CTET & State TET Exam > CTET & State TET Notes > Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams > Mind Map: Number System
Mind Map: Number System | Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
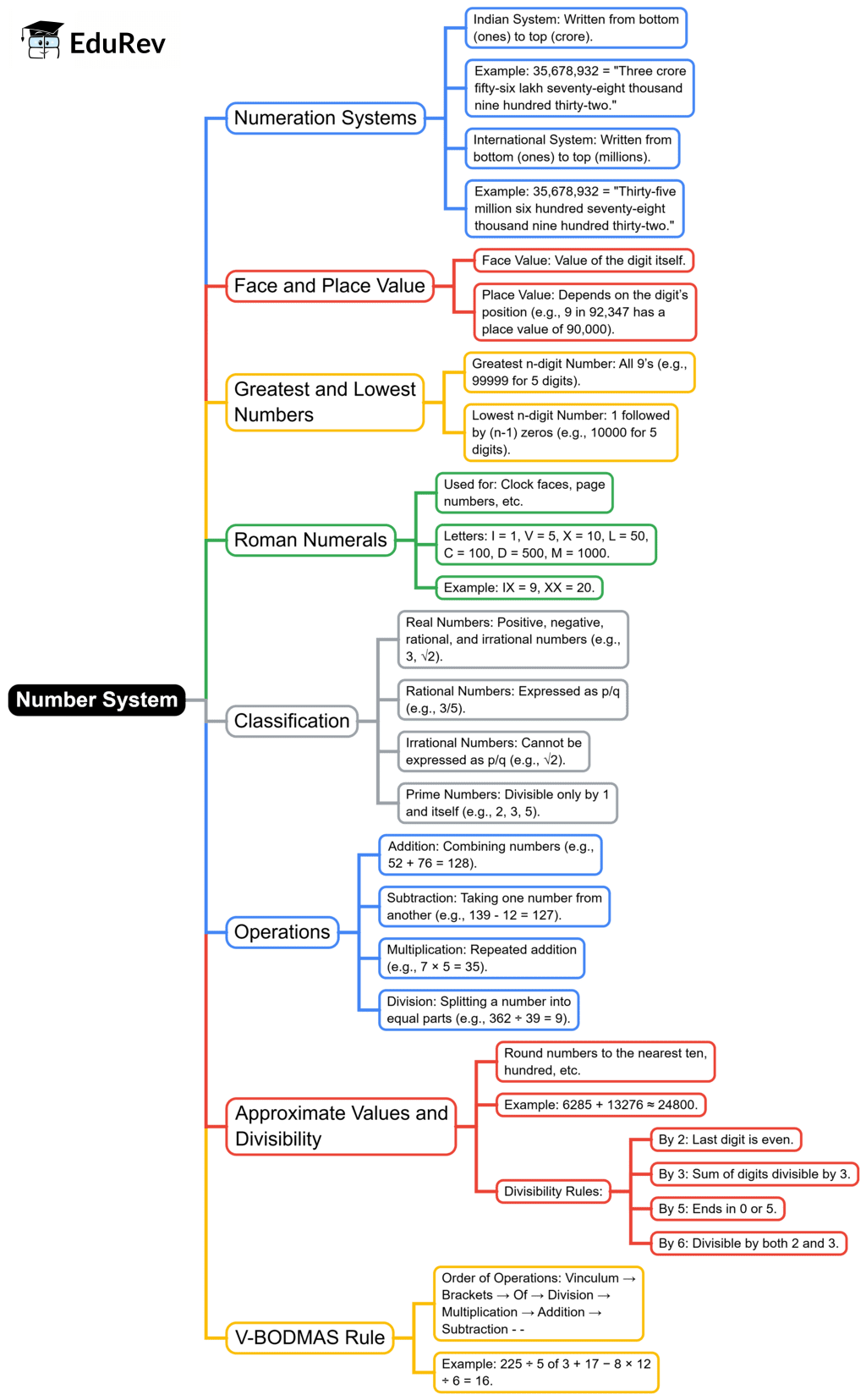
The document Mind Map: Number System | Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET is a part of the CTET & State TET Course Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams.
All you need of CTET & State TET at this link: CTET & State TET
|
82 videos|273 docs|69 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Number System - Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are the different types of number systems? |  |
Ans. The main types of number systems include natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. Natural numbers are the counting numbers (1, 2, 3, ...), whole numbers include natural numbers and zero, integers encompass whole numbers and their negative counterparts, rational numbers can be expressed as fractions, and irrational numbers cannot be expressed as fractions. Real numbers include both rational and irrational numbers.
| 2. How do you convert a decimal number to a binary number? |  |
Ans. To convert a decimal number to binary, divide the number by 2 and record the quotient and the remainder. Continue dividing the quotient by 2 until you reach 0. The binary representation is formed by writing the remainders in reverse order. For example, to convert the decimal number 10: 10 ÷ 2 = 5 (remainder 0), 5 ÷ 2 = 2 (remainder 1), 2 ÷ 2 = 1 (remainder 0), 1 ÷ 2 = 0 (remainder 1). Reading the remainders from bottom to top gives you 1010 in binary.
| 3. What is the importance of number systems in mathematics? |  |
Ans. Number systems are crucial in mathematics as they provide a framework for understanding and representing quantities. They help in performing arithmetic operations, solving equations, and understanding concepts such as limits and continuity in higher mathematics. Number systems also form the basis for various applications in computer science, engineering, and economics.
| 4. Can you explain the difference between rational and irrational numbers? |  |
Ans. Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero (e.g., 1/2, -3, 0.75). Irrational numbers, on the other hand, cannot be expressed as simple fractions, and their decimal expansions are non-repeating and non-terminating (e.g., √2, π). This distinction is fundamental in understanding the completeness of the number line.
| 5. How are real numbers represented on the number line? |  |
Ans. Real numbers are represented on the number line as points corresponding to each number's value. The line extends infinitely in both directions, with positive numbers to the right of zero and negative numbers to the left. The density property of real numbers means that between any two real numbers, there are infinitely many other real numbers, which allows for precise measurements and calculations.
Related Searches





















