Weekly Current Affairs (8th to 14th January 2025) Part - 1 | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
10 Years of UJALA and SLNP

Why in News?
- The Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All (UJALA) scheme, launched on 5th January 2015, marks its 10th anniversary as a transformative initiative in energy efficiency. UJALA has revolutionized household lighting, significantly reduced energy consumption, and contributed to India's environmental sustainability goals. The Street Lighting National Programme (SLNP), launched alongside UJALA, aims to replace conventional streetlights with energy-efficient Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs).
Key Takeaways
- The UJALA Scheme promotes energy efficiency by replacing traditional lighting systems with energy-saving LED bulbs.
- Over 36.87 crore LED bulbs have been distributed, leading to substantial energy and cost savings.
Additional Details
- UJALA Scheme: Launched in January 2015, the UJALA Scheme aims to save 85 lakh kWh of electricity and reduce 15,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide by replacing 77 crore traditional bulbs and 3.5 crore street lights with LEDs.
- Need for UJALA: Lighting accounts for approximately 18-27% of residential electricity use in India, with a significant reliance on less efficient lighting technologies.
- Efficiency of LEDs: LEDs save up to 90% energy compared to incandescent lamps (ICLs) and 50% compared to compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs).
- Key Features of UJALA: The cost of LED bulbs distributed under UJALA was reduced to Rs 70 per bulb from Rs 450 in 2014.
- Progress and Achievements: The initiative has led to annual energy savings of 47,883 million kWh, cost savings of Rs. 19,153 crore, and a reduction of 3.88 million tonnes of CO2 emissions.
Key Facts About Street Lighting National Programme
- Objectives: The SLNP aims to reduce energy consumption, lower operational costs for municipalities, and promote the transition to energy-efficient appliances.
- Implementing Agency: EESL collaborates with Urban Local Bodies (ULBs), Municipal Bodies, and Gram Panchayats (GPs) to execute the programme.
- Business Model: EESL covers initial costs, recovering investments through payments from municipalities, while ensuring 95% uptime for LED streetlights.
Comparison of ICLs, CFLs and LEDs
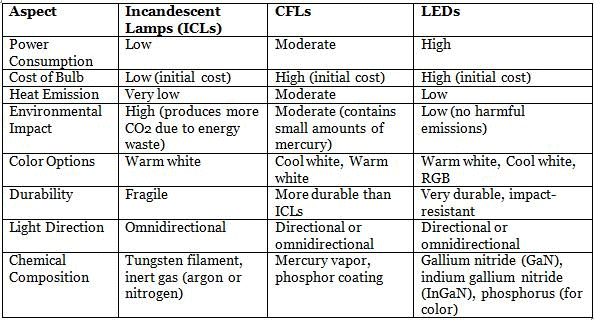
The UJALA scheme and SLNP have significantly advanced India's energy efficiency and sustainability objectives, leading to reductions in energy consumption and carbon emissions, while also generating economic savings. These government-led initiatives illustrate the impactful efforts towards a greener, energy-efficient future.
Mains Question:
- Examine the role of government-led initiatives such as the UJALA and SLNP schemes in addressing energy efficiency challenges in India.
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2023-24
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has issued the factsheet for the Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2023-24, which offers significant insights into consumption trends and the economic welfare of households in India.
Key Takeaways
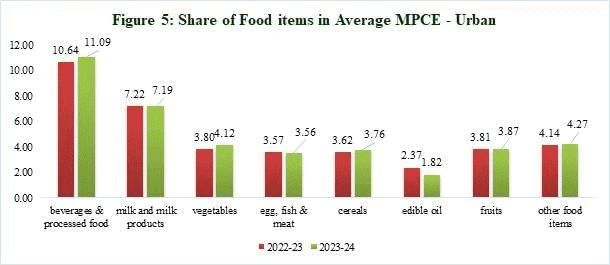
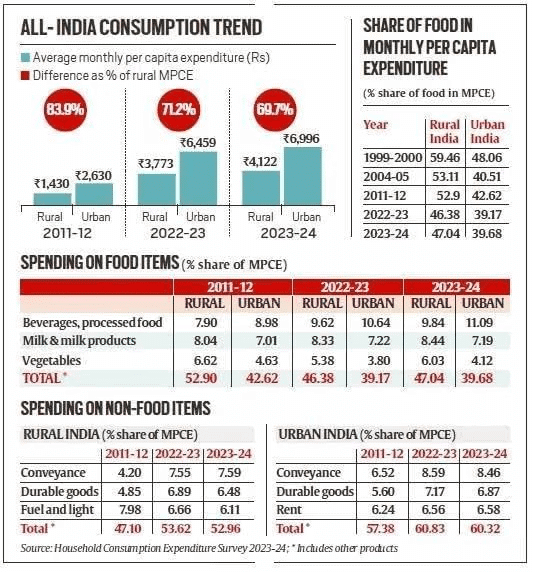
- Rising Consumption: There has been a notable increase in rural consumption, with the average monthly per capita expenditure (MPCE) rising to Rs 4,122, an increase of 9.3% from Rs 3,773 in 2022-23. Urban MPCE reached Rs 6,996, up by 8.3% from Rs 6,459 in the previous year.
- Narrowing Gap: The disparity in consumption between rural and urban areas has decreased from 83.9% in 2011-12 to 69.7% in 2023-24, indicating that rural consumption is growing at a faster pace.
- Regional Disparities: Sikkim recorded the highest MPCE, while Chhattisgarh had the lowest, highlighting significant regional differences in consumption.
- Consumption Inequality: The Gini coefficient for consumption inequality has decreased in both rural (from 0.266 to 0.237) and urban areas (from 0.314 to 0.284).
- Food and Non-Food Expenditure: Food expenditure increased in both rural (47.04%) and urban (39.68%) areas, with high spending on beverages, processed foods, and vegetables. Non-food expenditure comprised 52.96% in rural and 60.32% in urban areas.
- Fractile Consumption Patterns: Consumption spending decreased for the wealthiest 5% while significantly increasing for the bottom 5%, suggesting economic improvement for lower-income groups.
Additional Details
- Regional Differences: States such as Bihar have lower consumption levels, necessitating targeted interventions in education, healthcare, and employment to stimulate economic activity.
- Policy Implications: Rising rural consumption signals the success of welfare schemes like PM-KISAN and MGNREGA, suggesting that further policy support is needed to sustain this growth.
- Sectoral Shifts: Increased spending on services indicates a shift towards a service-driven economy, necessitating policies that focus on skill development.
- Urban Planning Needs: High urban expenditure on rent underscores the necessity for affordable housing and improved public transport infrastructure.
The findings of the HCES 2023-24 highlight important trends in consumption patterns and economic well-being in India. Policymakers need to consider these insights to create effective strategies for rural development, address regional disparities, and support the growing service sector to ensure sustainable economic growth.
Deciphering the Indus Valley Script
Why in News?
- Recently, the Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu, MK Stalin, announced a prize of USD 1 million for anyone who can successfully decipher the Harappan (Indus Valley) script. This has reignited interest in the longstanding mystery surrounding the Harappan script, which has resisted over 100 attempts by scholars to decode its meaning.
Key Takeaways
- The Indus Valley Script dates back to the Indus Valley Civilization (2600–1900 BCE) in present-day Pakistan and north-western India.
- This script remains undeciphered and was discovered in the 1920s by Sir John Marshall's archaeological team.
- Most inscriptions are short, with an average of 5 characters, raising questions about whether it represents a full language.
Additional Details
- Writing Style: Generally written from right to left, with longer texts occasionally using Boustrophedon style, where lines alternate directions.
- Brevity of Inscriptions: The short nature of the inscriptions has led to debates about the script's complexity and functionality.
- Nature of the Script: Likely a logosyllabic system that combines pictograms and syllables, similar to other ancient scripts.
- Theories About Its Language:
- Dravidian Hypothesis: Supported by researchers like Asko Parpola, suggesting connections to Old Tamil.
- Sanskrit Linkage: Early scholars like S.R. Rao linked it to the Vedic period, although this has been contested.
- Non-Linguistic Symbols: Some critics propose that the symbols served political, economic, or religious purposes rather than representing a language.
Challenges in Decipherment
- Lack of Bilingual Texts: The absence of bilingual inscriptions, akin to the Rosetta Stone, complicates the decipherment process.
- Short and Fragmentary Texts: The brevity of the inscriptions limits the ability to analyze grammar or patterns.
- Unknown Language: The script likely represents a language with no known descendants, creating challenges for linguistic comparison.
- Symbol Variations: Proposals for the number of signs in the script have varied widely, leading to confusion.
- Limited Archaeological Evidence: A small corpus of Harappan seals and unexplored sites hinder comprehensive analysis.
- Technological Constraints: Current AI and machine learning models face challenges with limited data and short inscriptions.
Significance of Deciphering the Indus Script
- Unlocking Harappan Language: Deciphering could identify the language family, offering insights into ancient India's linguistic roots.
- Understanding Harappan Culture: It may unveil religious beliefs, societal norms, and governance structures of the Harappans.
- Historical Continuity: Establishing connections between the Harappans and later civilizations could trace cultural and linguistic evolution in India.
- Global Relevance: The script's study contributes to understanding ancient writing systems and human communication evolution.
In conclusion, deciphering the Indus Valley Script holds significant potential for understanding the Harappan Civilization and its connections to later cultures, but several challenges remain that scholars must overcome.
Chhattisgarh Links Forest Ecosystem to Green GDP
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Chhattisgarh has become the first state in India to connect its forest ecosystem to the Green Gross Domestic Product (Green GDP). This innovative approach emphasizes the economic and environmental significance of forests, while focusing on biodiversity conservation and climate change mitigation. The initiative aligns with the broader goal of achieving sustainable development while promoting economic growth.
Key Takeaways
- Chhattisgarh is the first Indian state to link its forest ecosystem to Green GDP.
- The initiative underscores the importance of forests in economic and environmental contexts.
Additional Details
- What is Green Gross Domestic Product (Green GDP): Green GDP is a modified version of traditional GDP that takes into account the environmental costs of economic activities, including natural resource depletion and pollution. This approach provides a more accurate representation of a nation’s true wealth.
- Need for Green GDP: Traditional GDP measures economic output without considering sustainability or environmental degradation, whereas Green GDP ensures that economic growth aligns with sustainable practices.
- Formula: According to the World Bank, Green GDP is calculated as: Green GDP = NDP (Net Domestic Product) − (Cost of Natural Resource Depletion + Cost of Ecosystem Degradation).
What Does the Green GDP Link With Forests Mean for Chhattisgarh?
- Role of Forests in Chhattisgarh: The state recorded the highest increase in forest cover in the India State of Forest Report 2023, with 683.62 sq km of growth.
- Forests cover 44.2% of Chhattisgarh's geographical area and are crucial for carbon dioxide absorption, aiding in climate change mitigation.
- Forest products like tendu leaves, lac, honey, and medicinal plants significantly contribute to the rural economy.
- Chhattisgarh’s forests are integral to local tribal traditions and cultural heritage, with sacred groves revered as divine abodes.
Implications of Linking Forests with Green GDP
- This initiative emphasizes the economic and ecological value of forests, fostering a balance between development and sustainability.
- By prioritizing the preservation of natural resources, Chhattisgarh aims to ensure long-term environmental health for future generations.
How Does Green GDP Promote Sustainable Development?
- Sustainable Resource Use: Green GDP encourages responsible consumption, promoting sustainable production patterns.
- Climate Change Mitigation: It supports reducing reliance on fossil fuels and encourages renewable energy adoption.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Green GDP advocates for environmental preservation, safeguarding ecosystems and species.
- Incentivizes Green Investments: It promotes investment in sustainable technologies, driving inclusive and sustainable economic growth.
What Challenges Does the Green GDP Framework Face?
- Forest Cover Definition: The term "forest" in the India State of Forest Report includes plantations, which may not provide the same ecological benefits as natural forests.
- Political Agendas: Some states may manipulate data to secure funding, prioritizing plantations over natural forests, which can harm ecosystems.
- Local Body Integration: Lack of awareness among grassroots leaders makes it challenging to incorporate local bodies into the Green GDP framework.
- Lack of Clarity on Benefits: There is uncertainty regarding how Green GDP benefits will reach local communities, particularly tribes and forest dwellers.
- Methodological Differences: The absence of a universally accepted method for calculating Green GDP complicates comparisons across countries.
Way Forward
- A Clear Standard Framework: Governments should adopt consistent methodologies for calculating Green GDP.
- Public Scrutiny: Data transparency is essential to prevent manipulation and foster accountability.
- Prioritize Quality Over Quantity: Focus on restoring native forests and ecosystems for better environmental outcomes.
- Public Awareness: Educating communities about the benefits of Green GDP can enhance sustainability efforts.
In conclusion, Chhattisgarh's initiative to link its forest ecosystem with Green GDP represents a significant step towards integrating economic growth with environmental sustainability. This approach not only acknowledges the ecological value of forests but also sets a precedent for other states in India and beyond to follow.
Eradicating Manual Scavenging
 Why in News?
Why in News?
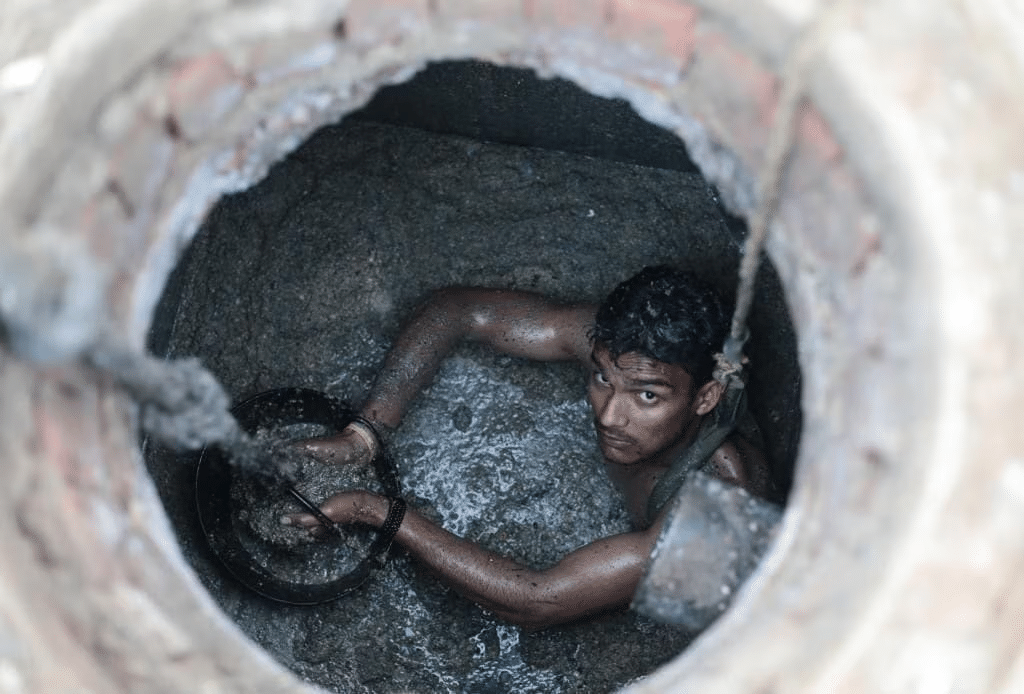
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) organized an open house discussion on 'Dignity and Liberty of the Individuals - Rights of Manual Scavengers'.
Key Takeaways
- Manual scavengers face serious health risks due to exposure to human waste.
- Social stigma and economic challenges keep manual scavengers trapped in poverty.
- Women manual scavengers experience double discrimination due to gender and societal stigma.
- The Supreme Court has provided guidelines to eradicate manual scavenging.
Additional Details
- Health: Manual scavengers are frequently exposed to human waste, leading to a high susceptibility to diseases such as Hepatitis, tetanus, and cholera. The presence of poisonous gases like hydrogen sulphide in septic tanks poses a serious asphyxiation risk, which can result in sudden death. Government data indicates that 377 persons died between 2019 and 2023 due to hazardous cleaning of sewers.
- Social Stigma: Manual scavengers are often treated as untouchables, which reinforces social exclusion and perpetuates the caste system.
- Economic Challenges: Manual scavengers receive meager pay, often below minimum wage, which keeps them in a cycle of poverty. They typically work on a contractual or daily-wage basis, lacking job security and benefits.
- Double Discrimination: Women represent a significant portion of manual scavengers and face both gender discrimination and societal stigma, including sexual harassment and exploitation.
- Psychological Issues: The stigma surrounding their profession often leads to mental health challenges such as anxiety and depression.
- Drug Use: To cope with the stress and stigma associated with their work, many manual scavengers resort to drug use, exacerbating their health problems.
Supreme Court Guidelines on Manual Scavenging
In the Dr. Balram Singh Case of 2023, the Supreme Court issued 14 directions to the Union, State, and Union Territories aimed at completely eradicating manual scavenging. Some of the key directives include:
- Eradication of Manual Sewer Cleaning: Implement phased measures to eliminate manual sewer cleaning.
- Rehabilitation of Sewage Workers: Provide compensation (Rs 30 lakhs for death, Rs 10-20 lakhs for disabilities), employment for the next of kin, and education for dependents.
- Accountability for Outsourced Work: Establish accountability mechanisms, including contract cancellations and penalties.
- NALSA Involvement in Compensation: NALSA will manage compensation disbursement models.
- Monitoring and Transparency: Create a portal to track deaths, compensation, and rehabilitation efforts.
Way Forward
- Mechanization: The introduction of automated or semi-automated equipment offers a safer and more efficient method for managing sanitation work. Robotic arms or vacuum trucks can perform this work remotely, minimizing human exposure to hazardous environments.
- OHS Standards: Recognizing sanitation work as a hazardous occupation under the Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code 2020 (OSH Code 2020) could greatly improve safety standards and enforcement.
- Health Screenings: Implement periodic health screenings for sanitation workers across all Urban Local Bodies (ULBs), focusing on respiratory and dermatological conditions, with clear treatment and prevention protocols.
- Expand the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM): Include the health and dignity of sanitation workers, emphasizing safety and empowerment.
- Capacity Building: Provide training and safety gear for workers. Offer financial assistance for technological innovations in hazardous waste cleaning. Incentivize mechanization, train workers, and empower women-led Self-Help Groups (SHGs) for sustainable livelihoods.
In conclusion, addressing the challenges faced by manual scavengers requires comprehensive reforms, strong judicial support, and a commitment to social equity and human rights.
Strengthening India-Maldives Defence Cooperation
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- India's Defence Minister Rajnath Singh has reinforced India’s commitment to bolstering the Maldives' defence capabilities during discussions with the Maldivian Defence Minister. This initiative aligns with India's "Neighborhood First" policy and aims to enhance bilateral security and defence cooperation between the two nations.
Key Takeaways
- India has a historical role as a primary defence partner for the Maldives.
- Recent efforts include providing defence equipment, training, and capacity building for the Maldives National Defence Force (MNDF).
Additional Details
- Historical Context: India has acted as a crucial ally in times of crisis, exemplified by Operation Cactus in 1988 and support during the 2004 tsunami. The SAGAR vision emphasizes India's proactive approach to regional security.
- Defence Projects: Key projects include infrastructure developments like the Composite Training Centre for MNDF and the construction of the Coast Guard "Ektha" Harbour. India also announced a free refit of the Maldivian Coast Guard Ship Huravee, representing mutual trust.
- Training and Capacity Building: Approximately 70% of MNDF's training needs are met by India, with over 1,500 personnel trained in Indian defence academies. Exercises like "Ekuverin" and trilateral exercises such as "Dosti" enhance operational synergy.
- Institutional Mechanisms: The Annual Defence Cooperation Dialogue (DCD) initiated in 2016 facilitates ongoing discussions on defence cooperation, with the latest meeting held in New Delhi in September 2024.
The significance of India-Maldives defence cooperation is profound, particularly in the context of regional security in the Indian Ocean. The Maldives' strategic location near critical shipping lanes enhances its importance as a partner for India.
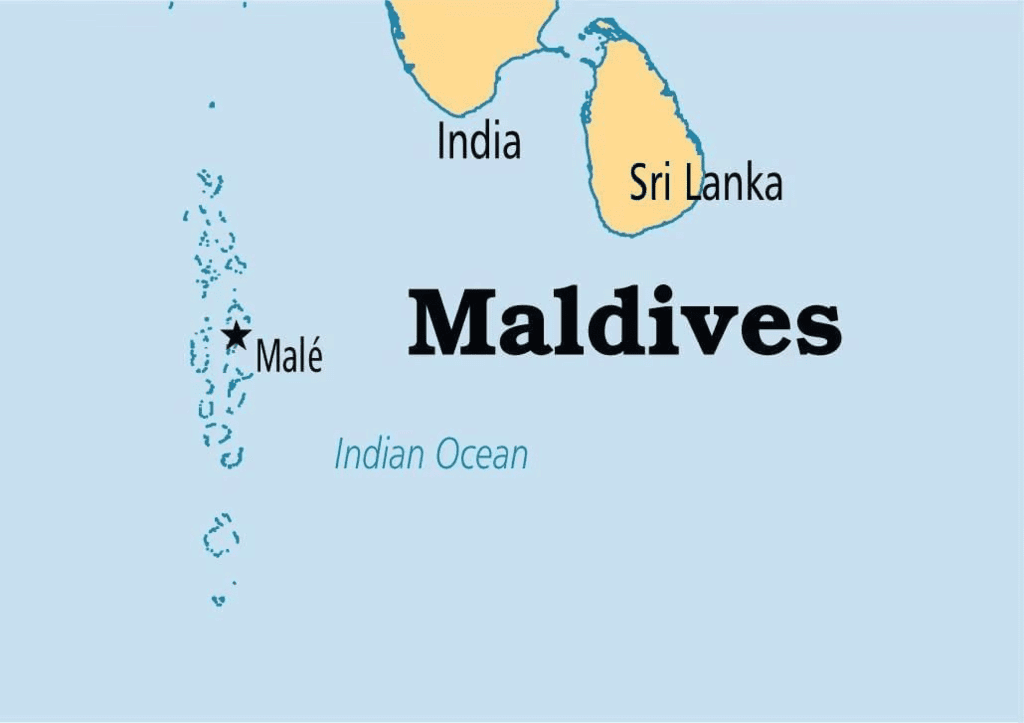
Geographical Significance
- The Maldives is situated at a pivotal point in the Indian Ocean, functioning as a "toll gate" between major chokepoints.
- About 50% of India's external trade and 80% of its energy imports pass through these routes, making the Maldives vital for maritime traffic monitoring and regional stability.
Economic and Social Benefits
- India provides essential supplies, including rice and medicines, and has played a crucial role during crises, such as the 2014 Male Water Crisis.
- India's humanitarian aid during disasters has reinforced its reputation as a reliable partner.
Countering External Influence
- India's cooperation with the Maldives serves to counteract the growing influence of external powers, notably China, thereby reinforcing India's leadership role in promoting regional peace.
Challenges in India-Maldives Defence Ties
- Geopolitical Rivalries: China's expanding presence through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative raises concerns for India, as Chinese investments challenge India's strategic dominance.
- Internal Political Changes: The "India Out" campaign in 2023 reflects rising anti-Indian sentiments and calls for the withdrawal of Indian military personnel, impacting defence priorities.
- Security Threat: The presence of radical Islamist groups in the Maldives poses a direct threat to India, potentially using the Maldives as a base for targeting Indian interests.
Way Forward
- Multilateral Collaboration: Encouraging Maldives' engagement in regional frameworks like the Indian Ocean Rim Association to enhance maritime security.
- Infrastructure Projects: Prioritize completion of key infrastructure initiatives to provide alternatives to Chinese investments.
- People-Centric Initiatives: Foster goodwill through civil-military projects, medical aid, and cultural exchanges to strengthen ties between the nations.
Mains Question:
- Discuss the significance of India-Maldives defence cooperation in the context of regional security in the Indian Ocean.
|
164 videos|798 docs|1153 tests
|
















