Science and Technology: December 2024 UPSC Current Affairs PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
NISAR Satellite
Why in news?
The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) satellite is a collaborative project between the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), scheduled for launch in early 2025. This satellite is notable for being the first to carry both NASA’s L-band radar and ISRO's S-band radar systems.
What is NISAR?
- About:
- The NISAR satellite is a product of a partnership agreement established in 2014 between the US and India.
- It will be launched from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Andhra Pradesh, India.
- This satellite will be placed in low Earth orbit using the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark II.
- Objective:
- NISAR aims to provide comprehensive global mapping every 12 days.
- It will collect vital data on various environmental factors, including ecosystems, ice mass, vegetation, sea level rise, groundwater levels, and natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes, and landslides.
- Feature:
- Thermal Blanketing: Gold-colored thermal blankets are incorporated to maintain the satellite's temperature during its operations.
- Key Components:
- Radar Payload: This is the primary instrument responsible for surface observation.
- Spacecraft Bus: It supplies power, communication, navigation, and pointing control essential for the satellite's operations.
- Antenna and Reflector: Features a 12-meter diameter drum-shaped wire-mesh reflector, the largest of its kind in space, which enhances the focus and capabilities of radar signals.
- Technological Advancements:
- Dual Radar Systems: NISAR integrates two radar systems—NASA’s L-band radar and ISRO’s S-band radar.
- L-band Radar: This radar can penetrate dense vegetation to detect ground motion, making it particularly useful for monitoring volcanic and seismic activities.
- S-band Radar: It enhances the accuracy of surface monitoring, operating on a wavelength of 8-15 cm and a frequency range of 2-4 GHz.
- Dual Radar Systems: NISAR integrates two radar systems—NASA’s L-band radar and ISRO’s S-band radar.
GS3/Science and Technology
3rd Indian Space Conclave and India’s First Analog Mission
Why in news?The Indian Space Conclave held in New Delhi highlighted the advancements in India's space capabilities, particularly in the realm of Satellite Communication (Satcom) and partnerships with the Indo-European Union in space. Significant discussions focused on Satcom’s potential to enhance Digital India and support India's ambitious space objectives. Additionally, India launched its first Mars and Moon analog mission in Leh, Ladakh, spearheaded by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). This mission aims to replicate extraterrestrial conditions for testing space habitats.
- Key Highlights of the 3rd Indian Space Conclave:
- Satellite Communication (Satcom):
- The Minister of State for Communications and Rural Development emphasized the transformative impact of Satcom on Digital India.
- Satcom applications are vital across various sectors including telecommunications, disaster management, agriculture, healthcare, and education, particularly in reaching underserved areas.
- The SatCom Reform 2022 policy encourages innovation and fosters public-private partnerships in space technology.
- India’s Rise as a Global Space Leader:
- India's accomplishments, such as Chandrayaan-3 and the upcoming Gaganyaan missions, underscore its prominent position in space exploration.
- India aims to be a global partner in space, developing a robust network that complements existing terrestrial infrastructure.
- Indo-EU Space Collaboration:
- The ambassador acknowledged India's dynamic role in space, highlighting shared aspirations in space exploration.
- Proposed collaborative efforts include initiatives in Earth observation, training, and space security.
- The upcoming 2025 EU-India Summit is expected to enhance cooperation in space governance and peaceful applications.
- India plans to launch the EU’s Proba-3 satellite for solar observation, marking a significant milestone in Indo-EU collaboration.
- Space Startups:
- The emergence of over 300 space-focused startups in India post-2020 reforms is recognized as a driver of economic growth and innovation.
- This growth is countering brain drain by attracting Indian talent back from international agencies like NASA.
- Ambitions of India’s Space Program:
- India's future goals include the Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission, a crewed lunar landing by 2040, and the establishment of an Indian space station by 2035.
- Plans for space tourism by 2040 highlight India's commitment to innovative and inclusive approaches to space exploration.
- What is India’s First Mars and Moon Analog Mission?
- About:
- Analog missions serve as field tests in environments that mimic extreme conditions of space.
- These missions are essential for addressing challenges related to spaceflight research.
- This mission, led by ISRO in collaboration with AAKA Space Studio and the University of Ladakh, is supported by the Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council.
- Objective:
- The mission aims to simulate life in an interplanetary habitat, addressing the challenges of establishing a sustainable base beyond Earth.
- Focus areas include studying habitat conditions on Mars and the Moon, sustainability, life support systems, and psychological well-being in isolation to understand human adaptation to harsh environments.
- Ladakh, Ideal for Space Testing:
- Ladakh was selected for its unique environmental features that closely resemble those found on Mars and the Moon.
- The region's high altitude, dry climate, and significant temperature variations provide an excellent setting for testing space habitat technologies.
- With temperatures fluctuating from 15°C to -10°C, the mission replicates the thermal conditions of extraterrestrial environments.
- Oxygen levels in Ladakh are about 40% of those at sea level, allowing for effective testing of life support systems designed for low-pressure conditions similar to those found on Mars.
- The region's rocky and sandy soil also mirrors Martian and lunar regolith, making it suitable for research on rover mobility and in-situ resource utilization.
- Technological Testing:
- Researchers will evaluate advanced technologies essential for supporting space habitats, including:
- Circadian Lighting: This system mimics natural daylight cycles to help maintain sleep patterns and overall well-being of astronauts.
- Hydroponics: A sustainable system for growing food in space, ensuring proper nutrition for astronauts.
- Standalone Solar Power System: This provides renewable energy to support habitat independence.
- Significance of Analog Mission:
- Analog missions allow scientists to observe the physical, mental, and operational conditions of space missions while remaining on Earth.
- These missions prepare astronauts for upcoming explorations to asteroids, Mars, and the Moon.

Drishti Mains Question:
How does India’s Mars and Moon analog mission contribute to the country’s space exploration goals?
GS3/Science and Technology
RNA Editing
Why in News?
Recently, Wave Life Sciences, a biotechnology firm in the United States, has made history by becoming the first organization to treat a genetic disorder through RNA editing at the clinical level.
- Key Facts About RNA Editing
- About: RNA editing refers to the alteration of messenger RNA (mRNA) nucleotides after deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesizes mRNA but before protein production occurs. mRNA comprises segments known as exons and introns, where exons are the coding regions that will produce proteins, while introns are non-coding segments removed prior to protein synthesis.
- Types: RNA modifications can be categorized into three main types:
- Addition: Involves the insertion of a nucleotide.
- Deletion: Entails the removal of a nucleotide.
- Substitution: Involves swapping one nucleotide for another.
- Mechanism: This process utilizes a group of enzymes known as adenosine deaminase acting on RNA (ADAR). Scientists pair the effects of ADAR with a guide RNA (gRNA) that directs ADAR to specific locations in the RNA for the intended modification.
- Clinical Use: Wave Life Sciences successfully applied RNA editing to treat α-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), which is an inherited disorder, using a therapy named WVE-006. RNA editing holds potential for treating various conditions such as Huntington’s disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, obesity, Parkinson’s disease, neurological disorders, heart diseases, and more.
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
- Definition and Structure: RNA is a type of nucleic acid found in all living cells. It shares structural similarities with DNA but is usually single-stranded. The backbone of RNA is composed of alternating phosphate groups and ribose sugars, with bases including adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
- Types of RNA:
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes to facilitate protein synthesis.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Constitutes the central component of ribosomes and plays a crucial role in catalyzing protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Transfers amino acids to ribosomes during the process of protein synthesis.
- Regulatory RNAs: Involved in regulating gene expression.
- Functional Significance: RNA is vital for various cellular processes, including cell construction, immune responses, and the transportation of amino acids.
- Role in Viruses: Certain viruses utilize RNA as their genetic material, which highlights the importance of RNA in biological processes.
GS3/Science and Technology
Tardigrades Genes for Innovation
Why in news?Recently, researchers are exploring a range of unique tardigrade features to inspire advancements in medicine, biotechnology, and space exploration.
What are the Key Facts About Tardigrades?
- About: Tardigrades, scientifically classified under Tardigrada, are tiny, eight-legged organisms often referred to as water bears or moss piglets. They are microscopic and lack a backbone.
- Species and Evolution: These organisms belong to the phylum Tardigrada. Fossils of tardigrades are known to exist from about 90 million years ago during the Cretaceous Period, while molecular analyses indicate that they may have originated at least 600 million years ago.
- Adaptations: Tardigrades are remarkable for their resilience, capable of surviving extreme conditions such as high radiation, starvation, oxygen deprivation, and extreme cold, including subzero temperatures. They thrive in some of Earth's most extreme environments, including the Arctic, deep-sea floors, deserts, and even the vacuum of space.
- Cryptobiosis: One of the most fascinating survival strategies of tardigrades is their ability to enter a state called cryptobiosis, during which their biological activities cease. This adaptation allows them to endure severe environmental stresses like dehydration, freezing temperatures, and radiation exposure.
- DODA1 Gene: Research indicates that the DODA1 gene plays a crucial role in synthesizing betalains, a type of antioxidant that helps protect tardigrade cells from radiation damage, enabling them to recover and return to normal functioning after facing extreme conditions.
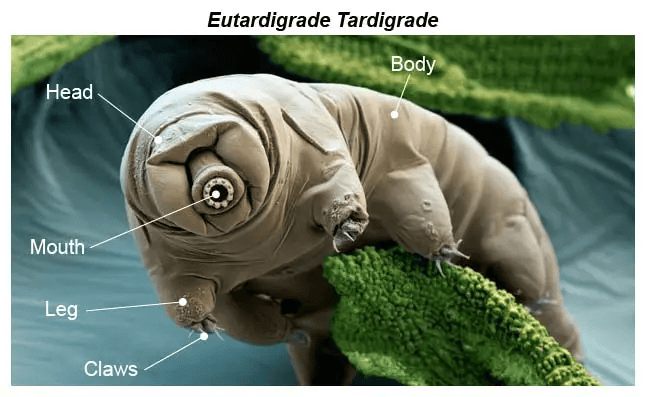
How Tardigrade Properties Could be Applied for Human Use?
- Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDPs): Tardigrades produce heat-soluble IDPs that can enhance the tolerance of microbes to desiccation (drying out). This property could be harnessed to develop more resilient microorganisms and other organisms.
- Small Heat Shock Proteins: When these proteins are introduced into microbial systems, they can enhance the stability and survival of microbes in hot or dry conditions, potentially benefiting various biotechnological applications.
- Protein Stability: The ability of tardigrades to maintain protein stability in extreme environments can be leveraged to extend the shelf life and effectiveness of vaccines, antibodies, and enzymes used in medical applications.
- Cell Preservation: The mechanisms that allow tardigrades to resist cellular damage might be beneficial in cell therapies, improving the transport and storage of cells, ultimately enhancing treatment delivery.
- Space Exploration: The insights gained from tardigrade resilience could lead to the development of advanced protective measures for humans and materials exposed to the harsh conditions of outer space.
GS3/Science and Technology
Biotechnology Experiments for India's Upcoming Space Station
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) have entered into an agreement to design and implement experiments that will eventually be incorporated into the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), which is planned for development between 2028 and 2035.
Why have ISRO and DBT Collaborated for Space Experiments?
- The primary challenges faced in space missions include ensuring a consistent supply of nutrients, food preservation, managing the effects of microgravity and radiation, and addressing health concerns such as cancers, cataracts, and loss of bone and muscle mass.
- The Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) aims to tackle these challenges using advancements in biotechnology.
Potential Experiments:
- Studying how weightlessness affects muscle degradation in astronauts.
- Identifying algae species that could either provide nutrients or enhance food preservation methods.
- Examining the potential of processing specific algae for jet fuel production.
- Evaluating the effects of radiation on the health of crew members aboard space stations.
What is Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS)?
- BAS is India's proposed indigenous space station designed for scientific research.
- The construction of BAS will occur in three phases and will consist of five modules.
- The initial module, referred to as BAS-1, is anticipated to be launched in 2028, with the entire station expected to be fully operational by 2035.
Key Details about the BAS:
- Orbit: The BAS is intended to orbit the Earth at an altitude of approximately 400 to 450 kilometers.
- Weight: The total weight of the station will be around 52 tonnes.
- Crew: Astronauts will have the capability to remain in orbit for 15 to 20 days.
- Modules: The BAS will include a crew command module, a habitat module, a propulsion module, and docking ports.
- Purpose: The station will facilitate scientific research, including microgravity experiments, Earth observation, and promoting innovation.
- Collaboration: The BAS aims to enhance international collaboration with various countries and space agencies.
- Program: The program will be led by ISRO, with involvement from industry, academia, and other national agencies.



















