landfills)
- Global methane emissions are estimated at around 580 million tonnes annually, with about 40% from natural sources and 60% from human activities (anthropogenic emissions). Their reduction is considered a relatively feasible climate action.
- The largest anthropogenic source of methane emissions is agriculture, accounting for approximately 25%, closely followed by the energy sector (coal, oil, natural gas, and biofuels).
What Global Efforts are Underway to Reduce Methane?
- Global Methane Pledge (GMP): Launched at CoP26 in 2021 (Glasgow climate pact), this initiative aims to cut methane emissions by at least 30% below 2020 levels by 2030. It is led by the US and EU, with 158 participating countries representing over 50% of global anthropogenic methane emissions. India has chosen not to sign the Global Methane Pledge.
- UN Environment Programme (UNEP): This organization spearheads initiatives like the International Methane Emissions Observatory (IMEO) and the Oil and Gas Methane Partnership, focusing on monitoring and reducing methane emissions from the energy, agriculture, and waste sectors.
- International Energy Agency: The IEA's Global Methane Tracker serves as a crucial tool in efforts to reduce emissions across the energy sector.
- Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC): This coalition assists countries in implementing measures to reduce methane emissions.
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Reports: These reports highlight the necessity of reducing methane emissions to meet global climate targets and offer guidelines for nations to incorporate methane reduction in their climate strategies.
Why Did India Reject the Global Methane Pledge?
- Impact on Agricultural Livelihoods: In India, major sources of methane emissions stem from enteric fermentation (a digestive process in ruminant animals) and rice cultivation. These practices are critical for small and marginal farmers, who are essential to India's agricultural sector. The methane emissions from these activities are considered "survival" emissions, directly affecting food production and farmers' livelihoods rather than being linked to luxury consumption.
- Food Security Concerns: As one of the largest producers and exporters of rice, any reduction in methane emissions, especially from rice farming, could threaten food security and impact both domestic supply and export capabilities. This potential decline in agricultural output could further endanger farmers' incomes and rural economies.
- Shifting From CO2: India argues that CO2, which has a lifespan of 100-1000 years, is the primary driver of climate change. The Pledge's focus on methane reduction, which has a shorter atmospheric lifespan, shifts the burden of CO2 reduction.
- Sovereign Right to Determine Climate Actions: India's Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement do not enforce sector-specific emissions reduction targets, allowing the nation to decide its climate actions based on its circumstances and priorities. After evaluation, the Indian government concluded that signing the Pledge would not align with its national interests.
How is India Reducing Methane Emissions?
- India’s Participation in Climate Agreements: India is a participant in the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), including the Kyoto Protocol and Paris Agreement, which aim to decrease greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA): This initiative, implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, promotes climate-resilient practices, including methods to reduce methane emissions in rice farming.
- National Innovations in Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA):The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has developed various technologies aimed at lowering methane emissions in rice cultivation:
- System of Rice Intensification (SRI): Increases rice yield by 36-49% while using 22-35% less water than traditional methods, thereby reducing methane emissions.
- Direct Seeded Rice (DSR): This method reduces methane emissions since it bypasses the need for raising nurseries, puddling, and transplanting.
- Crop Diversification Programme: Encourages a shift from rice cultivation to other crops such as pulses, oilseeds, maize, and cotton, which results in lower methane emissions from rice fields.
- Capacity Building Programs: Krishi Vigyan Kendras across the country conduct awareness sessions for farmers on climate-resilient and methane-reducing agricultural techniques.
- National Livestock Mission:This initiative, managed by the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD), promotes:
- Breed Improvement and Balanced Rationing: Providing livestock with balanced and high-quality diets to lower methane emissions.
- Green Fodder Production and Silage Making: Encouraging the production of green fodder, chaff cutting, and total mixed ration practices to minimize emissions from livestock.
- Gobardhan Scheme (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources): This program incentivizes the use of cattle waste for generating clean energy and organic fertilizer, thereby reducing methane emissions from livestock waste in rural areas.
- New National Biogas and Organic Manure Programme: This initiative encourages the use of cattle waste for clean energy production in villages.
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the significance of methane emissions in the context of global warming and climate change.
|
201 videos|1014 docs|2272 tests
|




















