NCERT Summary: The Delhi Sultans (Class 7) | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Emergence of Delhi as an Important City
In the 12th century, Delhi rose to prominence under the Tomara Rajputs and Chauhans, becoming a major commercial center with rich merchants and numerous temples.
 The Rulers of Delhi
The Rulers of Delhi
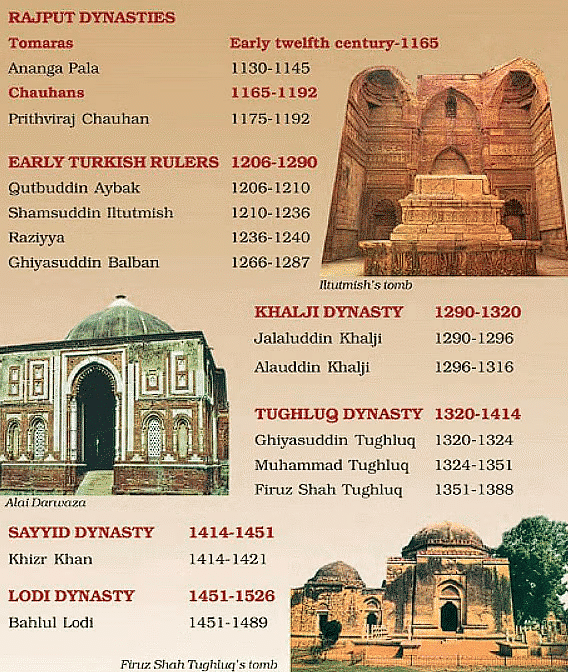
- Tomaras: Established Delhi as a regional center and ruled until the mid-12th century when defeated by the Chauhans.
- Chauhans: Continued the city's development after taking over from the Tomaras. Coins minted in Delhi, known as Dehliwal, were widely circulated.
- Early Turkish Rulers: Further enhanced Delhi's significance.
- Sultanate Dynasties: Contributed to Delhi’s growth, administration, and social structure.
- Emergence as a Major Capital: Delhi transformed into a major capital under the Delhi Sultanate in the early 13th century
Note: In ancient times, regions like the Kaveri delta were the centers of large kingdoms. However, Delhi was not mentioned as a capital in early historical records because it became important only in the 12th century.
Understanding Delhi under the Sultans
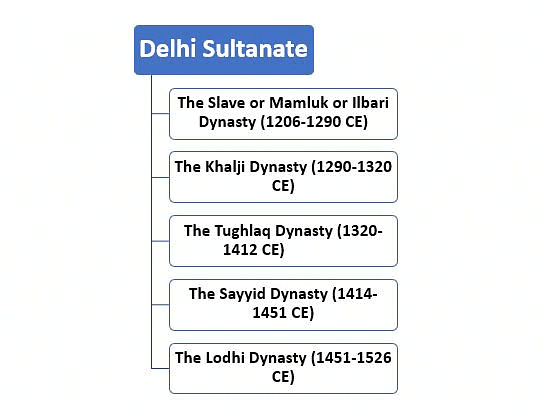
Delhi's transformation into a major capital began with the establishment of the Delhi Sultanate in the early 13th century. The Delhi Sultanate was formed by five dynasties:
- Tarikh and Tawarikh: Histories were called tarikh (singular) or tawarikh (plural) and were written in Persian, the administrative language of the time.
- Authors: Written by learned men such as secretaries, administrators, poets, and courtiers, these histories recounted events and offered advice to rulers on governance, emphasizing the importance of just rule.
- The Circle of Justice: In the 13th century, Fakhr-i Mudabbir explained that a king needs soldiers, who require salaries funded by revenue from peasants. Peasants can only pay this revenue if they are prosperous and happy, which depends on the king promoting justice and honest governance.
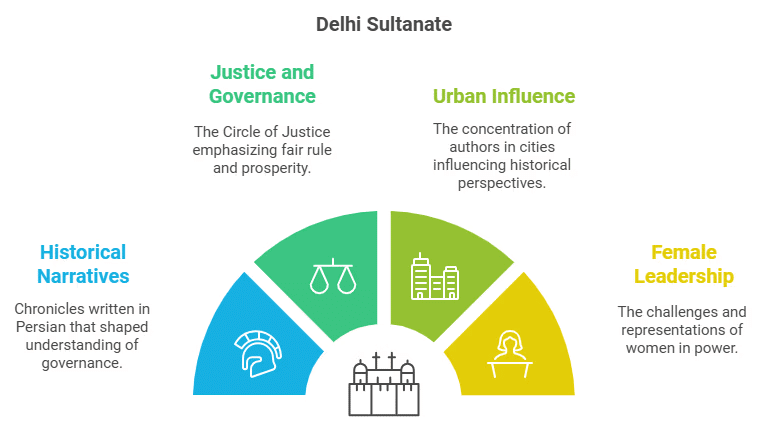
- Urban Focus and Motivation: The authors of tawarikh mainly lived in cities like Delhi and rarely in villages. They often wrote histories seeking rewards from the Sultans and advised rulers to maintain an "ideal" social order based on birthright and gender distinctions, though not everyone agreed with these ideas.
- Sultan Raziyya: Ascended in 1236 as the daughter of Sultan Iltutmish but faced resistance due to her gender, leading to her removal in 1240. Minhaj-us-Siraj believed Raziyya’s rule violated the divine social order, which held that women should be subordinate to men. He questioned her success as a female ruler.
- Other Female Rulers: Raziyya identified herself as Iltutmish’s daughter, while Queen Rudramadevi presented herself as a man, and Queen Didda of Kashmir was affectionately called "didi" by her subjects.
A closer Look: Administration under the Khaljis and Tughluqs
During the Khalji and Tughluq dynasties, the Delhi Sultanate implemented notable administrative changes, favoring loyal slaves over aristocrats for key roles. This era saw centralization of power, with direct control over land revenue and ongoing challenges from external threats and geographical barriers.
Governance Approach: The Delhi Sultans, particularly Iltutmish, preferred loyal slaves (bandagan) over aristocrats and landed chieftains for administrative roles due to their dependence on the Sultan, though this reliance sometimes led to political instability.
Preference for Slaves: Sultans believed experienced slaves were more reliable than sons but faced criticism for appointing individuals of humble birth to high positions, which shocked the elites and drew criticism from Persian historians.
Appointment of Low-born Individuals: Khaljis and Tughluqs continued the practice of appointing slaves and individuals of humble origin to important offices, causing discontent among the elite.
Muqtis and Iqtas: Military commanders were appointed as governors (muqtis) of territories (iqta), responsible for military campaigns and law enforcement, funded by local revenues. They were appointed temporarily and restricted to prescribed taxes to maintain control.
Centralization of Power: Alauddin Khalji centralized control by taking over land revenue assessment and collection, reducing the power of local chieftains and placing revenue collection under the Sultan's direct administration.
Challenges in Administration: Geographical barriers and resistant local chieftains limited the Delhi Sultanate’s control, particularly in forested and mountainous regions.
External Threats: The Sultanate faced Mongol invasions during the reigns of Alauddin Khalji and Muhammad Tughluq, necessitating the mobilization of large standing armies and posing significant administrative challenges.
The Sultanate in the Fifteenth and Sixteenth Centuries
The fifteenth and sixteenth centuries were a period of transformation for the Delhi Sultanate. During this time, the Sayyid and Lodi dynasties controlled Delhi and Agra until 1526. This era saw the rise of independent regional states and new ruling groups, significantly shaping the political landscape of India.
- Sayyid and Lodi Dynasties: Dominated Delhi and Agra until 1526.
- Regional Powers: Independent leaders governed regions such as Jaunpur, Bengal, Malwa, Gujarat, Rajasthan, and South India, establishing prosperous states and capitals.
- Emergence of New Ruling Groups: The Afghans and Rajputs became prominent forces in the region.
- Influential States: Several small but well-governed states emerged, impacting the political dynamics.
- Sher Shah Suri: Began his career in Bihar, later defeated Mughal emperor Humayun, and established the Sur dynasty.
- Administrative Innovations: Introduced effective administrative reforms inspired by Alauddin Khalji’s methods.
- Legacy: Sher Shah Suri’s administrative practices influenced Mughal Emperor Akbar’s approach to unifying the Mughal Empire.
Hope you have understood the chapter well. Watch the video below to improve your understanding.
|
122 videos|653 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: The Delhi Sultans (Class 7) - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What were the key factors that led to the emergence of Delhi as an important city during the Sultanate period? |  |
| 2. How did the administration under the Khaljis differ from that of the Tughluqs? |  |
| 3. What were the major achievements of the Delhi Sultans in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries? |  |
| 4. How did the Delhi Sultanate influence the culture and society of medieval India? |  |
| 5. What challenges did the Delhi Sultans face in maintaining their rule? |  |