UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > Cheat Sheet: The Himalayas
Cheat Sheet: The Himalayas | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
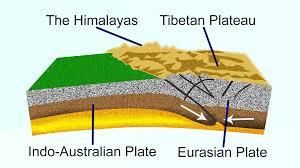
The Himalayas, derived from the Sanskrit words "Him" (snow) and "Alaya" (abode), mean the "Abode of Snow". They are the youngest and highest fold mountain ranges in the world and stretch across five countries — India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, and Pakistan. Formed due to the collision of the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates, the Himalayas continue to rise and remain seismically active. These mighty mountains are not just a geographic marvel but also a cultural, ecological, and strategic lifeline for South Asia.
Extent & Dimensions
- Length: ~2,400 km (W to E)
- Width: 250–400 km
- Between Rivers: Indus (west) to Brahmaputra (east)
- Passes through: India, Nepal, Bhutan, Tibet (China), Pakistan
Formation of the Himalayas
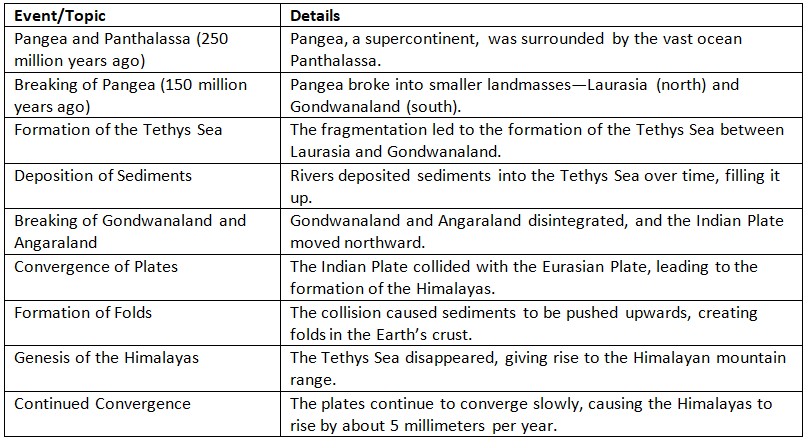
Longitudinal Division of Himalayas
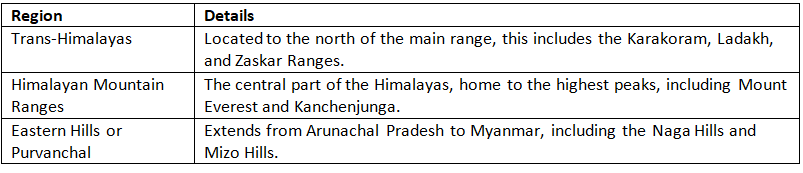
The Trans-Himalayas

The Himalayan Ranges

The Eastern Hills or Purvanchal

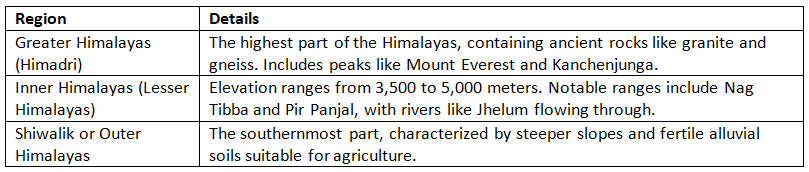
Regional Division of Himalayas

Syntaxial Bends of Himalayas

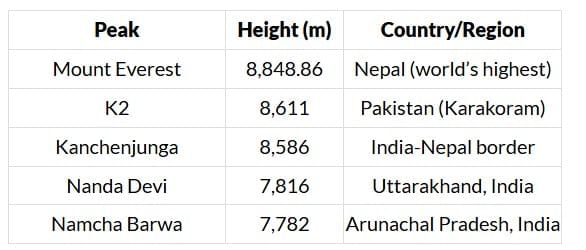
Major Peaks
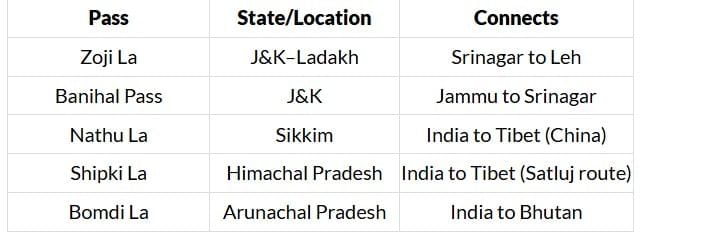
Important Passes
Key Characteristics
- Youngest Fold Mountains
- Tectonically Active – frequent earthquakes
- Rich in biodiversity
- Source of perennial rivers
- Acts as a climatic barrier
Importance of the Himalayas
- Climate Regulation: Blocks cold winds, traps monsoon moisture
- River Source: Origin of major river systems
- Agriculture: Fertile valleys and terrace farming
- Biodiversity: Forests, endemic species, national parks
- Cultural: Pilgrimage sites like Amarnath, Badrinath, Kedarnath
- Strategic: Natural boundary with China and Pakistan
The document Cheat Sheet: The Himalayas | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
175 videos|624 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: The Himalayas - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the major geographical features of the Himalayas? |  |
Ans. The Himalayas are characterized by their towering peaks, including some of the highest mountains in the world such as Mount Everest and K2. This mountain range spans five countries: India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, and Pakistan. The Himalayas consist of various geographical features, including deep valleys, plateaus, glaciers, and diverse ecosystems. The range is also home to numerous rivers, such as the Ganges, Indus, and Brahmaputra, which originate from the glaciers of the Himalayas.
| 2. What is the significance of the Himalayas in terms of biodiversity? |  |
Ans. The Himalayas are renowned for their rich biodiversity, housing a wide variety of flora and fauna. The range is home to over 10,000 species of plants, many of which are endemic to the region. It also supports diverse wildlife, including iconic species such as the snow leopard, red panda, and Himalayan tahr. The varying altitudes and climates create distinct ecosystems, ranging from subtropical forests to alpine meadows. This biodiversity is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and provides valuable resources for local communities.
| 3. How do the Himalayas affect the climate of the surrounding regions? |  |
Ans. The Himalayas play a critical role in influencing the climate of the surrounding regions. They act as a barrier to cold winds from Central Asia, resulting in a warmer climate in the Indian subcontinent. The range also traps monsoon winds, leading to heavy rainfall on the southern slopes, while the northern slopes experience arid conditions. This orographic effect contributes significantly to the agricultural patterns and water availability in the regions adjacent to the Himalayas.
| 4. What are some cultural aspects associated with the Himalayas? |  |
Ans. The Himalayas hold immense cultural significance for various communities living in their vicinity. They are considered sacred in several religions, including Hinduism and Buddhism. Many important pilgrimage sites, such as Haridwar and Badrinath, are located in the Himalayas. The region is also rich in traditional practices, art, and crafts that reflect the lifestyle of the indigenous people. Festivals and rituals associated with the mountains are integral to the cultural identity of these communities.
| 5. What are the main challenges facing the Himalayas today? |  |
Ans. The Himalayas face several challenges, primarily due to climate change, deforestation, and urbanization. Glacial melting is accelerated by rising temperatures, leading to increased flooding and changes in water availability. The biodiversity of the region is threatened by habitat loss and invasive species. Additionally, the pressure from tourism and infrastructure development poses risks to the fragile ecosystems. Sustainable development practices are essential to address these challenges and preserve the unique environment of the Himalayas.
Related Searches
















