Revision Notes: Digestion & Absorption | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Digestion |

|
| Human Digestive System |

|
| Digestion of Food |

|
| Disorders of the Digestive System |

|
Digestion
- The process of conversion of complex food substances to simple absorbable forms is called digestion.
- Intracellular: When the process of digestion occurs within the cell in the food vacuole, then it is termed Intracellular Digestion.
Examples: Protozoa, Porifera, Coelenterata, and free-living Platyhelminthes - Extracellular: When the process of digestion occurs outside the cell, then it is termed Extracellular Digestion.
Examples: Coelenterates and phylum Platyhelminthes to phylum Chordata.
Digestion in vertebrates occurs in the digestive tract or alimentary canal.
- The various parts involved in digestion can be broadly grouped in two groups:
(a) Digestive tract or alimentary canal
(b) Digestive glands - On the basis of the embryonic origin, the alimentary canal of vertebrates can be divided into three parts:
(i) Fore gut / Stomodaeum: Ectodermal. It includes buccal cavity / oral cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach and small part of duodenum.
(ii) Mid gut/Mesodaeum: Endodermal. It includes small intestine and large intestine.
(iii) Hind gut/Proctodaeum: Ectodermal. It includes the anal canal and anus.
Human Digestive System
- The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that processes food.
- It converts ingested food so that it can be assimilated by the organism.
The human digestive system consists of following parts: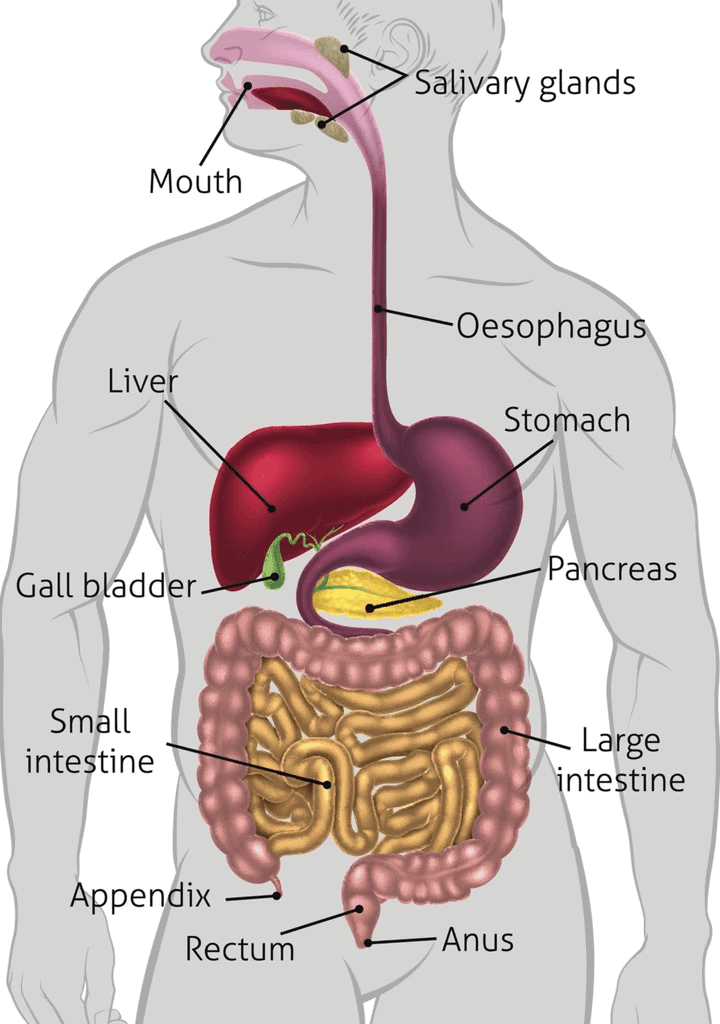 Human Digestive System
Human Digestive System
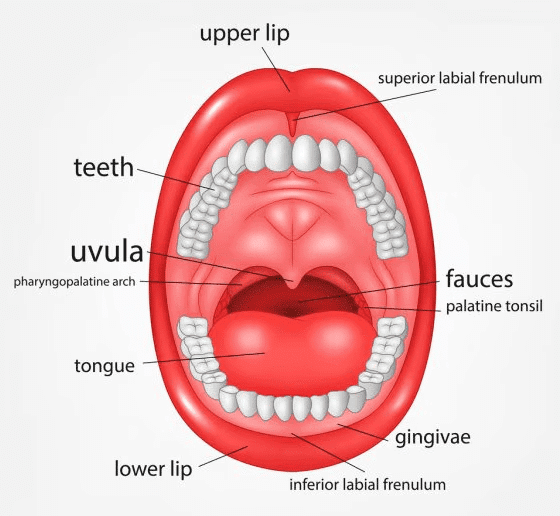
1. Mouth
- Mouth is also known as the oral cavity or buccal cavity.
- It is the first portion of the alimentary canal.
- Food and saliva are received by mouth.
- Mouth has inner lining of mucous membrane epithelium.
2. Digestive Glands
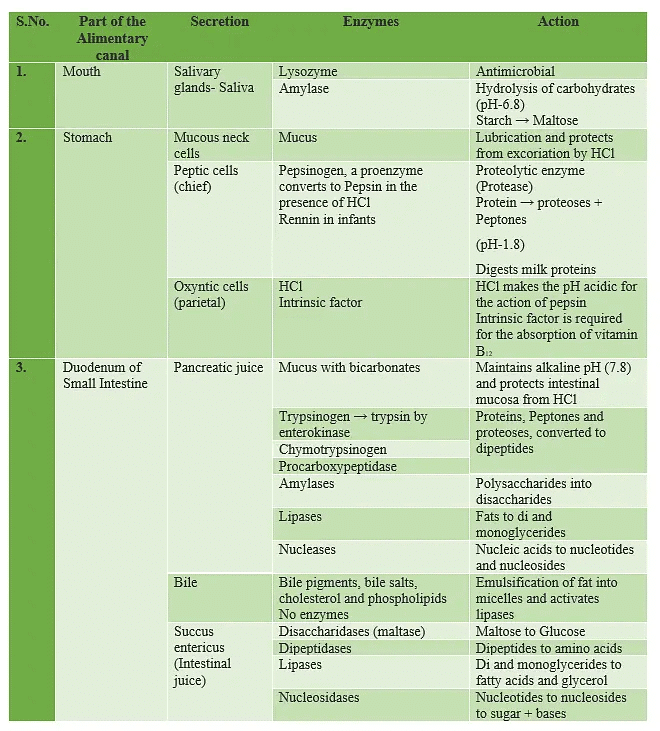
(i) Salivary Glands- These are the exocrine glands that produce saliva.
- These are the glands with ducts which also secrete amylase.
- Amylase is an enzyme that breaks down starch into maltose.
- Three types of salivary glands are:
(a) Parotid Gland
(b) Submandibular Gland
(c) Sublingual Gland
(ii) Gastric Glands
- The gastric glands (fundic gland) secrete acids and digestive enzymes.
- Secretion of gastric gland is called gastric juice.
- There are approximately 35 million gastric glands present in human stomach.
(iii) Intestinal Glands
- Intestinal glands in mammals is a collective name for crypts of Liberkuhn (secretes alkaline enzymatic juice) and Brunner’s glands (secrete mucous).
- Intestinal glands secrete intestinal juice or succus entericus.
(iv) Pancreas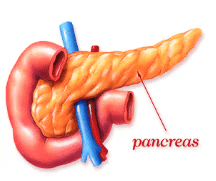
- Pancreas has two different kind of tissue- exocrine and endocrine.
- Pancreatic secretion is stimulated by cholecystokinin and secretin both.
- Complete digestive juice is pancreatic juice as it contains amylolytic, lipolytic and proteolytic enzymes.
- It produces several important hormones like insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide.
(v) Liver
- Liver is the largest digestive gland of the body, weighing about 1.2 to 1.5 Kg in an adult human.
- It is situated in the abdominal cavity, just below the diaphragm and has two lobes (small left and large right lobe).
- The liver has a wide range of functions to perform in the body:
(a) It detoxifies various metabolites.
(b) It helps in protein synthesis.
(c) Various biochemical necessary for digestion are produced by liver.
3. Pharynx
- It is the opening of oral and nasal cavities.
- It is classified as:
(i) Nasopharynx
(ii) Oropharynx
(iii) Laryngopharynx
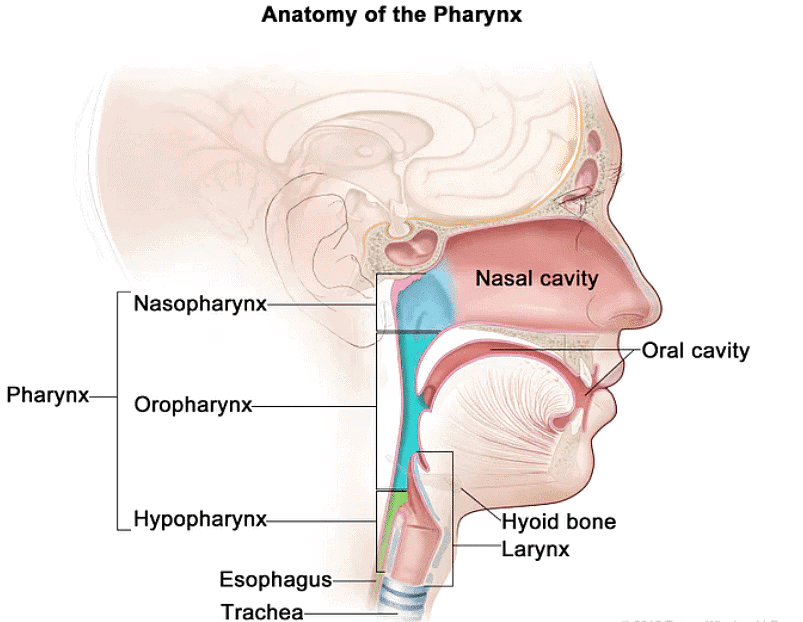
4. Oesophagus
- Oesophagus connects pharynx with stomach. Opening of oesophagus is regulated by gastro-oesophageal sphincter.
5. Stomach
- It is a J-shaped, muscular, hollow and dilated part of the digestive system. It is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine.
- It has 1 liter capacity. It secretes protein-digesting enzymes (proteases) and strong acids which aid in food digestion.
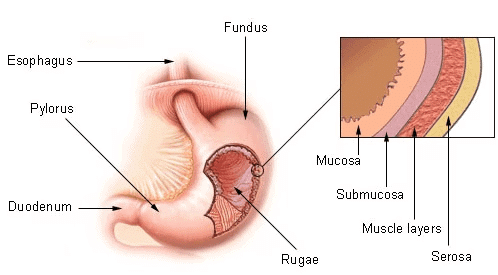
- The stomach has three parts:
(i) Cardiac: The part of the stomach into which oesophagus opens.
(ii) Fundus: It is the air-filled portion of stomach.
(iii) Pyloric: The portion of the stomach that opens into the small intestine.
6. Small Intestine
- It is the part of the gastrointestinal tract that comes after the stomach and is followed by the large intestine.
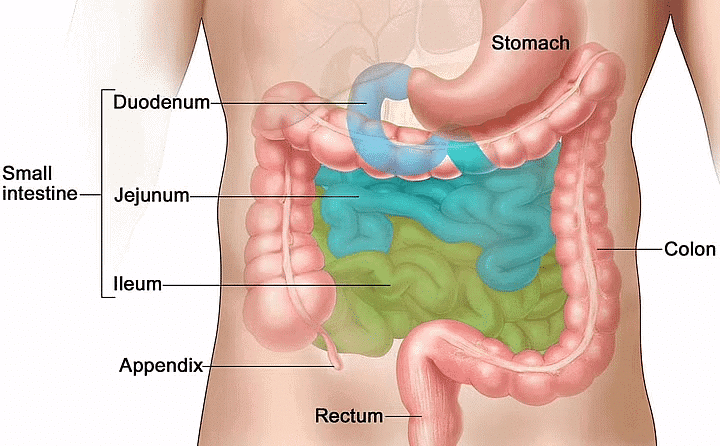
- Small intestine distinguished into three parts:
► Duodenum: It is ‘U’ shaped first part of the small intestine.
► Jejunum: It is the longer, coiled middle portion.
► Ileum: Ileum is the highly coiled posterior part of the small intestine.
7. Large Intestine
Large intestine consists of three parts:
(i) Caecum: It is a small blind sac. Vermiform appendix is a finger-like blind tubular projection of caecum.
(ii) Colon: The Caecum opens into colon. Colon has three distinct parts-
- Ascending colon
- Transverse colon
- Descending colon
(iii) Rectum: It is the final straight portion of the large intestine.
Digestion of Food
The digestion of food starts from the mouth itself. The masticated food mixed with saliva makes a small mass of food called a bolus. The bolus moves to pharynx and oesophagus by the process of deglutition (swallowing). Various enzymes get mixed with the food at different parts of the alimentary canal and facilitate digestion.
Disorders of the Digestive System
Many bacterial, protozoan, parasitic and viral infections cause inflammation of the intestine. Some of the common disorders are jaundice, vomiting, diarrhoea, constipation, indigestion, etc.
The diseases due to malnutrition are very common in developing and underdeveloped countries.
- Protein Energy Malnutrition (PEM) causes Marasmus and Kwashiorkor in infants and children.
- Marasmus- It is due to a deficiency of protein and calories intake. The condition is characterised by thinning of limbs, extreme emaciation, dry and wrinkled skin and mental impairment.
- Kwashiorkor- It is due to a deficiency of protein. There is wasting of muscles, but some fat is still present under the skin. The condition is characterised by swelling and extensive edema of body parts.
|
90 videos|490 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Digestion & Absorption - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main organs involved in the human digestive system? |  |
| 2. How does the digestion of food occur in the human body? |  |
| 3. What are some common disorders of the digestive system? |  |
| 4. What is the role of enzymes in the digestion process? |  |
| 5. How is nutrient absorption facilitated in the small intestine? |  |




















