UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 27th November 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Polity
Sambhal Mosque Dispute: Legal Controversy and Communal Tensions
Source:The Hindu
Why in news?
Violence has erupted in Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh, following a district court's order for a survey of the Shahi Jama Masjid, resulting in at least four fatalities and numerous injuries.
About the Sambhal Mosque Dispute:
- Background:
- A petition was submitted in the Sambhal district court alleging that the 16th-century Jama Masjid was constructed on the site of an ancient temple, the Hari Har Mandir.
- This claim is akin to those made regarding other mosques in Varanasi, Mathura, and Dhar.
- The petitioners requested a survey to determine the historical and religious significance of the site.
- The Shahi Jama Masjid is a protected site under the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act of 1904 and is classified as a Monument of National Importance by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- This legal status renders the case both legally and culturally sensitive.
- Court-ordered surveys and resulting unrest:
- A court-mandated photographic and videographic survey was initially carried out smoothly with the involvement of local authorities and mosque committee members.
- However, a subsequent survey led to violent confrontations when a petitioner arrived with chanting supporters, igniting protests near the mosque.
- Allegations of police firing emerged, resulting in the deaths of five individuals, including teenagers, with local residents accusing the police of excessive force and property destruction, claims which the police have denied.
- Allegations of the locals:
- Concerns were raised about the survey order being issued immediately after the petition was filed, without allowing the Hindu side to contest the claims in a higher court.
- The survey commenced before any formal challenge could be made, disregarding essential procedural protections.
Historical Context of the Jama Masjid:
- Construction:
- The Jama Masjid was built during the reign of Mughal Emperor Babur (1526–1530) by his general, Mir Hindu Beg, and is a notable example of early Mughal architecture.
- It is one of three mosques constructed during Babur's rule, the others being the mosque in Panipat and the Babri Masjid in Ayodhya, which was demolished in 1992.
- Architectural features:
- The mosque is situated on a hill in the center of Sambhal and features a large square mihrab hall topped by a dome, supported by arches.
- It was constructed using stone masonry and plaster, resembling other mosques such as the one in Budaun.
- Significant repairs were made during the reigns of Jahangir and Shah Jahan in the 17th century.
- Historical debate:
- Some researchers suggest the mosque may have Tughlaq-era origins, with modifications added by Babur.
- Local traditions assert that the mosque incorporates remnants of a Vishnu temple, believed to be the site associated with the arrival of Kalki, the tenth avatar of Vishnu.
Legal Context of the Jama Masjid:
- The Places of Worship Act, 1991:
- This dispute has rekindled discussions regarding the Places of Worship Act, which aims to maintain the religious character of all sites as they were on August 15, 1947, with the exception of the Babri Masjid case.
- Key provision: Section 3 of the Act prohibits the alteration of places of worship into sites for different religious denominations.
- The objective of this Act is to avert future disputes over religious sites and to uphold India's secular integrity.
- Challenges to the Act:
- The petition in Sambhal challenges the mosque's religious status, which goes against the stipulations of the 1991 Act.
- Petitioners reference comments by Justice D.Y. Chandrachud in 2022, suggesting that determining a religious site's character may not breach the Act.
- Currently, four petitions questioning the Act are pending in the Supreme Court, along with disputes in Varanasi, Mathura, Dhar, and now Sambhal.
Broader Implications of the Sambhal Mosque Dispute:
- Legal precedents:
- The interpretation of the 1991 Act is crucial amidst growing challenges and legal disputes.
- Historical accountability:
- There is a pressing need to balance archaeological studies with the imperative of communal harmony.
- Communal peace:
- Ensuring the prevention of violence and fostering coexistence among diverse communities is essential.
Conclusion:
- The Sambhal Mosque dispute highlights the intricate relationship between historical narratives, legal frameworks, and social cohesion in India's diverse society.
GS2/Polity
Women who helped draft the Constitution of India
Source:Indian Express
Why in news?
On Constitution Day (November 26), President Droupadi Murmu emphasized the significant roles played by women in the Constituent Assembly of India.
- The 299-member assembly included 15 women (two of whom later resigned), representing various regions and viewpoints. Notable figures such as Sarojini Naidu, Sucheta Kripalani, and Vijaya Lakshmi Pandit were accompanied by many lesser-known women who actively participated in discussions on critical topics like gender, caste, and reservations.
Ammu Swaminathan: A Pioneering Voice for Women in the Constituent Assembly
- Ammu Swaminathan was born in Palakkad, Kerala, and married Subbarama Swaminathan in her teens, asserting her need for independence in daily life.
- Among her children was Captain Lakshmi Sahgal, a prominent figure in the Indian National Army.
- Her political engagement was ignited by her experiences opposing restrictive widowhood practices that her mother faced.
- Swaminathan ran for elections on a Congress ticket and, as a member of the Constituent Assembly, she championed the Hindu Code Bill and gender equality, despite facing resistance from the predominantly male assembly.
- Post-independence, she was elected from Dindigul, Tamil Nadu, and served as India's goodwill ambassador to various countries, including Russia, China, and the US.
Annie Mascarene: Advocate for Universal Franchise and Local Autonomy
- Born in 1902 into a Latin Christian family in Travancore, Annie Mascarene faced societal barriers but excelled academically and pursued law, later becoming an educator.
- She was politically active during the upheaval in Travancore, influenced by caste and gender reforms initiated by local royals.
- Mascarene joined the All Travancore Joint Political Congress and later the Travancore State Congress, advocating for universal adult franchise and enduring violence from opponents.
- In the Constituent Assembly, she supported a strong central government while also advocating for local government autonomy.
- After leaving the Congress due to factionalism, she successfully ran as an independent candidate from Thiruvananthapuram in 1952, marking a significant achievement in Indian politics.
Begum Qudsia Aizaz Rasul: A Trailblazing Woman in Politics
- Begum Qudsia Aizaz Rasul was born into a royal family in Punjab and pursued formal education despite facing opposition, including a fatwa against her convent education.
- After marrying Nawab Aizaz Rasul, she broke away from purdah customs and entered the political realm, winning a non-reserved seat in 1936 despite conservative backlash.
- As a member of the Muslim League, she campaigned for women's rights and opposed religiously segregated electorates.
- Initially, she saw potential benefits in the idea of Pakistan but ultimately chose to remain in India, concerned for the welfare of poor Muslims post-Partition.
- She later joined the Congress and served in the Rajya Sabha from Uttar Pradesh in 1952, also contributing to the promotion of women's hockey in India.
Dakshayani Velayudhan: A Pioneer for Dalit Rights and Equality
- Dakshayani Velayudhan was the first Dalit woman to graduate in science in Cochin and served in the Cochin Legislative Council.
- Belonging to the Pulaya community, which was viewed as "slaves," she faced discrimination, including exclusion from practical experiments in college.
- She eventually married a social worker in a simple ceremony officiated by a leprosy-afflicted person, with Mahatma Gandhi and Kasturba present.
- As a member of the Constituent Assembly in 1946, she opposed Ambedkar's call for separate electorates, arguing it would foster division and hinder national unity.
- Though financial difficulties limited her political career, she remained active in the Dalit movement and returned to politics in 1971, though she finished fourth in the Lok Sabha elections as an independent candidate.
Renuka Ray: A Trailblazer for Women’s Rights
- Renuka Ray was born in Pabna (now in Bangladesh) into a prominent family and was inspired by Mahatma Gandhi in 1920, leading her to leave college to join the freedom struggle.
- She raised awareness through grassroots efforts and spent time at Sabarmati Ashram, later studying at the London School of Economics where she met Satyendra Nath Ray, her future husband.
- Upon her return to India, she became a strong advocate for women’s rights, particularly focusing on divorce and inheritance laws.
- Ray represented women’s organizations in the Central Legislative Assembly in 1943 and joined the Constituent Assembly in 1946.
- She supported the Hindu Code Bill and opposed reserved seats for women in legislatures, viewing such measures as obstacles to women's progress.
- Although she lost the 1952 general election from Hooghly, she won in 1957 and contributed to governance in Bengal before returning to social work, reflecting her lifelong commitment to women's empowerment and social justice.
GS3/Environment
GELEPHU MINDFULNESS CITY
Source: The Week

Why in news?
Bhutan, known for introducing the concept of gross national happiness, is embarking on an ambitious project to establish a “mindfulness city.” The “Gelephu Mindfulness City” (GMC) is currently in the fundraising phase to initiate this innovative urban development.
Overview of Gelephu Mindfulness City (GMC)
- GMC is a pioneering urban development concept in Bhutan, envisioned by His Majesty King Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck.
- Location: Situated in Gelephu, which is in the south-central region of Bhutan.
- Area: The project spans over 2,500 square kilometers, marking it as one of Bhutan's most significant urban development initiatives.
- Special Administrative Region (SAR): GMC will be Bhutan's inaugural SAR, enjoying executive autonomy and legal independence.
Key Features of GMC
- Mindfulness and Sustainability: The city is designed to merge economic development with principles of mindfulness, holistic living, and sustainability.
- Economic Hub: Positioned strategically at the intersection of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and China, GMC is set to become a major hub for regional connectivity and economic exchange.
- Zero Carbon City: It aims to be a "Zero Carbon" city, reflecting Bhutan's dedication to sustainable development practices.
- Infrastructure: The city will feature advanced infrastructure, including inhabitable bridges, an international airport, and healthcare facilities that integrate both Western and traditional medicine.
- Protected Areas: The design incorporates a national park and a wildlife sanctuary, promoting biodiversity and environmental protection.
Vision and Values of GMC
- Gross National Happiness (GNH): The development is rooted in the principles of GNH, encouraging a focus on conscious and sustainable business practices.
- Buddhist Heritage: Inspired by Bhutan’s rich spiritual traditions, GMC aims to foster an environment conducive to mindful living.
- Business Environment: Enterprises will be evaluated and welcomed based on their adherence to Bhutanese cultural values, commitment to sustainable development, and respect for national sovereignty.
GS2/Governance
Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI)
Source:Times of India
Why in News?
The Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI) has published its Half-Yearly Complaints Report for the financial year 2024-25, highlighting a significant occurrence of misleading and illegal advertisements, particularly in the real estate and offshore betting sectors.
About Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI):
- ASCI is a voluntary self-regulatory organization representing the advertising industry in India.
- Founded in 1985, it is registered as a non-profit entity under Section 25 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- The organization is dedicated to promoting self-regulation in advertising to safeguard consumer interests.
- ASCI ensures that advertisements comply with its Code for Self-Regulation, which mandates that ads be legal, decent, honest, truthful, and not harmful, while also promoting fairness in competition.
- It addresses complaints regarding advertisements across various media, including Print, Television, Radio, hoardings, SMS, Emails, websites, product packaging, brochures, promotional materials, and point-of-sale displays.
Structure:
- The organization is governed by a Board of Governors consisting of 16 members from notable businesses, media agencies, and advertising sectors.
- The Consumer Complaints Council (CCC) is responsible for investigating complaints and determining if advertisements comply with ASCI's standards.
- A Secretariat, led by the Secretary General, manages the day-to-day functions of ASCI.
- Although ASCI is not a governmental body, its influence is recognized; for instance, in 2006, the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting mandated that all television advertisements in India adhere to ASCI's codes.
- ASCI is also part of the Executive Committee of the International Council on Ad Self-Regulation (ICAS).
GS2/Polity
INDIA’S FEDERAL VISION
Source:Indian Express

Why in news?
The Indian Constitution, adopted on 26 November 1949 and enacted on 26 January 1950, marks an important occasion to consider the federal structure defined in the Constitution. This structure plays a crucial role in balancing unity and diversity, decentralization, and democratic governance.
Background:
- Indian federalism is a constitutional choice reflecting a balance between unity and diversity, promoting decentralization and democratic decision-making.
Unique features of India’s federalism
- India is termed a 'quasi-federal' republic, embodying both federal and unitary characteristics.
- The federal structure divides powers between the central and state governments while incorporating unitary features for flexible governance.
Key federal features established by the Constitution include:
- Dual polity: The governance system consists of a central Union government and state governments.
- Constitutional supremacy: All laws enacted must align with the Constitution.
- Rigid amendment procedures: The Constitution safeguards its federal framework through stringent amendment processes.
- Division of power: The Seventh Schedule of the Constitution delineates powers between central and state governments into three lists:
The three lists
- Union List: Subjects exclusive to the Union Parliament, including defense and foreign affairs.
- State List: Subjects under state legislatures, such as police, public health, and agriculture.
- Concurrent List: Subjects where both Union and state governments can legislate, with Union laws prevailing in case of conflict. Examples include education and marriage.
This framework prevents power concentration at any governmental level.
Changes made to the three lists
- Over time, adjustments have been made to the three lists to reflect changing governance needs.
- Initially, the Constitution outlined 98 subjects in the Union List, 66 in the State List, and 47 in the Concurrent List. Presently, these numbers have shifted to 100, 59, and 52, respectively, indicating significant changes over the years.
- The 42nd Amendment Act of 1976 was particularly impactful, transferring key subjects from the State List to the Concurrent List, such as education and forests.
Examples of subjects moved to Concurrent List
- The inclusion of education in the Concurrent List aimed to standardize educational quality nationwide, enabling the Union government to implement national policies like the Right to Education Act, 2009.
- Forests were also moved to the Concurrent List to address environmental concerns, allowing the Union government to enact laws such as the Forest Conservation Act, 1980.
Contemporary challenges
- The division of powers as articulated in the Seventh Schedule demonstrates adaptability in balancing centralization with regional autonomy to respond to governance needs.
- New challenges, such as climate change and cybercrime, cross territorial boundaries, necessitating collaborative efforts between state and central governments.
GS3/Environment
Cyclone Fengal
Source:Economic Times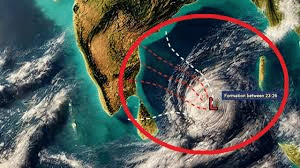
Why in news?
A weather depression in the Southwest Bay of Bengal has intensified into a deep depression, with expectations of further development into a cyclonic storm. This intensification is supported by the current proximity to regions with elevated sea surface temperatures (SST).
Origin of the Name ‘Fengal’
- The name 'Fengal' was suggested by Saudi Arabia and has its roots in Arabic.
- This name reflects a blend of linguistic heritage and cultural identity.
Cyclone Naming Process:
- In the North Indian Ocean, cyclones are named by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP).
- This naming panel consists of 13 member countries, including Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Pakistan.
- Each participating country submits a list of potential cyclone names, which are used sequentially as storms develop in the region.
- This systematic approach has been in place since 2004, facilitating clear identification and effective communication regarding storms to the public.
What are Cyclones?
- Cyclones are defined as wind systems that rotate inward towards a low-pressure area.
Categories:
- Tropical cyclones (caused by temperature variations) and Temperate cyclones (formed from extra-tropical air mass influences).
Geographical Causes
- Tropical cyclones require specific environmental conditions to form:
- Warm sea surface temperatures exceeding 27°C.
- The Coriolis force to aid in rotation.
- Pre-existing low-pressure systems to initiate cyclone formation.
- Minimal vertical wind speed differences.
- Upper air divergence to promote storm development.
Features
- Cyclones originate over warm water bodies, gaining energy from the condensation of warm water in cumulonimbus clouds.
- The Coriolis force influences wind rotation, resulting in:
- Anti-clockwise rotation in the northern hemisphere.
- Clockwise rotation in the southern hemisphere.
- Cyclone activity typically ceases around 30° latitude, where the warmth necessary for cyclone sustenance diminishes.
GS3/Economy
National Milk Day
Source: India Today

Why in the News?
National Milk Day is observed on November 26 to commemorate the birth anniversary of Dr. Verghese Kurien, known as 'The Milkman of India'. He played a pivotal role in making India self-sufficient in milk production.
About
- National Milk Day is celebrated on November 26 to honor Dr. Verghese Kurien's significant contributions to India's dairy sector and the White Revolution.
- This day marks India's journey to becoming the world's largest milk producer.
Contributions made by Verghese Kurien
- Dr. Kurien was born on November 26, 1921, in Kozhikode, Kerala.
- He was instrumental in establishing Amul in 1949, transforming it into a globally recognized dairy brand.
- He served as the inaugural chairman of the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB).
- Dr. Kurien led Operation Flood, a groundbreaking initiative that revolutionized India's dairy industry, ensuring self-sufficiency in milk production.
- He received numerous accolades, including the Ramon Magsaysay Award for Community Leadership in 1963.
About the White Revolution and Milk Production in India
- The White Revolution began in 1970 with Operation Flood, aiming to boost milk production and decrease reliance on milk powder imports.
- This initiative empowered dairy farmers by promoting a cooperative model for milk production.
- By the late 1990s, India emerged as the world's largest milk producer, surpassing the United States.
- Milk production increased significantly, rising from 21.2 million tonnes in 1968-69 to over 55 million tonnes by 1991-92.
- The initiative also helped establish essential infrastructure, including milk supply chains, processing plants, and storage facilities, making milk more accessible to the public.
- It notably enhanced the income and livelihoods of rural farmers, contributing to job creation and economic growth.
- As of 2022-23, India ranks first globally in milk production, contributing 24% to the world's total, with a production volume of 230.58 million tonnes.
GS2/Polity
Constitution Day of India
Source:NDTV
Why in News?
Constitution Day, also known as Samvidhan Divas, is celebrated every year on November 26 to commemorate the adoption of the Constitution of India by the Constituent Assembly in 1949. This year marks the 75th anniversary, a significant milestone reflecting on the constitutional journey of India and its fundamental principles.
- The Constitution of India was adopted on November 26, 1949, and came into force on January 26, 1950, establishing India as a sovereign, democratic republic. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, the chief architect of the Constitution, expressed both hope and concern regarding India's ability to uphold its independence and the values enshrined in the Constitution.
- In 2015, the Government of India officially declared November 26 as Constitution Day, following an announcement by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment. This day aims to educate citizens about the Constitution and its foundational values of justice, equality, liberty, and fraternity. Dr. Ambedkar famously noted that if issues arise under the new Constitution, it would not be due to a flawed document but rather the failings of humanity.
- On November 26, 2024, India celebrated the 75th anniversary of the Constitution's adoption. The President, Vice-President, Prime Minister, Speaker, Ministers, MPs, and other dignitaries gathered for the Constitution Day celebrations in the Central Hall of Samvidhan Sadan.
Highlights from PM Modi's Speech:
- Tributes and Significance:PM Modi celebrated the 75th Constitution Day, honoring the members of the Constituent Assembly and the victims of the 26/11 Mumbai Terror Attacks, reaffirming India's commitment against terrorism.
- Constitution’s Adaptability:He described the Constitution as a "living, evolving guide" that adapts to India's challenges, referencing its relevance after the abrogation of Article 370 in Jammu & Kashmir.
- Vision of a Developed India (Viksit Bharat):He emphasized socio-economic justice, highlighting welfare programs that have provided 53 crore bank accounts, 4 crore pucca houses, 10 crore gas connections, and 12 crore tap water connections.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity:Achievements include electrifying 2.5 crore households and enhancing connectivity with 4G/5G services in remote areas, underwater broadband in Andaman & Nicobar, and digitized land records under PM Swamitva Yojana.
- Modern Infrastructure Development:The review of accelerated ₹18 lakh crore infrastructure projects via the PRAGATI platform aims for timely completion and national progress.
- National Unity:He concluded with a call for integrity and national interest, stressing the spirit of "Nation First" to uphold the Constitution for future generations.
Highlights from Chief Justice of India Sanjiv Khanna's Speech:
- Defense of the Judiciary:The CJI noted that judges are appointed to ensure impartial decisions free from external influences, warning against the dangers of judges campaigning for votes.
- Judicial Independence: He emphasized that judicial independence serves as a bridge for coordination among government branches while maintaining their separateness, with judges guided solely by the Constitution and the law.
- Balancing Criticism:Judges receive mixed responses to their decisions and benefit from constructive feedback to enhance efficiency and accountability.
- Transparency and Accountability:The judiciary values openness to identify inefficiencies and improve its systems, stressing the importance of being public-centric and transparent.
- Global Standing:India’s constitutional courts are recognized globally as powerful but face varying opinions regarding their mandates and adherence to the status quo.
- Pendency of Cases: The CJI highlighted the substantial backlog of cases, with progress in clearance rates: 101.74% for district courts and 97% for the Supreme Court in 2024.
- Judiciary’s Role:Judges prioritize serving the public, fostering transparency, and effectively addressing critiques.
GS3/Environment
Global Matchmaking Platform
Source:DTE

Why in News?
Recently, the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and the Climate Club launched the Global Matchmaking Platform (GMP).
About Global Matchmaking Platform:
- The GMP aims to accelerate the decarbonization process of industries that produce high emissions in emerging and developing economies.
- This initiative was conceived in December 2023 during the 28th United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP28), coinciding with the launch of the Climate Club.
- It facilitates connections between the specific needs of countries and global resources, including technical expertise and financial aid, aimed at reducing emissions in sectors that consume significant energy and produce emissions.
- The platform links countries with a diverse network of partners who provide extensive technical and financial assistance to support industrial decarbonization efforts.
- These delivery partners play a crucial role in several areas, such as:
- Policy development to guide countries towards effective emissions reduction strategies.
- Transfer of innovative technologies that can help in reducing emissions.
- Facilitating investments necessary for the transition to low-emission industrial practices.
- Providing assistance to enhance national emissions reduction goals.
- This mechanism enables countries to customize their decarbonization approaches while simplifying access to resources and guidance from partner organizations, thereby facilitating significant reductions in emissions.
- The GMP is being established as a supportive framework under the Climate Club, with its secretariat managed by UNIDO.
- Moreover, its operations are backed by the Climate Club interim Secretariat, which is co-hosted by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the International Energy Agency (IEA).
GS2/International Relations
Design Law Treaty
Source:Outlook India
Why in News?
After nearly two decades of negotiations, the member states of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) adopted the landmark Design Law Treaty (DLT).
About Design Law Treaty:
- The DLT aims to standardize the procedures surrounding industrial design protection, making the registration process more efficient and accessible across different countries.
- For the treaty to take effect, it requires the ratification of 15 contracting parties.
Key features
- A grace period of 12 months is allowed after a design is first disclosed, meaning this initial disclosure will not undermine the design's validity for registration.
- Applicants receive relief measures that offer flexibility, preventing the loss of rights due to missed deadlines.
- The treaty streamlines the process for renewing design registrations.
- It encourages the adoption of electronic filing systems for design registrations and the digital exchange of priority documents.
- Technical assistance will be provided to developing and least-developed countries to help them implement the treaty effectively.
Benefits
- The DLT aims to make streamlined design protection accessible to all, with a focus on supporting Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs), startups, and independent designers.
- By standardizing the requirements for design registration, the DLT lessens administrative burdens, fostering global innovation in design.
- In conjunction with initiatives like the Startup India program and the Startups Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP) scheme, these measures are designed to empower startups and SMEs, helping them secure design rights on a global scale, which in turn enhances their competitiveness and promotes market expansion.
- India has recently signed the final act of this treaty.
|
44 videos|5359 docs|1133 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 27th November 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the historical significance of the Sambhal Mosque in the context of communal tensions in India? |  |
| 2. What are the key legal issues surrounding the Sambhal Mosque dispute? |  |
| 3. How does the Sambhal Mosque dispute reflect broader implications for Indian society? |  |
| 4. Who were some prominent women involved in the drafting of the Indian Constitution, and what were their contributions? |  |
| 5. What role did Ammu Swaminathan play in the Indian Constituent Assembly? |  |
















