Best Study Material for UPSC Exam
UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Mindmap: Anti- Defection Law
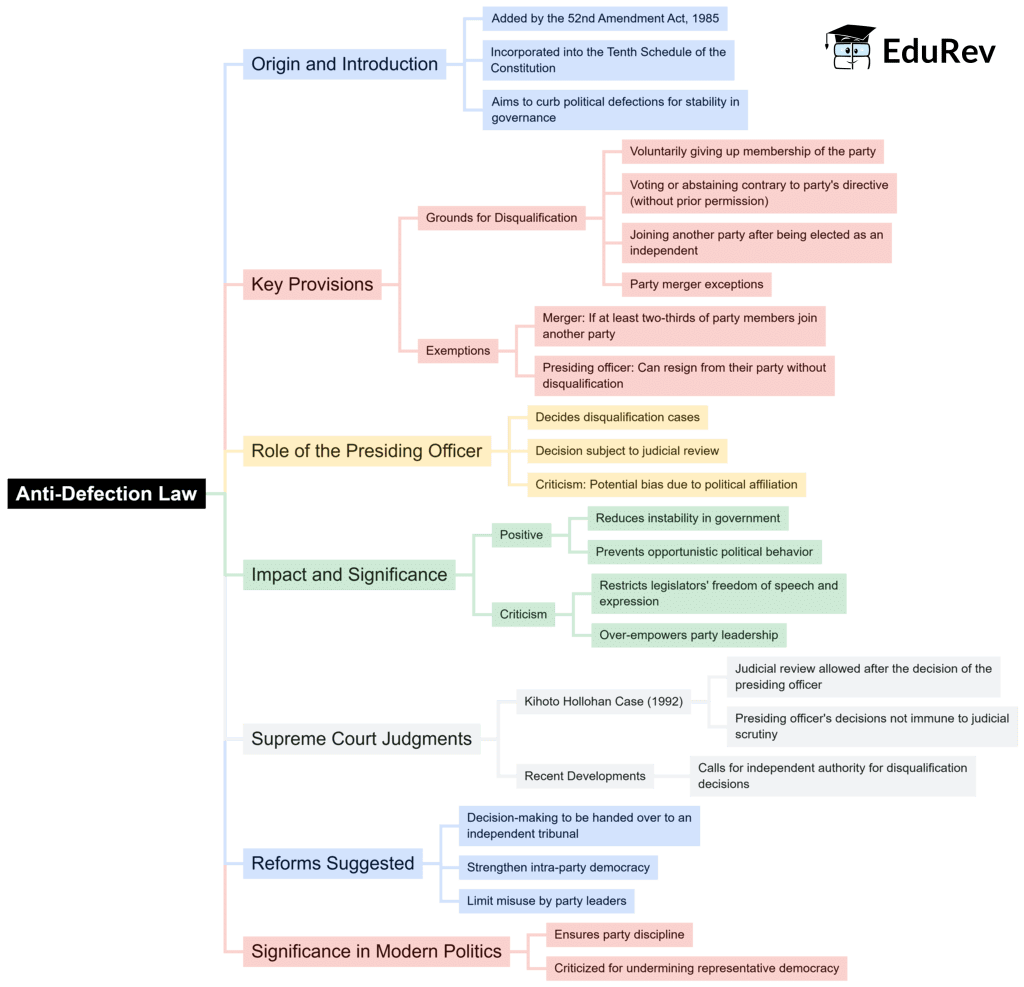
Mindmap: Anti- Defection Law | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
The document Mindmap: Anti- Defection Law | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
144 videos|639 docs|203 tests
|
FAQs on Mindmap: Anti- Defection Law - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the Anti-Defection Law in India? |  |
| 2. What are the key provisions of the Anti-Defection Law? |  |
Ans. The key provisions of the Anti-Defection Law include disqualification of members who defect from their party, exceptions for splits in parties, and provisions for merging with another party. Specifically, if a member joins a party after the election, they can be disqualified unless they are part of a recognized split or merger.
| 3. How does the Anti-Defection Law impact political parties in India? |  |
Ans. The Anti-Defection Law significantly impacts political parties by promoting party loyalty and discouraging members from switching parties for personal gain. It helps maintain the integrity of political parties and ensures that elected representatives remain accountable to their electorate, thereby fostering a stable political environment.
| 4. What are the criticisms of the Anti-Defection Law? |  |
Ans. Critics argue that the Anti-Defection Law restricts the rights of individual legislators, undermines democratic principles, and may lead to the misuse of power by party leaders. Additionally, it has been suggested that the law does not effectively address the root causes of defections and may inadvertently encourage horse-trading and political instability.
| 5. How does the Anti-Defection Law relate to the role of the Speaker in the legislative assembly? |  |
Ans. The Speaker of the House plays a crucial role in the implementation of the Anti-Defection Law, as they have the authority to decide on disqualification petitions against members. The Speaker's decisions can greatly influence the political landscape, and the impartiality of the Speaker is essential to uphold the law's integrity and ensure fair treatment of all members.
Related Searches