UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 11th December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
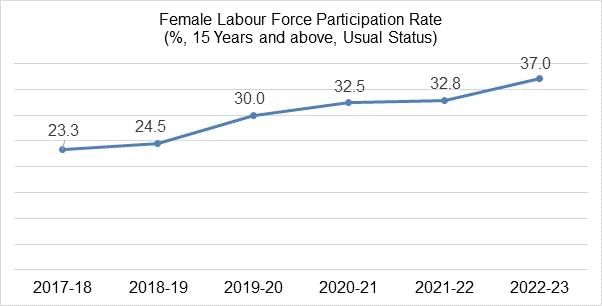
Female Labour Force Participation Rate Rose During 2017-18 to 2022-23
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The female Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) in India has witnessed a significant increase from 2017-18 to 2022-23. This trend reflects the growing involvement of women in the workforce, particularly in rural areas, despite existing regional disparities.
- Rural LFPR increased from 24.6% to 41.5%, a growth of 69%.
- Urban LFPR rose from 20.4% to 25.4% during the same period.
- Government initiatives have aimed at empowering women and enhancing their participation in the workforce.
Additional Details
- What is LFPR? LFPR refers to the proportion of people aged 15 and older who are employed or actively seeking employment, divided by the total working-age population. It reflects the demand for jobs in the economy.
- Regional Disparities: States like Bihar, Punjab, and Haryana show low female LFPR despite their differing economic conditions, while northeastern states have recorded notable improvements.
- Government Initiatives:
- Mudra Loans: Financial support for women entrepreneurs.
- Drone Didi Scheme: Skills development for women in technology sectors.
- Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana: Promotes women-led development through self-help groups.
- Despite the positive trend, challenges remain, including lower participation among married women and the need for sustainable job opportunities.
The rise in female LFPR from 2017-18 to 2022-23 indicates a significant shift in women's employment, especially in rural regions. Policymakers must focus on targeted interventions and effective implementation of women-centric schemes to ensure continued growth in female workforce participation.
GS3/Science and Technology
The Significance of ANI versus OpenAI
Source:The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The lawsuit against OpenAI in India is poised to establish key precedents for defining the legal accountability of AI developers regarding the content generated by their platforms within the country.
- ANI alleges that OpenAI used its copyrighted news content without permission.
- Claims of verbatim reproduction of ANI's articles by ChatGPT.
- Concerns over false attribution and misinformation linked to ChatGPT's outputs.
- ANI seeks legal restraints to prevent OpenAI from using its content.
Additional Details
- Unauthorized Use of Copyrighted Content: ANI claims that OpenAI used its copyrighted news content to train its models without necessary permissions, constituting copyright infringement.
- Verbatim Reproduction: ANI argues that responses generated by ChatGPT are either identical or significantly similar to its original articles, violating copyright protections.
- False Attribution and Fabricated Information: Instances have been noted where ChatGPT has misattributed statements or created false interviews, thereby harming ANI's reputation.
- Ineffectiveness of Opt-Out Policy: ANI states that OpenAI’s opt-out policy fails as their content remains accessible through other sites, allowing unauthorized scraping.
- Request for Legal Restraints: ANI is seeking an injunction to prevent OpenAI from using or reproducing its content.
Broader Implications
- Liability of AI Platforms: This case raises questions about the accountability of AI platforms using publicly available content for training.
- Fair Use and Exceptions: The court's decision could clarify the application of fair use and exceptions related to text and data mining in AI.
- Territoriality in Data Storage: OpenAI's defense argues its operations outside India complicate Indian copyright law application, raising issues of data sovereignty.
Future Implications for AI Development
- Setting Legal Precedents: The outcome may influence future legal standards for AI companies regarding their responsibilities to content creators.
- Impact on Licensing Agreements: This case could lead to more formal licensing agreements between media organizations and AI firms.
- Regulatory Framework Development: Lawmakers may need to create new regulations that address the use of copyrighted material in AI contexts.
- Challenges for Smaller Publishers: Smaller publishers may struggle to negotiate terms with AI companies, impacting media diversity.
Way Forward
- Establish a Balanced Regulatory Framework: Policymakers should create clear guidelines for AI platforms regarding copyrighted material, including provisions for fair use.
- Promote Collaborative Licensing Models: Media organizations and AI firms should develop formalized agreements for content use in AI training.
This lawsuit highlights the critical intersection of AI technology and copyright law, shedding light on the need for updated legal frameworks to address emerging challenges in the digital age.
GS3/Science and Technology
Deepening India’s Steps as a Key Space-Faring Nation
Source:The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India has set ambitious objectives for its space programme over the next two decades, with a focus on developing powerful, reusable rockets such as the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)’s upcoming Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV).
- Successful soft landing of Chandrayaan-3 near the lunar south pole.
- Launch of India's first space-based solar observatory, Aditya L1.
- Preparations for the Gaganyaan mission to send Indian astronauts into orbit by 2025.
- Increased budget allocation for the Department of Space for 2024-2025.
Additional Details
- Chandrayaan-3 Mission: India became the fourth country to achieve a soft landing on the Moon, demonstrating significant advancements in space exploration technology.
- Aditya L1 Mission: This mission focuses on studying the outer atmosphere of the Sun, contributing essential data to the field of solar science.
- Gaganyaan Preparations: With extensive testing of human-rated launch vehicles, ISRO is gearing up for its goal of launching Indian astronauts into space by 2025.
- Budget Increases: The Indian government's allocation of approximately $1.5 billion reflects a strong commitment to enhancing space capabilities and infrastructure.
- Future Plans: India aims for a crewed lunar landing by 2040 and the establishment of a lunar space station, along with a planned space station by 2035.
International Collaboration in Space Ambitions
- Commercial Partnerships: Collaborations with international companies, such as SpaceX, highlight India’s openness to utilize foreign technology for satellite launches.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Recent reforms have made the Indian space sector more accessible to foreign investments, enhancing domestic technological capabilities.
- Collaborative R&D: Engaging with global partners can provide access to advanced technologies, accelerating the development of projects like reusable rockets.
In conclusion, India's strategic focus on enhancing its space capabilities through ambitious missions, increased funding, and international collaboration positions it as a key player in global space exploration efforts.
GS3/Science and Technology
Bluetooth Low Energy Gateway
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The iHub – AWaDH (Agriculture and Water Technology Development Hub) at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Ropar has recently launched a pioneering Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Gateway and Node System under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS). This innovative system represents a cost-effective solution for connecting Bluetooth-enabled sensors to cloud platforms, facilitating seamless data transmission and real-time monitoring across various sectors.
- First-of-its-kind system for connecting BLE sensors to cloud platforms.
- Enables real-time environmental monitoring and advanced analytics.
- Applicable in agriculture, logistics, and environmental resilience sectors.
Additional Details
- Robust Connectivity:The BLE Gateway offers compatibility with 4G, WiFi, and LAN, allowing for flexible networking options.
- Long-Range Communication: It supports data transmission up to 1 km in line-of-sight (LOS) scenarios.
- Data Aggregation:The system collects and processes data from multiple connected nodes, streamlining analysis and decision-making.
- Weatherproof and Compact Design: Built to withstand extreme weather conditions while remaining user-friendly.
- Wireless Connectivity:Reduces installation costs by eliminating the need for extensive wiring, supporting remote deployments.
- Low Power Consumption:Designed for energy-efficient performance, ensuring prolonged operation.
- Scalability:Capable of managing over 100 connected BLE nodes, making it ideal for large-scale IoT networks.
- Firmware Over-The-Air (FOTA):Facilitates remote firmware updates, minimizing manual intervention.
- Compatibility:Fully supports integration with mobile apps, cloud platforms, and various sensors, enhancing flexibility.
Potential Applications
- Agriculture: Supports precision farming by monitoring critical factors like soil moisture and air quality, promoting better control and sustainable practices.
- Logistics:Ensures optimal environmental conditions for perishable goods during cold storage and transit, mitigating spoilage risks.
- Smart Cities and Industrial Sites:Utilizes the system for large-scale monitoring networks to improve operational efficiency and security.
- Real-time Data Transmission:Allows proactive responses to changes such as temperature spikes or unauthorized movements, enhancing resource management.
This BLE Gateway system is poised to revolutionize IoT applications across various sectors, significantly improving data security and operational efficiency.
GS3/Science and Technology
Radioactive Diamond Battery
Source: BBC
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Scientists from the University of Bristol and the UK Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) have developed the world’s first carbon-14 diamond battery, marking a significant advancement in energy technology.
- The diamond battery utilizes carbon-14, a radioactive isotope with a half-life of 5,700 years.
- It operates by capturing fast-moving electrons from within the diamond structure, similar to how solar panels harness light particles.
- Potential applications include powering medical devices like pacemakers and hearing aids, which can last for years without requiring battery replacements.
- It is particularly suited for extreme environments, such as space, where conventional battery replacement is impractical.
Additional Details
- Carbon-14: A radioactive isotope of carbon, carbon-14 emits short-range radiation that is quickly absorbed by solid materials, making it safe for use in various applications.
- The diamond battery's longevity could revolutionize power supply in healthcare and space missions, eliminating the need for frequent power source replacements.
This innovation promises to provide a sustainable and long-lasting power solution, particularly beneficial in fields where reliability and longevity are crucial.
GS3/Environment
Champions of the Earth Award
Source:Times of India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India’s renowned ecologist, Madhav Gadgil, has been recognized as one of the six recipients of the prestigious Champions of the Earth Award for the year 2024. This accolade highlights his significant contributions to environmental conservation.
- The Champions of the Earth Award was established in 2005 by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- This award is regarded as the UN’s highest environmental honor, celebrating leaders in environmental protection.
- Each year, UNEP acknowledges individuals and organizations that devise innovative and sustainable solutions to combat the challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution.
Additional Details
- Categories of Awards:The Champions of the Earth Award is presented in four distinct categories:
- Policy Leadership:Recognizes public sector officials who drive global and national environmental initiatives.
- Inspiration and Action: Honors leaders who take significant steps to inspire positive environmental change.
- Entrepreneurial Vision:Acknowledges visionaries who innovate for a cleaner future through new technologies.
- Science and Innovation:Celebrates trailblazers who develop technologies that provide substantial environmental benefits.
- Madhav Gadgil's recognition emphasizes the importance of sustainable practices and environmental stewardship in addressing global ecological challenges.
The Champions of the Earth Award serves as a reminder of the critical efforts being made worldwide to safeguard our planet and the individuals leading the charge.
GS3/Economy
New Policy Initiatives in Agriculture Sector
Source:DD News
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Government of India is actively supporting State governments through various policy measures and budgetary allocations aimed at improving the welfare of farmers, recognizing agriculture as a State subject.
- Introduction of several key initiatives approved by the Union Cabinet.
- Focus on improving agricultural productivity and infrastructure.
Additional Details
- Clean Plant Programme (CPP):Launched on 09.08.2024 with an outlay of ₹1,765.67 crore to enhance the quality and productivity of horticulture crops. Key features include:
- Providing disease-free planting material.
- Promoting climate-resilient varieties.
- Reducing crop losses and improving quality.
- Digital Agriculture Mission: Aims to create a robust digital ecosystem for farmers by providing timely and reliable crop-related information through various platforms including Agristack and Krishi Decision Support System (DSS).
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund Scheme:Introduced on 28.08.2024, offering loans up to ₹2 crores with a 3% interest subvention for enhancing agricultural infrastructure across India.
- National Mission on Edible Oils – Oilseeds (NMEO-Oilseeds):Launched on 03.10.2024 with an allocation of ₹10,103 crore aimed at boosting domestic oilseed production and achieving self-reliance in edible oils.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF):Initiated on 25.11.2024 with a financial outlay of ₹2,481 crore to promote natural farming practices across India.
- Additional Key Programmes:Include the National Pest Surveillance System and AgriSURE fund for rural enterprises.
These initiatives represent a comprehensive effort by the government to modernize the agricultural sector, enhance productivity, and ensure the welfare of farmers in India.
GS3/Environment
UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION TO COMBAT DESERTIFICATION (UNCCD)
Source:DTE
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The significance of indigenous peoples in combating desertification was emphasized at the 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) to the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), held in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. This recognition aligns with previous acknowledgments from other COPs, stemming from the 1992 Earth Summit, including the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change and the Convention on Biodiversity, which have also valued the traditional wisdom of indigenous communities.
- The UNCCD is a global agreement focused on combating desertification, land degradation, and drought (DLDD).
- Adopted in 1994 and came into force in 1996, it aims to promote sustainable land management and ecosystem restoration.
- The convention is based in Bonn, Germany, and is one of the three Rio Conventions established during the Earth Summit in 1992.
Additional Details
- Objective:The primary goal is to combat desertification and mitigate drought effects through national action programs (NAPs) that utilize a bottom-up approach.
- Focus Areas:
- Prevention of desertification in drylands, including arid, semi-arid, and dry sub-humid areas.
- Promotion of land degradation neutrality (LDN).
- Encouragement of community participation and sustainable land management practices.
- Binding Treaty:The UNCCD is the only legally binding international agreement that connects environmental concerns with development and land management.
- Strategic Framework: The current framework (2018–2030) aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly targeting land degradation neutrality under SDG 15.3.
India ratified the UNCCD in 1996 and hosted the 14th Conference of Parties (COP 14) in New Delhi in September 2019. Key initiatives aligned with UNCCD include the Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas (2021), which maps degradation across states, and the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) along with the National Afforestation Programme.
GS2/Polity
Opposition Set to Submit Notice for Resolution to Impeach Dhankhar
Source:Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
In a significant political development, approximately 60 Opposition Members of Parliament (MPs) from the INDIA bloc submitted a notice to the Rajya Sabha Secretary General P.C. Mody, requesting the removal of Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar, who serves as the Chairperson of the Rajya Sabha. This unprecedented move is based on allegations of biased conduct by Dhankhar since he took office.
- The Vice President can be removed via a resolution passed by Parliament under Article 67(b) of the Constitution.
- This removal process, commonly referred to as impeachment, is distinct from the impeachment process for the President.
Additional Details
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 63: Establishes the office of the Vice President.
- Article 64: States that the Vice President is the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
- Article 67(b): Details the procedure for removing the Vice President.
- Procedure for Removal:
- Initiation requires the removal resolution to be moved in the Rajya Sabha, signed by at least one-fourth of its total members.
- A 14-day notice is mandatory before the motion is considered.
- A special majority is required for the resolution to pass, needing approval from the Lok Sabha with a simple majority of members present and voting.
- Grounds for Removal: The Constitution does not specify grounds for the removal, allowing Parliament to decide, making the process more political.
- Comparison with Presidential Impeachment:
- Presidential impeachment (Article 61) involves a judicial inquiry and requires a two-thirds majority in both Houses.
- The Vice President's removal process is simpler and relies solely on parliamentary procedure.
- Note: The removal process has never been initiated in India's history, indicating the stability and largely ceremonial nature of the Vice President's office.
This recent political move highlights the ongoing tensions within the Parliament and raises questions about the impartiality of the Vice President's role in legislative proceedings.
GS2/Governance
AMRIT GYAAN KOSH PORTAL
Source:PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Union Minister, Dr. Jitendra Singh, has launched the “Amrit Gyaan Kosh” Portal aimed at enhancing governance training for public administrators in India. This initiative emphasizes the portal's role as a comprehensive platform that goes beyond merely being a repository of information, focusing on promoting self-reliance in governance training.
- The Amrit Gyaan Kosh Portal is designed to strengthen governance training.
- It is developed collaboratively by the Capacity Building Commission and Karmayogi Bharat.
- The portal is hosted on the iGOT (Integrated Government Online Training) platform.
Additional Details
- Governance Training: The primary objective is to enhance governance training by offering a repository of best practices and case studies.
- Self-Reliance:The portal encourages self-reliance in governance training through the provision of indigenous resources.
- Global Standards: Resources available on the portal adhere to global standards while addressing India's unique administrative challenges.
- Content Highlights:The platform includes case studies that connect theory with practical application, teaching notes for educators, and covers various policy themes such as health, education, agriculture, and digital governance.
- Significance:The Amrit Gyaan Kosh aligns with 15 of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and promotes collaboration and innovation across different sectors.
- Transformative Outcomes:The initiative aims to equip educators and public administrators with advanced skills in case writing and teaching methodologies.
This portal represents a significant step towards enhancing the quality of governance training in India, fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement among public administrators.
GS1/Geography
Geographical Indication Tagged Products
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?
During the Ashtalakshmi 2024 event, several products with Geographical Indication (GI) tags were showcased, highlighting their unique characteristics and the cultural heritage of the regions they originate from.
Key Takeaways
- Adi Kekir Ginger from Arunachal Pradesh is known for its medicinal properties.
- Dalle Khursani, a popular red pepper from Sikkim, is celebrated for its pungency and economic importance.
- The Naga King Chilli, recognized globally for its heat, reflects Naga cultural identity.
- Kaji Nimu, a distinctive lemon variety from Assam, is essential in local cuisine and remedies.
Additional Details
- Adi Kekir Ginger: This aromatic ginger is cultivated by the Adi tribe in the Dibang Valley of Arunachal Pradesh. It's renowned for its medicinal uses, addressing issues like digestive problems and menstrual discomfort.
- Dalle Khursani: A fiery red pepper from Sikkim, it thrives in organic conditions and is used in local pickles and pastes. Over 5,000 families depend on its cultivation for their livelihoods.
- Naga King Chilli: Hailing from Nagaland, this is one of the hottest chilies globally, cultivated by about 100 families. It holds significant cultural value in Naga cuisine, enhancing traditional dishes.
- Kaji Nimu: Known for its size and flavor, this lemon variety is integral to Assamese cuisine and traditional treatments, showcasing the region's agricultural richness.
The showcase of these GI tagged products not only emphasizes their unique qualities but also underscores the importance of preserving local agricultural practices and cultural heritage.
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
















