Weekly Current Affairs (8th to 14th October 2024) Part - 1 | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
GS2/Governance
National Health Account (NHA) Estimates 2020-21 and 2021-22

Why in news?
- Recently, the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has released the estimates for the fiscal years 2020-21 and 2021-22. These reports are the eighth and ninth editions of the NHA series, offering a comprehensive overview of the country's healthcare expenditure.
What are the Key Findings of NHA Estimates for 2020-21 and 2021-22?
Rising Government Health Expenditure (GHE):
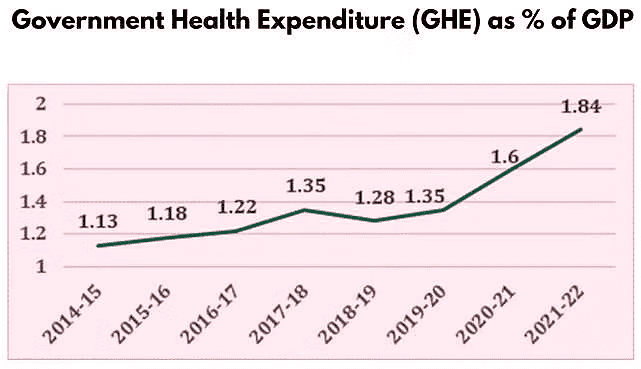
- The share of GDP rose from 1.13% in 2014-15 to 1.84% in 2021-22.
- The share of GHE in General Government Expenditure (GGE) increased from 3.94% in 2014-15 to 6.12% in 2021-22.
- This growth reflects the government's commitment to enhancing public healthcare services, particularly due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
Decline in Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE):
- From 2014-15 to 2021-22, the share of Total Health Expenditure (THE) decreased from 62.6% to 39.4%.
- This reduction is attributed to government efforts to increase public health spending and improve access to healthcare.
- The government's share in Total Health Expenditure rose from 29% in 2014-15 to 48% in 2021-22, indicating a greater reliance on public health services.
Increased Share of Government Health Expenditure in Total Health Expenditure (THE):
- THE increased from 29% in 2014-15 to 48% in 2021-22.
- This rise indicates improved access to medical services and enhanced financial protection for individuals.
Total Health Expenditure:
- India's THE was estimated at Rs. 7,39,327 crores, representing 3.73% of the GDP, with per capita spending of Rs. 5,436 in 2020-21.
- In 2021-22, India's Total Health Expenditure rose to Rs. 9,04,461 crores, constituting 3.83% of GDP, with a per capita expenditure of Rs. 6,602.
Growth in Social Security Expenditure (SSE) on Health:
- There has been a positive trend in the country's health financing.
- The share of SSE in Total Health Expenditure rose from 5.7% in 2014-15 to 8.7% in 2021-22.
- This includes government-funded health insurance and social health insurance programs.
- Increased SSE directly reduces out-of-pocket payments for healthcare, helping to prevent financial hardship.
Distribution of Current Health Expenditure:
- In 2020-21, the Union Government's share of Current Health Expenditure (CHE) was Rs. 81,772 crores (12.33% of CHE).
- By 2021-22, the Union Government's CHE share increased to Rs. 1,25,854 crores (15.94%) while State contributions rose to Rs. 1,71,952 crores (21.77%).
What are National Health Accounts?
- NHA estimates are based on the globally recognized System of Health Accounts (SHA) framework established in 2011 by the World Health Organization.
- This framework allows for inter-country comparisons by providing a standardized method to track and report healthcare expenditures.
- The NHA details financial flows within India’s health system, showing how funds are collected and spent across the healthcare sector.
- India's NHA estimates follow the National Health Accounts Guidelines for India, 2016, with updates reflecting changes in the healthcare landscape.
- Methodology and estimates are regularly updated to align with the dynamic nature of the Indian health system and evolving policies.
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the objectives and key components of the National Health Mission (NHM) in India. Evaluate its effectiveness in improving healthcare access and outcomes in rural and underserved areas.
GS2/Governance
Effectiveness of Fast Track Special Courts
Why in news?
- India's Fast-Track Courts, established to accelerate the resolution of serious criminal cases, are currently under evaluation regarding their effectiveness. Despite an initial increase in their numbers, the count of operational courts has seen a decline.
What are FTSCs?
- FTSCs are judicial bodies created in India to speed up the trial process for serious crimes, especially sexual offenses, including rape and violations under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act (POCSO Act).
- They were established following the enactment of the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act in 2018, which introduced severe penalties, including the death penalty for rape offenders.
- The establishment of FTSCs was formalized in August 2019 through a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, aligning with directives from the Supreme Court of India.
Reasons for Establishing FTSCs:
- The establishment of FTSCs was a response to the alarming increase in sexual offenses and the lengthy trial durations in traditional courts, which resulted in significant delays in delivering justice to victims.
Extension of the FTSCs:
- The FTSCs Scheme, which initially launched for one year in 2019, has been extended by the Union Cabinet for another three years, from 2023 to 2026.
What are the Challenges Faced by FTSCs?
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Fast-track courts often operate from facilities that are poorly equipped, lacking essential resources such as modern technology and adequate space to manage case loads effectively.
- Judicial Overload: Despite their intended purpose, these courts frequently deal with overwhelming case volumes, resulting in delays that contradict their primary goal of providing expedited justice.
- Inconsistent Implementation: The establishment and functioning of fast-track courts can differ greatly across various states, leading to unequal access to justice and varying applications of legal standards.
- Quality of Judicial Personnel: The process of recruiting and training judges and support staff may not always meet the specialized demands of fast-track courts, negatively impacting the quality of judicial decisions.
- Limited Public Awareness: There is a widespread lack of understanding among the public regarding the operations and processes of fast-track courts, which can affect their effectiveness and accessibility.
Way Forward
- Infrastructure Development: Invest in upgrading and expanding court facilities to ensure fast-track courts are properly equipped to manage their caseloads.
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Implement specialized training initiatives for judges and support staff to enhance their skills, particularly for cases that involve sensitive issues.
- Streamlined Judicial Processes: Establish clear procedural guidelines and best practices to enhance efficiency while ensuring the integrity of the judicial process, allowing for quicker resolutions without compromising fairness.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Launch programs to educate the public on the roles, processes, and advantages of fast-track courts, fostering greater community engagement and trust in the judicial system.
- Legislative Reforms: Advocate for changes to existing laws to better support the operational needs of fast-track courts, ensuring that procedural frameworks align with their objectives.
Mains Question:
Q. Critically evaluate the role and effectiveness of Fast Track Special Courts (FTSCs) in India.
GS3/Defence & Security
DRDO's Deep Tech Efforts for Defence

Why in News?
- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is set to initiate a new program focused on advancing innovative military technologies. This initiative will support five deep-tech projects, with each receiving up to Rs 50 crore, to foster the indigenisation of defence products and enhance national security. This effort is backed by a Rs 1-lakh crore fund introduced in the Interim Budget 2024-2025, aimed at facilitating transformative research in the defence sector.
What are the Key Points About the Projects?
- Objective: DRDO seeks to minimize dependence on foreign imports for the systems, subsystems, and components necessary for the tri-services through indigenisation.
- Futuristic and Disruptive Tech: The organisation has earmarked three broad categories for project proposals: indigenisation, futuristic and disruptive technologies, and cutting-edge technology.
- Focus Areas: Key areas of research include quantum computing, blockchain, and artificial intelligence, all of which promise to significantly transform existing markets and societal norms.
- Global Context: Similar initiatives are being executed by state defence research organisations worldwide, such as the US DARPA, which serves as a model for DRDO's deep tech initiative.
- Investment Mechanism: Funding for these projects will be managed through DRDO's Technology Development Fund (TDF), which collaborates with private sectors, particularly MSMEs and startups, to create necessary military hardware and software.
What is the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)?
- About: DRDO operates as the R&D wing of the Ministry of Defence, aiming to equip India with advanced defence technologies.
- Achievements: Its efforts have led to significant indigenous developments, including the Agni and Prithvi missile series, the Light Combat Aircraft Tejas, and various radar and electronic warfare systems, thereby bolstering India's military capabilities.
- Formation: Established in 1958, DRDO resulted from merging the Technical Development Establishment of the Indian Army, the Directorate of Technical Development & Production, and the Defence Science Organisation.
- Laboratories: DRDO comprises a network of over 50 laboratories focused on diverse fields like aeronautics, armaments, electronics, combat vehicles, and engineering systems.
Technology Clusters of DRDO:
- Aeronautics: Concentrates on the design and development of aviation technologies, such as aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
- Armament and Combat Engineering: Responsible for developing weapon systems, artillery, and ammunition for defence forces.
- Missiles and Strategic Systems: Focuses on missile technology, including both ballistic and cruise missiles.
- Electronics and Communication Systems: Engages in creating radar systems and communication devices for military applications.
- Life Sciences: Develops technologies for human survival in extreme conditions, such as protective gear and life-support systems.
- Materials and Life Sciences: Engages in advanced materials, nanotechnology, and biotechnology for defence applications.
What are the Achievements of DRDO?
- Agni and Prithvi Missile Series: Successful development of ballistic missile systems, enhancing India's strategic capabilities significantly.
- Tejas Light Combat Aircraft (LCA): An indigenous multi-role fighter aircraft developed with collaboration from other agencies.
- Akash Missile System: A medium-range surface-to-air missile system providing air defence to the Indian Army and Air Force.
- BrahMos Missile: The world's fastest supersonic cruise missile developed in collaboration with Russia.
- Arjun Main Battle Tank (MBT): An indigenous battle tank designed for the Indian Army, featuring advanced firepower and protection systems.
- INSAS Rifle Series: An indigenous development of small arms for the Indian armed forces.
- Light Combat Helicopter (LCH): Developed to meet specific operational requirements.
- NETRA UAV: An indigenous unmanned aerial vehicle designed for surveillance and reconnaissance.
- Submarine Sonar Systems: Development of sonar and underwater communication systems for the Indian Navy's submarines.
What are the Challenges Faced by DRDO?
- Delays in Project Execution: Many projects have encountered significant delays affecting deployment and resulting in cost overruns.
- Technology Gaps and Dependence on Imports: Despite a robust production base, India still relies on imports for major systems and components, limiting its technological independence.
- Budgetary Constraints: While the budget for DRDO has increased, the growth is still modest compared to the government's strong push for modernization.
- Collaboration with Industry and Academia: Establishing efficient partnerships with private industries and academic institutions remains a challenge for DRDO.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Industry Collaboration: Enhancing partnerships with private sectors and MSMEs to accelerate innovation in defence technology.
- Focus on Time-bound Execution: Implementing stricter timelines and agile project management to reduce delays.
- Increased Investment in R&D: Allocating more resources for research and development to bridge technological gaps.
- Fostering Global Collaborations: Expanding partnerships with international defence research agencies to gain access to advanced technologies.
Mains Question:
Q. Analyze the significance of DRDO’s technology clusters and highlight notable achievements in recent years. How do these achievements contribute to India's strategic autonomy?
GS3/Science and Technology
The Nobel Prize in Physics 2024
Why in News?
- The Nobel Prize in Physics 2024 has been awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to John J. Hopfield and Geoffrey E. Hinton, two pioneers whose groundbreaking work laid the foundation for modern artificial neural networks (ANNs) and machine learning (ML). Their contributions have significantly influenced various fields, including physics, biology, finance, medicine, and applications in Artificial Intelligence (AI), such as OpenAI's ChatGPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer).
 What is the Contribution of John Hopfield?
What is the Contribution of John Hopfield?
Hopfield Network:
- John Hopfield is renowned for developing the Hopfield network, a type of recurrent neural network (RNN) that has been pivotal in the evolution of ANNs and AI.
- Introduced in the 1980s, the Hopfield network is capable of storing simple binary patterns (0s and 1s) across a network of artificial nodes (neurons).
- A notable feature is its associative memory, which enables the retrieval of complete information from incomplete or distorted inputs, akin to how the human brain recalls memories prompted by familiar stimuli.
- The network operates based on Hebbian learning, which is a neuropsychological concept where repeated interactions among neurons strengthen their connections.
- By leveraging principles from statistical physics, Hopfield made it possible for the network to execute pattern recognition and noise reduction by minimizing energy states, thereby advancing neural networks by emulating biological brain functions.
Impact:
- Hopfield’s model has been instrumental in addressing computational tasks, completing patterns, and enhancing image processing techniques.
What is the Contribution of Geoffrey Hinton?
Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs):
- Building on Hopfield's foundation, Hinton developed a learning algorithm for Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) in the 2000s, which paved the way for deep learning through the stacking of multiple neuron layers.
- RBMs learn from examples rather than explicit instructions, marking a revolutionary shift that enables machines to identify new patterns based on previously learned data similarities.
- These machines can recognize unfamiliar categories if they resemble learned patterns, showcasing their adaptability.
Applications:
- Hinton’s innovations have ushered in breakthroughs across numerous sectors, including healthcare diagnostics, financial modeling, and AI technologies like chatbots.
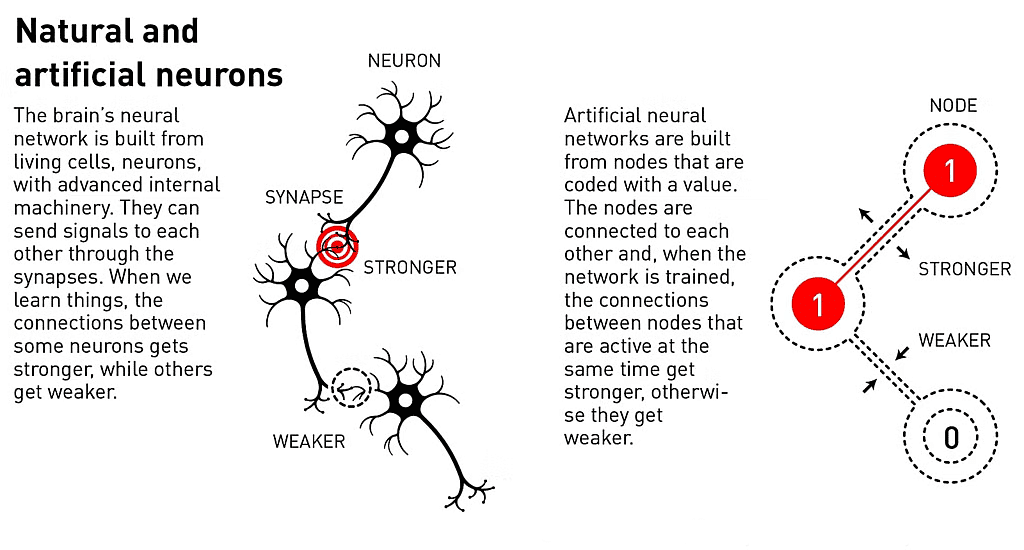
What are Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)?
About:
- ANNs draw inspiration from the brain's structure, where interconnected biological neurons collaborate to perform complex tasks.
- In ANNs, artificial neurons (nodes) collectively process information, facilitating data flow like synapses in the brain.
Common Architectures of ANNs:
- Trained on sequential or time-series data, RNNs develop machine learning models capable of making predictions based on sequential inputs.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs):
- Optimized for grid-like data such as images, CNNs utilize three-dimensional data for tasks like image classification and object recognition.
Feedforward Neural Networks:
- The simplest architecture, it allows information to flow in one direction from input to output with fully connected layers, distinguishing it from more complex networks.
Autoencoders:
- Designed for unsupervised learning, they compress input data to retain only essential features before reconstructing the original data.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs):
- GANs consist of two networks: a generator that creates fake data and a discriminator that differentiates between real and fake data.
- This adversarial training approach enhances model robustness, producing realistic, high-quality samples, and serves as a versatile tool for tasks like image synthesis and style transfer.
What is Machine Learning?
Definition:
- Machine learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that utilizes data and algorithms to enable computers to learn from experiences and enhance their accuracy over time.
Operating Mechanism:
- Decision Process: Algorithms classify or predict data based on input, which can be either labeled or unlabeled.
- Error Function: This function measures the accuracy of model predictions against known examples.
- Model Optimization Process: The model iteratively adjusts its weights to refine predictions until it achieves a satisfactory level of accuracy.
Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning vs. Neural Networks:
- Hierarchy: AI includes ML; ML encompasses deep learning, which relies on neural networks.
- Deep Learning: A specific subset of machine learning using deep neural networks capable of processing unstructured data without labeled datasets.
- Neural Networks: A particular type of machine learning model organized in layers (input, hidden, output) that replicate the functioning of the human brain.
- Complexity: As one progresses from AI to neural networks, the complexity and specificity of tasks increase, with deep learning and neural networks serving as specialized tools within the broader AI context.
Mains Question:
Q. Analyze the impact of neural networks and machine learning on modern technology. Provide examples of their applications in various sectors.
GS3/Health
Ultra-Processed and Fast Foods Making India Diabetic

Why in News?
- Recently, a study published in the International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition highlights the role of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) found in ultra-processed and fast foods in India's increasing diabetes cases. The clinical trial was the first of its kind in India and was funded by the Department of Biotechnology under the Ministry of Science and Technology.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
Role of AGEs:
- The high consumption of AGE-rich foods is a significant reason behind India's status as the "diabetic capital of the world," with over 101 million individuals affected.
- AGEs are harmful substances formed when sugars react with proteins or fats during high-temperature cooking methods like frying or roasting.
- These compounds contribute to oxidative stress, which is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, leading to inflammation and cellular damage.
Susceptibility to Diabetes:
- Ultra-processed foods (UPFs) can cause quick spikes in blood sugar levels and contribute to insulin resistance over time.
- These foods are typically low in fiber and high in calories, which can lead to weight gain and obesity, both of which are significant risk factors for diabetes.
Impact on Insulin Sensitivity:
- Dietary interventions that focus on low-AGE foods, primarily those cooked by boiling or steaming, have shown to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation compared to high-AGE diets.
- Reducing AGEs in the diet could be an effective strategy to lower diabetes risk, especially for individuals at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Why are Ultra-Processed Foods Harmful to Health?
Saturated Fats, Salt, and Sugar:
- Ultra-processed foods are usually high in saturated fats, salt, and sugar, contributing to various health issues such as heart disease and high blood pressure.
Negative Effects of Additives:
- These products often contain additives like preservatives, artificial colors, sweeteners, and emulsifiers, which may negatively impact health and contribute to inflammation, gut imbalances, and metabolic disorders.
Alters Nutrient Absorption:
- The processing of food can significantly change how the body processes it. For instance, whole nuts allow for less fat absorption compared to processed nuts from which oils are released, altering the nutrient profile and caloric intake.
Effects on Gut Health:
- High levels of sugar, unhealthy fats, and additives found in ultra-processed foods can disrupt the gut microbiome, crucial for digestion and immunity.
Overall Lifestyle Impact:
- Individuals who consume a large amount of ultra-processed foods often engage in other unhealthy behaviors, such as lack of physical activity and irregular eating patterns.
What are Types of Food Processing?
About:
- Food processing involves transforming raw agricultural products like grains, meats, vegetables, and fruits into more valuable and convenient food products with minimal waste.
Types of Food Processing:
- Minimally Processed: This includes fruits, vegetables, milk, fish, pulses, eggs, nuts, and seeds with no added ingredients and minimal alterations from their natural state.
- Processed Ingredients: These are added to other foods rather than eaten alone, such as salt, sugar, and oils.
- Processed Foods: These are made by combining minimally processed and processed ingredients, like jam, pickles, and cheese.
- Ultra-Processed Foods: These are industrially manufactured products that often contain ingredients not commonly found in home kitchens, such as additives like preservatives, colorings, and flavorings. They are typically high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and salt while being low in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Examples include sugary drinks, packaged snacks, instant noodles, and ready-to-eat meals.
Why is there an Increase in Consumption of Ultra-Processed Foods in India?
Urbanisation:
- Fast-paced lifestyles in urban areas often require quick and convenient food options, making ultra-processed foods appealing due to their easy availability and minimal preparation time.
Cultural Shifts in Dietary Preferences:
- There has been a significant cultural shift towards Western-style diets, characterized by increased consumption of fast food, sugary snacks, and ready-to-eat meals.
Rising Number of Working Women:
- Ultra-processed foods are often seen as time-saving solutions for busy individuals balancing work and home life.
Fresh Food Availability:
- In urban settings, the limited availability of fresh food options makes ultra-processed foods a convenient alternative for those struggling to access healthier choices.
Aggressive Marketing and Availability:
- Ultra-processed foods are heavily promoted, often with misleading health claims that attract consumers. Celebrity endorsements and targeted advertising, especially towards children, further enhance their appeal.
Status Symbol:
- There is a growing perception that consuming processed and packaged foods signifies a higher social status.
What are Recommendations to Curb Consumption of UPF?
Low-AGE Diet:
- It is advisable to adopt a diet low in AGEs, which includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products. Reducing bakery and sugary foods while incorporating non-starchy vegetables into meals is recommended.
Cooking Methods:
- Using low-temperature cooking methods, such as boiling or steaming, is encouraged over high-temperature cooking methods like frying to reduce AGEs in foods.
Clear Definition of HFSS Foods:
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) should define foods that are high in Fat, Sugar, and Salt (HFSS) to help identify harmful products and guide regulations regarding their sale and consumption.
Nutrient-Based Taxation:
- Implementing a higher tax on products high in fat, sugar, and salt would incentivize manufacturers to reformulate their products and make healthier options more affordable.
Revising PLI Scheme:
- Updating the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme to support nutrition-linked production can give healthier food products a competitive market advantage.
Restricting Promotions:
- Marketing regulations should be tightened to limit the promotion of HFSS foods, especially in media targeting children.
Strengthening Policies and Programs:
- Existing initiatives like Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 need expansion to specifically address the dual challenges of inadequate nutrition and diet-related diseases.
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the impact of ultra-processed foods (UPFs) on public health. What measures can be taken to discourage their consumption and promote healthier dietary practices?
GS2/Governance
Medical Ethics and Consumer Rights in India
Why in news?
- Recently, the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC) imposed a fine of Rs 35 lakh on Johnson & Johnson for providing defective medical devices. This action was taken following a consumer complaint from an individual who experienced complications due to a faulty hip replacement. This incident underscores the urgent necessity for strict adherence to medical ethics and established protocols in healthcare.
How Ethics Guide Medical Practices?
About Medical Ethics: Medical ethics is concerned with the appropriate conduct within the field of healthcare. It addresses the moral distinctions between right and wrong as perceived in various cultures and is focused on the responsibilities of healthcare professionals towards patients.
Principles of Medical Ethics:
- Respect for Autonomy: This principle acknowledges the patient's right to make informed decisions about their treatment, which includes obtaining proper informed consent.
- Beneficence: Healthcare providers must prioritize the health and well-being of patients throughout all medical procedures, acting in their best interests.
- Non-Maleficence: It is essential for medical practitioners and suppliers to avoid causing harm to patients and to provide necessary medical care without negligence.
- Justice: This principle emphasizes the need for equitable treatment of all patients, irrespective of their background, including religion, nationality, race, or social status.
Hippocratic Oath: The Hippocratic Oath serves as a crucial commitment for newly graduated medical professionals. It is recited during graduation ceremonies to bind them to a code of ethics, which is rooted in the Indian Medical Council (Professional Conduct, Etiquette, and Ethics) Regulations 2002. This oath emphasizes serving humanity, adhering to medical laws, respecting life, prioritizing patient welfare, maintaining confidentiality, expressing gratitude to educators, and fostering mutual respect among colleagues.
What is the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC)?
About: The NCDRC is a quasi-judicial body established in 1988 under the Consumer Protection Act (CPA), 1986. Its primary goal is to provide a cost-effective, prompt, and summary resolution of consumer disputes.
Provisions of the CPA, 1986:
- Jurisdiction: Section 21 of the CPA grants NCDRC the authority to handle complaints exceeding Rs 2 crore. It also has appellate and revisional jurisdiction over orders from State Commissions and District Forums.
- Appellate Authority: Consumers dissatisfied with decisions from District Forums can appeal to the State Commission, and if still unsatisfied, may escalate the issue to the NCDRC. Any individual aggrieved by the NCDRC's decision can appeal to the Supreme Court of India within 30 days, as per Section 23 of the Act.
- Scope of Coverage: The Act covers both 'goods' and 'services.'
- Consumer Forums:The Consumer Protection Act (CPA), 2019 allows for complaints to be filed at District, State, and National levels based on the claim's value:
- District Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (DCDRC): For claims up to Rs 50 lakh.
- State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (SCDRC): For claims between Rs 50 lakh and Rs 2 crore.
- National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC): For claims above Rs 2 crore.
What are the Issues of Medical Ethics in India?
- Informed Consent: Many patients do not receive adequate informed consent, especially in clinical trials involving vulnerable groups. An example is the controversies surrounding Covid-19 vaccine trials in various locations.
- Patient Privacy: There is a notable lack of effective measures to protect patient data and ensure confidentiality. For instance, a significant data breach in 2023 exposed the personal health information of millions from the ESIC database, including sensitive details like Aadhaar numbers and medical histories.
- Conflicts of Interest: Medical professionals sometimes have financial interests in the treatments they recommend. A case in 2023 involved a well-known cardiologist in Delhi who had financial ties to a stent manufacturing firm, receiving substantial compensation for consulting and holding equity stakes.
- Doctor-Patient Trust: The commercialization of healthcare and a lack of transparency have eroded trust between doctors and patients. An example includes government-employed doctors who engage in private practice and charge high fees.
- Regulatory Oversight: Weak enforcement of ethical guidelines leads to malpractice in clinical trials and patient care.
Way Forward
- Cultivating Ethical Awareness in Healthcare: Implementing comprehensive training programs and workshops to educate healthcare professionals on ethical principles and their practical applications is essential. Encouraging a culture of open dialogue and transparency within healthcare institutions can facilitate discussions on ethical dilemmas and share best practices.
- Structured Communication Protocols: Adopting structured communication techniques like the SBAR (Situation-Background-Assessment-Recommendation) can enhance clarity and minimize errors. Ensuring informed consent requires detailed explanations of procedures, risks, benefits, alternatives, and verification of patient understanding.
- Strengthening Redressal Mechanisms: The government can improve consumer complaint resolutions by leveraging existing frameworks for Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) and Online Dispute Resolution (ODR) through a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model.
- Creating a National Consumer Lok Adalat Helpline: A tech-enabled helpline can streamline communication between complainants, companies, and legal authorities, leading to quicker resolutions.
Mains Question:
Q. What is medical ethics? Discuss its significance, particularly in light of the deteriorating patient-physician relationship in India.
GS3/Environment
Floriculture in India

Why in news?
- The Jujumara area in Odisha's Sambalpur district has established one of the earliest Farmer Producer Organizations (FPO) in the state that focuses solely on floriculture. This initiative marks a shift from traditional paddy farming, supported by the National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI). Local farmers are now embracing flower cultivation, leading to significant economic benefits.
How is Floriculture Transforming Jujumara's Economy?
- Diversification of Income Sources: Farmers are moving away from paddy farming towards flower cultivation, reducing reliance on a single crop and improving income stability.
- Economic Benefits: Earnings from flower farming can surpass Rs 1 lakh per acre, compared to approximately Rs 40,000 per acre from traditional paddy, greatly enhancing farmers' incomes.
- Market Adaptation: Farmers utilize platforms like WhatsApp groups for market updates, aiding in informed production and sales decisions.
- Sustainable Practices: The incorporation of beekeeping with floriculture fosters biodiversity and offers additional income for farmers.
What is Floriculture?
- About: Floriculture is the cultivation of flowering and ornamental plants for various uses, including direct sales, cosmetics, perfumes, and pharmaceutical applications. It encompasses seed and plant material production through methods such as cutting, grafting, and budding.
- Market of Floriculture in India: Recognized as a "sunrise industry" by the Indian government, floriculture covered 297 thousand hectares in 2023-24 (2nd Advance Estimate). India exported around 20,000 metric tonnes of floriculture products valued at Rs 717.83 crores in 2023-24, with major markets including the USA, Netherlands, UAE, UK, Canada, and Malaysia. The sector is projected to grow to USD 5.9 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 7.4% from 2021-2030.
- Varieties: The floriculture industry in India includes cut flowers, pot plants, bulbs, tubers, and dried flowers. Key crops in the international cut flower market include Roses, Carnations, and Chrysanthemums. Notably, some flowers are cultivated in greenhouses, while others thrive in open fields.
- Leading Floriculture Regions: Significant floriculture centers include Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, and Maharashtra.
What are the Key Challenges in India's Floriculture Industry?
- Low Knowledge Base: As floriculture is relatively new, many farmers lack understanding of scientific and commercial practices, resulting in inefficiencies.
- Small Land Holdings: Many floriculture farmers operate on small plots, limiting their ability to invest in modern cultivation techniques.
- Unorganised Marketing: The marketing system is fragmented, lacking coordinated platforms for auctions and storage, making it hard for farmers to secure fair prices.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Poor post-harvest management and insufficient cold storage facilities lead to quality losses, especially for domestically sold flowers.
- Biotic and Abiotic Stresses: Open-field production subjects crops to various stresses, compromising their suitability for high-quality export markets.
- High Initial Costs: Initial investments for commercial floriculture are substantial, and farmers face challenges accessing affordable financing. More initiatives like the National Horticulture Board's soft loan program are necessary.
- Export Barriers: High air freight costs and limited cargo capacity hinder the competitiveness of Indian floriculture products in global markets.
What are India's Initiatives for Floriculture?
- APEDA (Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority): Provides support to floriculture exporters through cold storage and freight subsidies.
- CSIR Floriculture Mission: A nationwide initiative implemented in 22 states aimed at increasing farmers' income and fostering entrepreneurship through high-value floriculture using CSIR technologies.
- FDI in Floriculture: Allows 100% foreign direct investment under the automatic route, simplifying the investment process for foreign entities.
- Integrated Development of Commercial Floriculture Scheme: Offers access to quality planting materials, promotes off-season cultivation, and improves post-harvest management.
Way Forward
- Essential Service and Market Modernization: Classifying flowers as essential services, like fruits and vegetables, ensures uninterrupted supply during crises. Modernizing floriculture markets with solar-powered air-cooled pushcarts and improved packaging is essential.
- Micro-Irrigation and Mulching: Expanding the "Per Drop More Crop" initiative to include floriculture and promoting mulching techniques can enhance water efficiency and reduce labor.
- Skilling: Training tribal women and unemployed youth in dry flower production under initiatives like "Skilling India" and "Standup India" is vital.
- Support for Quality Planting Materials: Promoting certified nurseries and tissue culture labs ensures the availability of virus-free planting stock, enhancing biosecurity standards.
- Flori-Malls and Value Addition: Establishing integrated "Flori-Malls" with cold chains and processing units can help reduce waste and add value by transforming excess flowers into products like dyes and gulkand.
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the significance of floriculture and its role in transforming the rural economy.
|
164 videos|800 docs|1160 tests
|
















