UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Gist of Rajya Sabha TV / RSTV (now Sansad TV) > PM Gati Shakti: Transforming Infra & Connectivity
PM Gati Shakti: Transforming Infra & Connectivity | Gist of Rajya Sabha TV / RSTV (now Sansad TV) - UPSC PDF Download
PM Gati Shakti: Transforming Infra & Connectivity
Why in News?
- The PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan recently celebrated its third anniversary, highlighting the progress made in infrastructure and the renewed emphasis on India's logistics sector.
- This initiative has had a significant impact on India's infrastructure and logistics by promoting multimodal connectivity across various ministries and states.
Integrated Connectivity: PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan
- Launch and Purpose: The PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan was introduced in 2021 as a digital platform aimed at integrating various ministries, such as Railways and Roadways, for coordinated planning and execution of infrastructure projects.
- Focus Areas: The initiative emphasizes improving connectivity for people, goods, and services across different transport modes, enhancing last-mile connectivity, and reducing travel time.
Key Integrated Schemes:
- Bharatmala:. national highway development project to improve road infrastructure.
- Sagarmala: Focused on enhancing port infrastructure and coastal development.
- Inland Waterways: Promoting efficient movement of goods via rivers.
- UDAN:. regional air connectivity scheme to boost air travel in underserved regions.
Central Ministries and State Participation:
- The initiative involves 44 Central Ministries and 36 States and Union Territories (UTs) for coordinated planning and execution.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) have been established for key infrastructure and social sector ministries to ensure data accuracy and coordination.
Notable Achievements:
- Infrastructure Projects: Assessments of 208 major infrastructure projects worth Rs 15.39 lakh crore across various ministries have been conducted.
- Road Transport: The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) planned over 8,891 kilometers of roads using the Gati Shakti platform.
- Railways: The Ministry of Railways planned more than 27,000 kilometers of railway lines under the National Master Plan, with a significant increase in the completion of Final Location Surveys (FLS).
- Petroleum and Gas: The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas (MoPNG) streamlined the Detail Route Survey (DRS) process, drastically reducing report generation time.
- Renewable Energy:. 13 GW renewable energy project linking Leh (Ladakh) to Kaithal (Haryana) was optimally aligned for inter-state transmission, enhancing green energy capacity.
- Disaster Management: Goa utilized the Gati Shakti platform for developing a disaster management plan for flood-prone areas.
- Education: The Department of School Education and Literacy linked PM Shri Schools with local industries for district-specific skill training through the National Master Plan portal.
- Healthcare: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare mapped internet shadow areas to identify locations for new healthcare facilities.
- Skill Development: The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship identified locations for new training institutes near economic clusters.
- Rural Development: Integration of Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) and Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G) schemes for better asset planning.
- Tribal Affairs: Utilization of the PM JanMan portal to identify infrastructure gaps for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTG).
District Master Plan (DMP) Portal:
- The initiative is being extended to the district level through the development of a District Master Plan (DMP) portal.
- The portal will assist district authorities in collaborative infrastructure planning, gap identification, and scheme implementation.
- A beta version of the portal has been launched for 28 aspirational districts, with user accounts provided to these districts in September 2024.
What are Other Key Initiatives Taken to Boost the Logistics Sector?
- National Logistics Policy (NLP) 2022: The NLP, introduced in September 2022, aims to overhaul India's logistics framework by reducing costs, boosting infrastructure, and improving the country's standing in the World Bank's Logistics Performance Index (LPI).
- Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP): ULIP is a digital initiative that consolidates 33 logistics systems from 10 ministries to ensure smooth data sharing. It supports end-to-end cargo tracking and enhances transparency in logistics processes. With over 930 private companies registered, ULIP is actively improving coordination through various applications.
- Logistics Data Bank (LDB): LDB uses RFID technology to monitor the real-time movement of containerized cargo, offering visibility into the transport of EXIM goods across ports, railways, and highways. This system boosts transparency and allows stakeholders to oversee and optimize their supply chains effectively.
- Multi-Modal Logistics Parks (MMLPs): The government is establishing MMLPs to enable smooth transfers between different transportation modes. These parks will function as central hubs for freight movement, offering storage, warehousing, and value-added services all in one place.
- Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFC): India is building DFCs to improve the speed and efficiency of goods transport. The Western and Eastern DFCs aim to relieve congestion in existing rail networks and provide quicker, more reliable freight services, especially for heavy industries.
- LEADS (Logistics Ease Across Different States): The LEADS survey evaluates states based on the effectiveness of their logistics systems, promoting healthy competition among states to enhance infrastructure and services, thereby boosting overall logistics performance.
- Gati Shakti Sanchar Portal: This portal was introduced to expedite Right of Way (RoW) approvals necessary for telecom infrastructure development. It has sped up the installation of mobile towers and fiber networks, which are vital for advancing digital logistics solutions.
- 5G Rollout: The swift implementation of 5G services across India, with over 13 crore subscribers in its inaugural year, will improve real-time tracking, autonomous vehicle usage, and overall logistics efficiency. The government has approved more than 41,000 mobile towers for rural and remote areas to enhance digital connectivity.
What are Major Issues Related to India's Logistics Sector?
- India is currently facing significant challenges in its logistics sector, which are impacting the overall economy and the efficiency of goods transportation.
- The logistics costs in India are considerably higher compared to global standards, making Indian products less competitive in the international market.
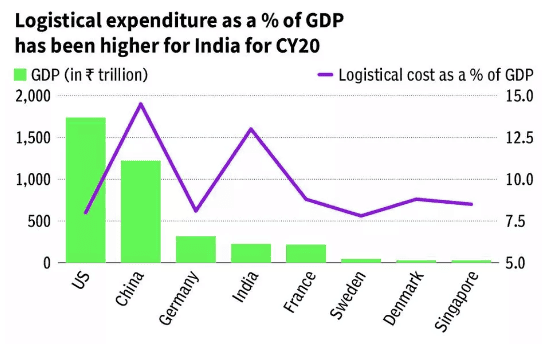
High Logistics Costs:
- Logistics costs in India are between 13-14% of GDP, while countries like Japan and Germany spend around 8-10%.
- This higher cost impacts the competitiveness of Indian products globally.
Fragmented and Unorganized Market:
- Over 90% of the logistics sector in India is unorganized, with many small players operating independently.
- This fragmentation hinders the integration of advanced technologies and standardization of services.
- There is a lack of uniformity in regulations and coordination among different modes of transport.
Inadequate Infrastructure:
- Indian logistics infrastructure, although improving, still faces bottlenecks such as poor road conditions, outdated rail networks, and congested ports.
- For instance, the average turnaround time for ships at major Indian ports, while better than before, still does not meet global standards.
Poor Multimodal Connectivity:
- There is a lack of seamless integration among different transport modes: roadways, railways, airways, and waterways.
- This inefficiency forces a heavy reliance on roadways, which are susceptible to delays and higher costs, while railways and waterways remain underused.
Insufficient Warehousing and Cold Chain Facilities:
- There is a critical shortage of modern warehousing facilities in India, especially in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
- Additionally, the cold chain infrastructure is inadequate, affecting the storage and transportation of perishable goods like food and pharmaceuticals, leading to increased wastage and costs.
Last-Mile Delivery Challenges:
- Last-mile delivery costs are a significant part of the total delivery cost, especially in urban areas where traffic congestion, limited parking, and poor addressing systems cause delays.
- This inefficiency directly affects delivery times and costs for businesses, particularly in e-commerce.
Regulatory Complexities:
- The logistics sector is hindered by multiple regulatory frameworks and the need for approvals at both central and state levels.
- Delays in clearances for large-scale logistics projects impede infrastructure development.
- A lack of coordination among different government ministries further delays project execution.
Skill Gaps and Workforce Shortages:
- Despite being a fast-growing employment sector, logistics in India faces a shortage of skilled manpower in areas like supply chain management, warehousing operations, and technological proficiency.
- Although there are initiatives to address these skill gaps, progress is slow.
Environmental Impact:
- The logistics sector is a major contributor to carbon emissions in India, primarily due to the dominance of road transportation for freight movement.
- While India aims to reduce carbon intensity, transitioning to greener logistics practices poses a challenge for the industry.
Way Forward
Focus on Multimodal Transport Solutions:
- Emphasize the development of multimodal transportation that integrates road, rail, air, and water networks.
- Invest in Dedicated Freight Corridors, inland waterways, and improve port infrastructure.
Enhance Technological Integration:
- Adopt cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain to improve supply chain visibility, streamline operations, and reduce costs.
Streamline Regulatory Frameworks:
- Introduce single-window clearances for logistics projects and harmonize rules across states.
- Streamlining regulatory processes will lead to faster infrastructure development and lower logistics costs.
Improving Cold Chain Infrastructure:
- Promote investments in cold storage facilities and refrigerated transport to ensure timely and safe delivery of perishables.
Increase Private Sector Participation:
- Encourage public-private partnerships (PPPs) in areas such as warehousing, cold storage, and transportation infrastructure.
Skill Development and Workforce Training:
- Invest in skill development programs focusing on supply chain management, warehousing operations, and digital logistics.
- Strengthen vocational training and create certification programs to bridge skill gaps.
Environmental Sustainability:
- Embrace greener practices like using electric vehicles (EVs) for last-mile delivery, developing green corridors for freight transport, and incentivizing clean energy adoption in warehouses and logistics hubs.
The document PM Gati Shakti: Transforming Infra & Connectivity | Gist of Rajya Sabha TV / RSTV (now Sansad TV) - UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Gist of Rajya Sabha TV / RSTV (now Sansad TV).
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
FAQs on PM Gati Shakti: Transforming Infra & Connectivity - Gist of Rajya Sabha TV / RSTV (now Sansad TV) - UPSC
| 1. What is PM Gati Shakti and what are its main objectives? |  |
Ans. PM Gati Shakti is a national master plan launched by the Government of India to enhance infrastructure and connectivity across the country. Its main objectives include reducing logistics costs, promoting integrated planning for infrastructure development, improving the efficiency of supply chains, and ensuring timely completion of projects. The initiative aims to facilitate holistic and coordinated development of various sectors like transportation, energy, and urban infrastructure.
| 2. How does PM Gati Shakti aim to improve logistics in India? |  |
Ans. PM Gati Shakti aims to improve logistics in India by creating a digital platform that provides real-time data on various infrastructure projects. It promotes the use of technology for better project planning and execution, ensuring that all stakeholders, including government agencies and private players, are aligned. This integrated approach is expected to streamline processes, reduce delays, and ultimately lower logistics costs, making Indian goods more competitive in global markets.
| 3. What role does technology play in the implementation of PM Gati Shakti? |  |
Ans. Technology plays a crucial role in the implementation of PM Gati Shakti. The initiative utilizes Geographic Information System (GIS) and other digital tools to create a comprehensive database of existing infrastructure and ongoing projects. This facilitates better planning and coordination among various ministries and departments. Additionally, the use of advanced analytics helps in monitoring progress and making informed decisions, ensuring that projects are completed on time and within budget.
| 4. What are the expected benefits of PM Gati Shakti for the Indian economy? |  |
Ans. The expected benefits of PM Gati Shakti for the Indian economy include enhanced connectivity which can lead to improved trade and investment, increased operational efficiency of logistics, and reduced overall costs for businesses. By fostering a more integrated infrastructure environment, the initiative is anticipated to stimulate economic growth, create jobs, and support the Make in India initiative by making it easier for manufacturers to access markets.
| 5. How does PM Gati Shakti align with India's broader developmental goals? |  |
Ans. PM Gati Shakti aligns with India's broader developmental goals by focusing on sustainable and inclusive growth. It supports the government’s vision of creating a robust infrastructure backbone that can drive economic development while also addressing regional disparities. By enhancing connectivity in remote and less developed areas, the initiative aims to promote balanced regional development, support rural livelihoods, and ensure that the benefits of economic growth reach all sections of society.
Related Searches





















