Best Study Material for UPSC Exam
UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Mindmap: State Legislature
Mindmap: State Legislature | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
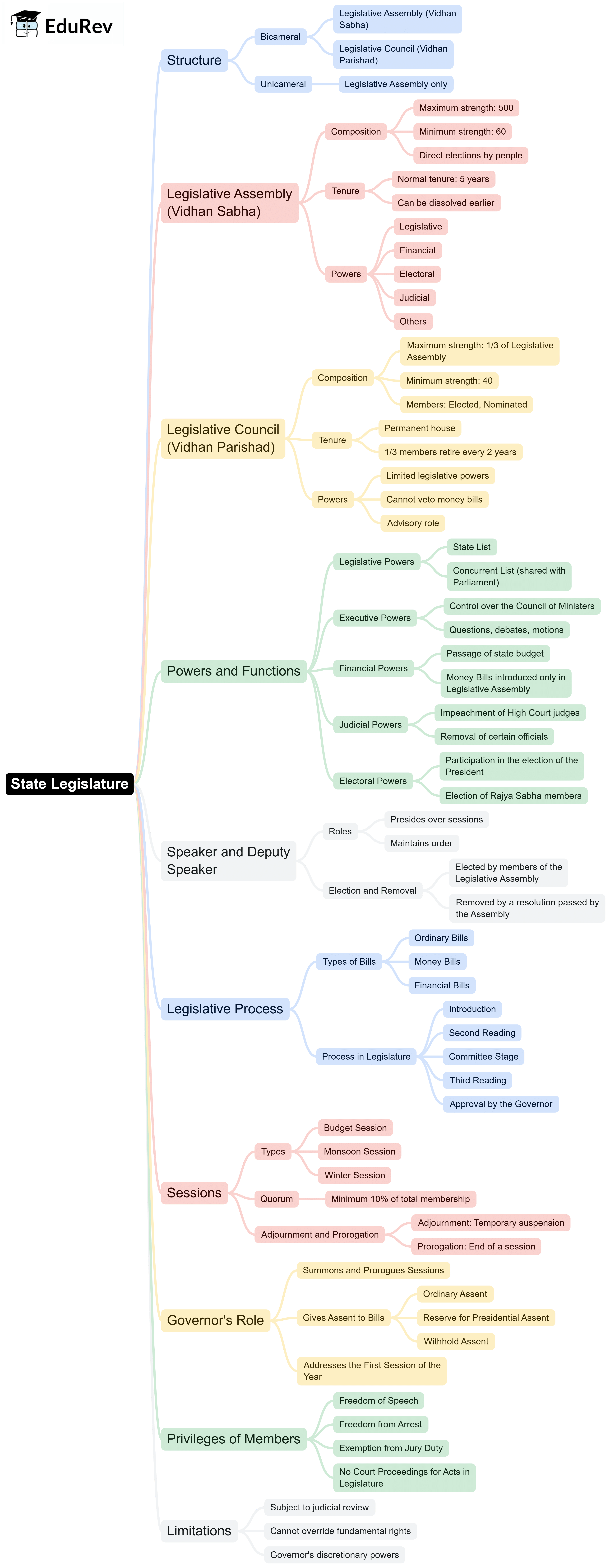
The document Mindmap: State Legislature | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
145 videos|630 docs|203 tests
|
FAQs on Mindmap: State Legislature - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the structure of the State Legislature in India? |  |
| 2. What are the main functions of the State Legislature? |  |
Ans. The main functions of the State Legislature include making laws on subjects enumerated in the State List and Concurrent List, approving the state budget, discussing and overseeing the executive's functioning, and representing the interests of the people. The State Legislature also has the power to amend the Constitution in relation to state matters.
| 3. How is the Chief Minister related to the State Legislature? |  |
Ans. The Chief Minister is the head of the government in a state and is usually the leader of the majority party in the Legislative Assembly. The Chief Minister is responsible for running the state's administration and is accountable to the State Legislature. They must have the confidence of the majority in the Legislative Assembly to remain in office.
| 4. What role does the Governor play in the State Legislature? |  |
Ans. The Governor acts as the constitutional head of the state and plays a crucial role in the functioning of the State Legislature. They summon and prorogue the sessions of the Legislature, give assent to bills passed by the Legislature, and can also dissolve the Legislative Assembly. The Governor's role is largely ceremonial, but they also have the power to exercise discretion in certain situations.
| 5. What are the eligibility criteria for becoming a member of the State Legislature? |  |
Ans. To become a member of the Legislative Assembly, a candidate must be at least 25 years old, a citizen of India, and not disqualified under any law. For the Legislative Council, the age requirement is 30 years. Additionally, candidates must be elected through a specified electoral process, which varies depending on the house they seek to join.
Related Searches































