UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 12th November 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
What is Gluten?
Source:Tribune India

Why in News?
Gluten is widely recognized for the allergic responses it can trigger in certain individuals.
About Gluten:
- Gluten is a protein that occurs naturally in the wheat plant and other grains.
- It is particularly present in cereal grains such as barley, wheat, and rye.
- When gluten-containing grains are mixed with water and kneaded, they form an elastic mass.
- The two primary proteins that contribute to gluten formation are gliadins and glutenins.
- Under microscopic examination, gluten appears as an elastic network of protein molecules.
- Gluten can be extracted, concentrated, and added to various foods to enhance protein content, texture, and flavor.
- It serves as a binding agent in processed foods, helping them maintain their shape.
- Furthermore, gluten allows dough to rise and contributes to its characteristic chewy texture.
- The properties of gliadins and glutenins make them valuable in the food industry.
Issues Associated with Gluten:
- An enzyme known as protease aids in protein digestion but is ineffective in breaking down gluten.
- When gluten reaches the small intestine undigested, it can lead to gastrointestinal issues.
Coeliac Disease:
- This condition is marked by a severe allergic reaction occurring in the small intestine.
- In response to gluten, the immune system produces a significant number of antibodies that attack the body's own proteins.
- Approximately 2% of the general population is affected by this disease.
GS3/Environment
Dicliptera Polymorpha
Source: DST

Why in News?
Recently, researchers discovered a new species of the genus Dicliptera in the Northern Western Ghats of India and named it as Dicliptera polymorpha.
About
- Dicliptera Polymorpha: This species stands out due to its unique characteristics, including its ability to withstand fire and its unusual dual-blooming cycle.
- Fire-Resilient Nature: It has a pyrophytic habit, meaning it has adapted to thrive in environments that experience frequent fires. This characteristic is essential for its survival in the harsh climatic conditions of its habitat.
- Dual-Blooming Pattern: In addition to its normal flowering period after the monsoon season, Dicliptera polymorpha has a second flowering phase that occurs due to grassland fires typically set by locals.
- Floral Characteristics: The species features unique inflorescence units known as cymules, which develop into spicate inflorescences. It is the only Indian species with this specific inflorescence structure, with its closest relatives found in Africa.
- Habitat and Adaptation: It is commonly found on slopes in open grasslands of the Northern Western Ghats. This area is subject to extreme weather conditions, including summer droughts and frequent human-induced fires. Despite these challenges, Dicliptera polymorpha has evolved to bloom twice a year.
- Flowering Phases: The first blooming phase occurs from early November to March or April after the monsoon, while the second flowering phase happens in May and June, triggered by the occurrence of fires.
- Woody Rootstocks: During the second flowering phase, the species develops dwarf flowering shoots from its woody rootstocks, resulting in a more abundant but shorter blooming period.
- Ecological Significance: The species' unique adaptations to fire and its limited distribution in the Western Ghats emphasize the importance of careful management of grassland ecosystems to ensure the survival of such specialized flora.
GS3/Health
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
Source:Nature
Why in news?
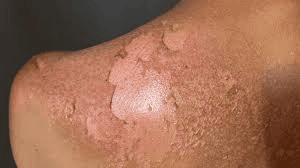
Researchers from Australia and Germany have achieved a groundbreaking milestone by curing patients diagnosed with Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN), a severe and potentially fatal skin condition.
About Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
- TEN, often referred to as Lyell's syndrome, is an uncommon but life-threatening skin disorder.
- It represents the most severe variant of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS).
- Both TEN and SJS are triggered by adverse reactions to medications, commonly antibiotics or anticonvulsants.
- Individuals with compromised immune systems are at a heightened risk of developing either SJS or TEN.
Symptoms of TEN
- The condition typically begins with painful, red patches on the skin that can spread rapidly.
- Skin can begin to peel off without forming blisters.
- Patients may experience raw patches of skin and discomfort.
- Fever is often present alongside the skin symptoms.
- The condition can extend to sensitive areas such as the eyes, mouth, throat, and genitals, including the urethra and anus.
Effects and Complications
- In TEN, significant areas of the skin, encompassing at least 30% of the body, can blister and peel, affecting mucous membranes like those in the mouth, eyes, and genitals.
- The skin serves as a crucial protective barrier; extensive damage can lead to severe fluid loss and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Serious complications may arise, including pneumonia, overwhelming bacterial infections (sepsis), shock, multiple organ failure, and even death.
- The mortality rate associated with TEN is approximately 30 percent.
Treatment for TEN
- TEN necessitates immediate medical intervention in a hospital setting.
- If a medication is identified as the cause of the skin reaction, it is promptly discontinued.
- While the skin is healing, supportive care is crucial, focusing on pain management, wound care, and ensuring adequate hydration.
GS3/Economy
'EV as a Service' Programme
Source:Statesman

Why in News?
Union Minister of Power and Housing & Urban Affairs launched the 'EV as a Service' programme of Convergence Energy Services Limited (CESL) at Major Dhyan Chand National Stadium.
About 'EV as a Service' Programme:
- The programme is designed to enhance electric mobility within government offices.
- It aims to introduce 5,000 electric cars (E-Cars) into various government departments over the next two years.
- This initiative is spearheaded by Convergence Energy Services Limited (CESL), which operates as a subsidiary of Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL).
- Utilizing a flexible procurement model, the programme permits the selection of different makes and models of E-Cars, enabling government offices to choose vehicles that best fit their operational needs.
- CESL has already deployed nearly 2,000 E-Cars across India and is working on facilitating the deployment of approximately 17,000 E-Buses.
- This initiative not only supports the government's vision for environmental sustainability but also aligns with India's ambitious target of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070.
What is CESL?
- CESL is a newly established subsidiary of the state-owned Energy Efficiency Services Limited, which is a joint venture involving public sector companies under the Ministry of Power, Government of India.
- It builds upon the experience of decentralized solar development in underserved rural communities in India.
- Over time, CESL aims to leverage battery energy storage to provide renewable energy solutions for agricultural pumps, street lighting, domestic lighting, and cooking appliances in rural areas.
- Additionally, CESL will focus on promoting battery-powered electric mobility and developing the necessary infrastructure while creating business models to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles in India.
GS3/Environment
Sirpur Lake
Source:The Print

Why in News?
Following directives from the National Green Tribunal, a team from the Indore Municipal Corporation, along with police, successfully removed encroachments and 30 stalls from the catchment area of Sirpur Lake recently.
About Sirpur Lake:
- Sirpur Lake is a human-made wetland located in Indore, Madhya Pradesh.
- This 670-acre lake is over 130 years old and was constructed by Maharaja Shivajirao Holkar to supply water to the city of Indore.
- The Indore City Gazette of 1908 includes numerous references to Sirpur Lake, which has historically been utilized for both water supply and recreational activities.
- It is characterized as a shallow, alkaline, nutrient-rich lake that experiences flooding during the monsoon season.
- Sirpur Lake supports a diverse ecosystem, including extensive wetlands, shrub forests, grasslands, tall trees, and varying water depths.
Fauna
- Sirpur Lake is home to 189 bird species across 55 families.
- It is one of the few remaining sites within city limits where water birds can be observed, making it a prime location for birdwatching.
- Commonly sighted species include the painted stork, bar-headed goose, Eurasian wigeon, and multiple egrets, herons, and kingfishers.
- The lake also hosts a variety of reptiles, insects, butterflies, and fish species.
- On January 7, 2022, Sirpur Lake was designated as a Ramsar site under the Ramsar Convention, highlighting its ecological significance.
GS3/Economy
Germany's Economic Struggles - Unraveling the Challenges Facing Europe’s Former Powerhouse
Source:Nature

Why in News?
German Chancellor Olaf Scholz stated he’s open to facing a confidence vote before Christmas after his coalition collapsed over economic management issues, with the vote initially planned for January 15. Germany’s economy grew slightly (0.2%) in Q3 after a contraction, reflecting a broader crisis affecting key industries, including Volkswagen. For the first time in its 87-year history, Volkswagen, Europe’s largest employer, is considering closing three of its 15 factories in Germany due to financial difficulties.
- Volkswagen, Germany’s largest carmaker and the world’s second-largest, is facing severe troubles that threaten the entire German automotive sector, the nation’s largest industry.
- The company plans to shut down up to three factories and lay off tens of thousands of workers due to declining sales and rising competition, particularly from China.
- This move reflects broader issues within Germany’s industrial landscape, with high energy costs, shrinking markets, and geopolitical tensions putting over 20% of the country’s industrial output at risk by 2030.
- The carmaker’s deepening troubles are set to have a domino effect through the entire German automotive industry.
- It is the country’s single-largest sector accounting for 5% of GDP and employing almost 800,000 people — over a third of whom work for Volkswagen.
- Germany was the only G7 economy to shrink last year (2023) and is set to be the group’s slowest-growing economy again this year.
- According to the IMF, its GDP per head shrank 1 percent between 2019 and 2023.
Reasons behind this crisis
- Volkswagen, a crucial pillar of the German economy, is struggling due to multiple factors including:
- A late shift to electric vehicles, leaving the industry lagging in the current energy landscape.
- Heavy reliance on internal combustion engines instead of transitioning to electric alternatives.
- Germany’s economic challenges are compounded by:
- Dependence on Russian gas, with deteriorating terms of trade following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, resulting in soaring natural gas prices.
- Reliance on authoritarian states like Russia and China, coupled with a failure to embrace the digital economy, which has hindered global competitiveness.
- The post-pandemic rebalancing of global demand shifting from manufactured goods to services, which has negatively impacted Germany’s economy.
Structural issues
- The recent crisis underscores deeper structural challenges within the German economy.
- Germany, once a model of high-tech manufacturing, is now viewed as uncompetitive with a potentially reduced output outlook.
- High levels of debt and deficits, driven by the government’s need to accommodate a diverse coalition, have raised concerns within the EU.
- Over-regulation and bureaucratic obstacles are further hindering smaller and mid-sized firms in the country.
GS3/Economy
Reclassifying FPIs as FDI
Source:Indian Express
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently announced new guidelines for Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) who wish to categorize their investments in Indian companies as Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) if their shareholding surpasses certain thresholds.
- Under these guidelines, FPIs must obtain necessary approvals from the government and the companies they invest in to ensure compliance with FDI regulations.
What is Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI)?
- FPI involves investments made by foreign entities in a country's financial markets or assets.
- These investments are typically short-term in nature.
- FPIs do not confer direct ownership rights in a company's assets.
- Common forms of FPI include securities like stocks and financial assets such as bonds or mutual funds.
- FPIs are generally more liquid, meaning they can be easily bought and sold depending on market conditions.
- In India, FPIs play a crucial role in providing investment capital, aiding the growth of the financial markets.
What is Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)?
- FDI refers to an investment made by an entity in one country into business interests in another country, involving a degree of control over the business operations.
- Typically, FDIs are made in economically open countries with a skilled workforce and favorable growth prospects.
- FDIs often include activities such as management participation, joint ventures, and the transfer of technology and expertise.
- In essence, FDI brings not just capital, but also skills, technology, and knowledge to the host country.
- Common examples of FDI include mergers, acquisitions, establishing new facilities, reinvesting profits, and intra-company loans.
- The stock of FDI represents the cumulative total of foreign investments less any disinvestments over a specified period.
How is FPI Different from FDI?
- The primary difference between FPI and FDI lies in the level of control or ownership over the business.
- FPI does not offer direct control, whereas FDI involves significant ownership, typically defined as owning 10% or more of a company’s shares.
Guidelines on Investment Limits for FPIs
- According to the Foreign Exchange Management (Non-Debt Instruments) Rules, 2019, an FPI's investment in any Indian company must not exceed 10% of the company's total paid-up equity capital on a fully diluted basis.
- If an FPI exceeds this limit, they must either divest the excess or reclassify the surplus as FDI within five trading days post the transaction settlement.
Approval Requirements for Reclassification
- To reclassify FPI holdings as FDI, investors must secure necessary government approvals.
- This process includes adherence to specific guidelines, particularly concerning investments from nations sharing land borders with India.
- Acquisitions must comply with FDI regulations, including entry routes, sectoral caps, and investment limits.
Role of the Investee Company
- FPIs are required to obtain consent from the companies they invest in to ensure compliance with sectoral caps and FDI regulations.
- This compliance allows the investee companies to verify that reclassified investments meet existing FDI rules and restrictions.
Sectoral Restrictions on Reclassification
- If reclassification to FDI is not permitted in certain sectors, the RBI guidelines prevent FPIs from pursuing this option.
- FPIs must clearly communicate their intent to reclassify and provide necessary documentation to their custodian.
Significance of the Guidelines
- The RBI's new framework aims to streamline FPI investments that exceed specified limits and ensure alignment with FDI regulations.
- These guidelines are designed to uphold regulatory consistency in foreign investments and maintain compliance with India's sectoral and governmental policies.
GS3/Environment
On improving wind energy generation
Source:The Hindu

Why in news?
Tamil Nadu, recognized as a frontrunner in wind energy, has over 30-year-old turbines and announced a new policy in August 2024 aimed at upgrading these aging windmills. However, this initiative faced opposition from wind energy producers, leading them to challenge the policy in the Madras High Court, which resulted in a stay on its implementation.
What is Tamil Nadu’s wind power capacity?
- Installed Capacity: As of November 2023, Tamil Nadu boasts an installed wind energy capacity of approximately 10,377.97 MW, making it the second-largest producer of wind energy in India, following Gujarat. This accounts for about 23% of India's total installed wind capacity.
- Age of Turbines: A significant number of Tamil Nadu's wind turbines are over 30 years old, raising concerns regarding their efficiency and the adoption of newer technologies.
- Potential for Repowering: The state has a repowering potential exceeding 7,387 MW. Upgrading or replacing older turbines could significantly boost energy generation capabilities.
What about national wind energy capacity?
- Total Potential: The National Institute of Wind Energy (NIWE) estimates India's wind power potential at 1,163.86 GW at 150 meters height, positioning India fourth globally in terms of installed capacity.
- Current Utilization: At a standard height of 120 meters, India's usable wind power potential is about 695.51 GW, with only roughly 6.5% currently utilized nationwide, and nearly 15% in Tamil Nadu alone.
- Leading States: The primary contributors to India's wind power are Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and Andhra Pradesh, collectively responsible for about 93.37% of the country’s installed capacity.
What does the repowering and refurbishing of wind turbines mean?
- Repowering: This process involves replacing outdated turbines with new ones, enhancing efficiency and output.
- Refurbishing: This entails upgrading specific components, such as gearboxes and blades, to improve performance without necessitating a complete replacement of the turbine.
- Regulatory Framework: The Tamil Nadu government has initiated a new policy intended to facilitate repowering and refurbishment. However, wind energy generators argue that the policy lacks effective measures to promote sustainable wind energy generation and financial viability.
Why are wind energy generators opposing the new policy of the TN government?
- Concerns from Generators: Wind energy producers have raised objections to the “Tamil Nadu Repowering, Refurbishment and Life Extension Policy for Wind Power Projects – 2024,” asserting that it fails to adequately foster wind energy production. They have sought legal recourse in the Madras High Court, resulting in a stay on the policy's implementation.
- Financial Viability Issues: The opposition is rooted in apprehensions that repowered turbines will be classified as new installations, without provisions for energy banking, adversely impacting financial returns on investments. Generators stress that without a favorable commercial framework, investments in repowering projects will likely decline.
Way forward:
- Revise the Policy to Ensure Financial Viability: The Tamil Nadu government should modify the policy to include incentives, such as energy banking for repowered turbines, thereby enhancing financial attractiveness for investors.
- Promote Technological Advancements and Infrastructure Upgrades: The policy should encourage the transition from older turbines to modern, high-capacity models and enhance wind energy transmission infrastructure to fully exploit Tamil Nadu’s wind resources.
Mains PYQ:
Do you think India will meet 50 percent of its energy needs from renewable energy by 2030? Justify your answer. How will the shift of subsidies from fossil fuels to renewables help achieve the above objective? Explain.
GS2/Governance
NGOs to Lose FCRA License over Conversions, Anti-Development Acts: MHA
Source:Indian Express

Why in News?
Central Government announced that any NGO involved in anti-developmental activities and forced religious conversions will face cancellation of their registration under Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 2010.
About Foreign Contribution Regulation Act:
The FCRA was initially enacted in 1976 to ensure strict oversight over voluntary organizations and political groups receiving foreign funding. In 2010, a revised version of the Act was introduced with stricter regulations.
Objective:
- To regulate foreign donations and ensure that these contributions do not negatively impact India’s internal security.
Nodal Ministry:
- Ministry of Home Affairs
- Applicable to all associations, groups, and NGOs intending to receive foreign donations.
Major Provisions Under the FCRA, 2010:
- It is mandatory for all NGOs to register under the FCRA.
- Initial registration is valid for five years and can be renewed if compliance with norms is maintained.
- Filing of annual returns, akin to Income Tax requirements, is compulsory for these NGOs.
- In 2015, new rules were established requiring NGOs to ensure that acceptance of foreign funds:
- Does not compromise the sovereignty and integrity of India.
- Does not affect friendly relations with foreign states.
- Does not disturb communal harmony.
- All NGOs must operate accounts in banks with core banking facilities to allow real-time access for security agencies.
For What Purpose a Registered NGO can Receive Foreign Contributions?
- Social
- Educational
- Religious
- Economic
- Cultural
Who Cannot Receive Foreign Funding?
- Candidates contesting elections
- Media persons
- Judges
- Government employees
- Political parties
Foreign Contribution Regulation Amendment Act, 2020:
- The Amendment includes Public Servants in the list of individuals prohibited from accepting foreign contributions.
- It disallows the transfer of foreign contributions to any other person, where 'person' encompasses individuals, associations, or registered companies.
- Makes it mandatory to provide Aadhaar numbers for anyone seeking prior permission, registration, or renewal.
- Enables government inquiries before renewing registration certificates.
- Allows the central government to permit the surrender of registration certificates.
- Mandates that all NGOs receiving foreign aid open an account at the State Bank of India’s New Delhi branch.
News Summary:
The Indian government has declared that NGOs involved in activities deemed anti-development, forced religious conversions, or actions threatening social or religious harmony may have their FCRA registration revoked. The announcement specifies that NGOs misusing foreign funds for personal benefits, engaging in undesirable activities, or having connections to extremist groups will also face registration cancellation. Furthermore, NGOs that do not utilize foreign funds in accordance with their stated purposes risk losing their FCRA registration.
GS3/Science and Technology
How AI can help chart pathways of sustainable development for India
Source:Indian Express

Why in news?
With an estimated 270 million people expected to migrate to cities in India over the next two decades, the challenges posed by rapid urbanization are significant. AI technology can play a crucial role in addressing these challenges by enhancing data management and coordination, aligning with India’s aim to become a developed nation by 2047.
- AI-Driven Decision Support
- AI systems can be utilized as decision support tools to evaluate the impact of policy changes, such as zoning modifications. By simulating different outcomes, these systems provide valuable insights that aid urban planning, focusing on both environmental and economic implications.
Enhancing Urban Infrastructure
- AI contributes to improving last-mile connectivity in public transportation systems. By continuously analyzing transit needs and traffic patterns, AI helps make public transport more efficient and accessible.
Multimodal Urban Transit Systems
- AI facilitates the integration of various urban transport modes, enabling coordinated planning across buses, trains, and other transit systems through a unified digital platform.
Digital Twins for Municipal Governance
- AI-powered digital twins can help municipal governments monitor urban dynamics and predict future needs. This technology enhances operational efficiency and supports data-driven governance.
Energy Distribution and Environmental Monitoring
- AI can optimize energy distribution networks, as demonstrated by collaborations like Airawat and Adani, and facilitate precise monitoring of air and water quality to enable real-time decision-making in governance.
What ethical and regulatory frameworks are necessary to ensure responsible AI deployment?
- Data Privacy and Security
- Given the extensive data required for AI applications in urban planning, it is vital to establish robust data privacy regulations to safeguard individual and community information.
- Transparency and Accountability
- AI-driven decisions, particularly those impacting urban infrastructure and environmental policies, must be transparent. Regulatory bodies should ensure that such decisions are auditable and that stakeholders are held accountable for the outcomes.
- Equity and Inclusivity
- AI systems should be designed to prevent biases that could adversely affect marginalized communities. Regulations must enforce fairness, ensuring that AI models promote equitable access and outcomes for all socioeconomic groups.
- Environmental Sustainability Mandates
- In light of India’s resource limitations, frameworks should prioritize AI implementations that are energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. Environmental impact assessments should be incorporated into the approval processes for new AI technologies.
What collaborative efforts are required among stakeholders to maximize AI’s impact on sustainable development?
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP)
- Collaboration between government, industry, and research institutions is crucial. Successful examples include Airawat’s partnerships with Adani and TCS, which aim to advance sustainable energy and urban management initiatives.
- Government Oversight and Support
- Government ministries, such as the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MOHUA), are pivotal in providing guidance and oversight to ensure that AI projects align with national sustainability goals and regulatory standards.
- Research and Academic Collaboration
- Involving academic institutions like IITs, as seen with Airawat, brings essential research expertise to AI solutions, encouraging innovation that meets India's specific challenges.
- Community Engagement
- Involving local communities in the development of AI solutions ensures that these technologies are relevant to real-life challenges, thereby increasing acceptance and effectiveness in addressing local sustainability issues.
- Standardized AI Governance Platforms
- Collaborations, such as those with the eGovernance Foundation’s DIGIT platform, are critical for creating standardized AI governance tools that can be implemented across various cities, promoting a unified approach to sustainable development across India.
GS3/Environment
Subansiri Lower Hydro Electric Project (SLHEP)
Source:Times of India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Power generation is set to commence at the highly controversial Subansiri Lower Hydroelectric Project from next year.
About Subansiri Lower Hydro Electric Project (SLHEP):
- It is a dam currently under construction, classified as a gravity dam.
- Located on the Subansiri River in North Eastern India, it lies on the borders of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- This project is designed as a run-of-river hydroelectric facility.
- Once completed, it will hold the title of the largest hydroelectric power plant in India.
- The development of this project is being managed by the National Hydro Power Corporation (NHPC), a state-run enterprise.
- Upon completion, the project will generate an impressive 2,000 MW of power, utilizing eight units of 250 MW each.
Key Facts about Subansiri River
- The Subansiri River is classified as a trans-Himalayan river and serves as a right-bank tributary of the Brahmaputra River.
- It is often referred to as the "Gold River" due to its historical association with gold dust.
- This river originates from the Himalayas in China, flowing eastward and southeastward into India.
- It traverses through regions of Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, and the Tibet Autonomous Region of China.
- The river merges with the Brahmaputra River in Lakhimpur district, marking its significance in the region.
- Spanning approximately 518 km in length, it encompasses a drainage basin covering 32,640 square kilometers.
- As the largest tributary of the Brahmaputra, it contributes around 7.92% to the total flow of the Brahmaputra River.
GS2/International Relations
What is Asia-Pacific Tele community (APT)?
Source:The Hindu

Why in news?
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India recently hosted the South Asian Telecommunication Regulators’ Council (SATRC) meeting, organized by the Asia-Pacific Telecommunity (APT), in Delhi.
About Asia-Pacific Telecommunity (APT):
- APT is an intergovernmental organization that was established in February 1979.
- Its primary goal is to promote the development of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) across the Asia-Pacific region.
- APT was founded through collaborative efforts between the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
- The organization currently has 38 member countries, 4 associate members, and over 140 affiliate members, which include private companies and academic institutions relevant to the ICT sector.
Functions:
- APT plays a vital role in fostering the growth of telecommunication services and enhancing information infrastructure within the region.
- It is instrumental in coordinating and harmonizing policies, regulations, and technical standards concerning ICT.
- APT conducts various preparatory activities for significant international conferences, such as:
- ITU Plenipotentiary Conference (PP)
- World Radiocommunication Conferences (WRCs)
- World Telecommunication Standardization Assemblies (WTSAs)
- World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS)
- World Telecommunication Development Conferences (WTDCs)
- The organization also hosts working groups and forums to tackle specific issues like spectrum management, policy formulation, and standardization.
- APT organizes various capacity-building programs related to ICT topics and initiates several pilot projects aimed at advancing ICT development in the region.
- Moreover, APT provides sub-regional platforms that help achieve common interests among its members.
- An example of this is the South Asian Telecommunication Regulators’ Council (SATRC), which is organized under APT.
- SATRC facilitates working groups focused on policy, regulation, and spectrum management to ensure harmonization among the concerned parties.
- The SATRC meeting is an annual event where leaders of telecommunication regulatory bodies from SATRC member countries convene to discuss and coordinate regulatory and other relevant issues related to telecommunications and ICT.
- SATRC comprises the heads of regulatory bodies from nine South Asian countries: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Iran, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
- Affiliate members from these nations are also actively involved in the activities of SATRC.
|
44 videos|5362 docs|1133 tests
|
















