Gandhi's Role in Movement - Hobbies PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| A Leader Announces Himself |

|
| The Making and Unmaking of Non-cooperation |

|
| The Salt Satyagraha: A Case Study |

|
| Quit India |

|
| The Last Heroic Days |

|
| Timeline |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
Mahatma Gandhi, known as the 'Father of the Nation,' played a crucial role in India's fight for freedom. His methods of non-violent protest and civil disobedience inspired millions and reshaped the nationalist movement in India. This chapter explores Gandhi's activities from 1915 to 1948, his interactions with different sections of society, and the popular struggles he led.
A Leader Announces Himself
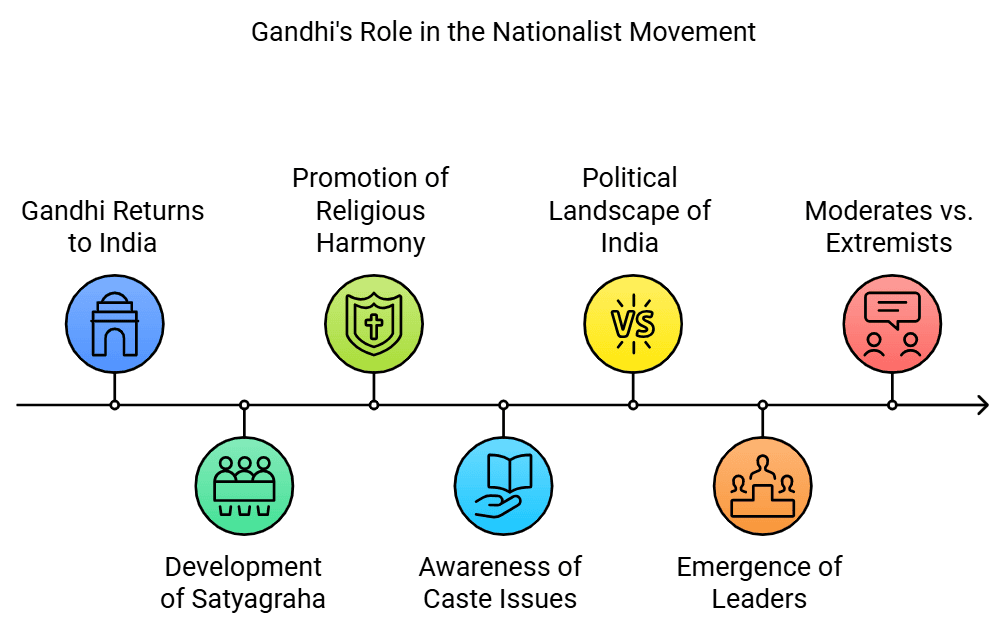
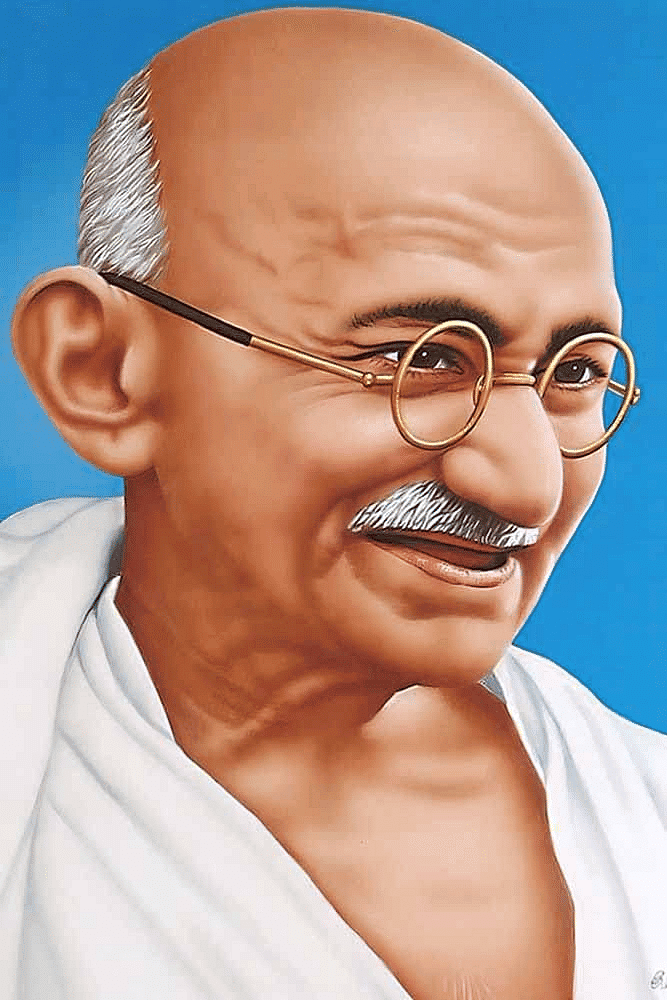
Return to India (1915)- Gandhi returned to India in January 1915 after two decades in South Africa, where he developed his method of non-violent protest called satyagraha.
- It was in South Africa that he initially worked to promote religious harmony and raised awareness among upper-caste Indians about the unfair treatment of lower castes and women through satyagraha.

Political Landscape of India
- In 1915, India was politically active with the Indian National Congress having branches in major cities and towns.
- Leaders like Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Bipin Chandra Pal, and Lala Lajpat Rai ("Lal, Bal, and Pal") had broadened the appeal of nationalism. These leaders supported military opposition against colonial rule.
- Moderates: unlike the other leaders, the moderates favored a slower and more convincing method, including Gandhi's political mentor, Gopal Krishna Gokhale and Mohammad Ali Jinnah.
First Major Public Appearance
- Gandhi's first significant public appearance in India was at the Banaras Hindu University (BHU) in February 1916.
- He criticized the Indian elite for their lack of concern for the laboring poor, emphasizing that India's salvation depended on addressing the plight of peasants.
Fun Fact
At the BHU event, many were surprised by Gandhi’s boldness as he was relatively unknown in India compared to his work in South Africa.
Key Insight
Gandhi's speech at BHU marked his intent to make Indian nationalism more representative of the common people, highlighting his commitment to social reform alongside political activism.
The Making and Unmaking of Non-cooperation
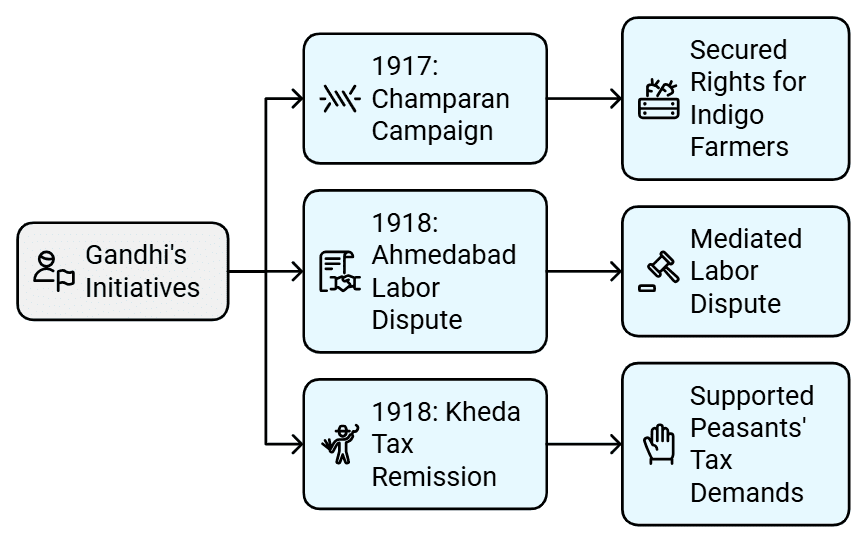
Early Initiatives- In 1917, Gandhi led a successful campaign in Champaran, Bihar, securing rights for indigo farmers against British planters.
- In 1918, he mediated a labor dispute in Ahmedabad and supported peasants in Kheda demanding tax remission due to crop failure.
Rowlatt Act and Jallianwala Bagh Massacre
- Gandhi called for a countrywide protest against the Rowlatt Act of 1919, leading to widespread unrest. In towns throughout North and West India, life stopped as shops closed, and schools shut down due to the bandh call.
- The Jallianwala Bagh massacre, where British troops killed hundreds of unarmed protesters, intensified nationalistic fervor.

Non-cooperation Movement (1920-1922)
- Gandhi launched the non-cooperation Movement, urging Indians to boycott British institutions and goods.
- The movement saw widespread participation, including strikes, boycotts, and acts of civil disobedience across India.
Knitting a Popular Movement
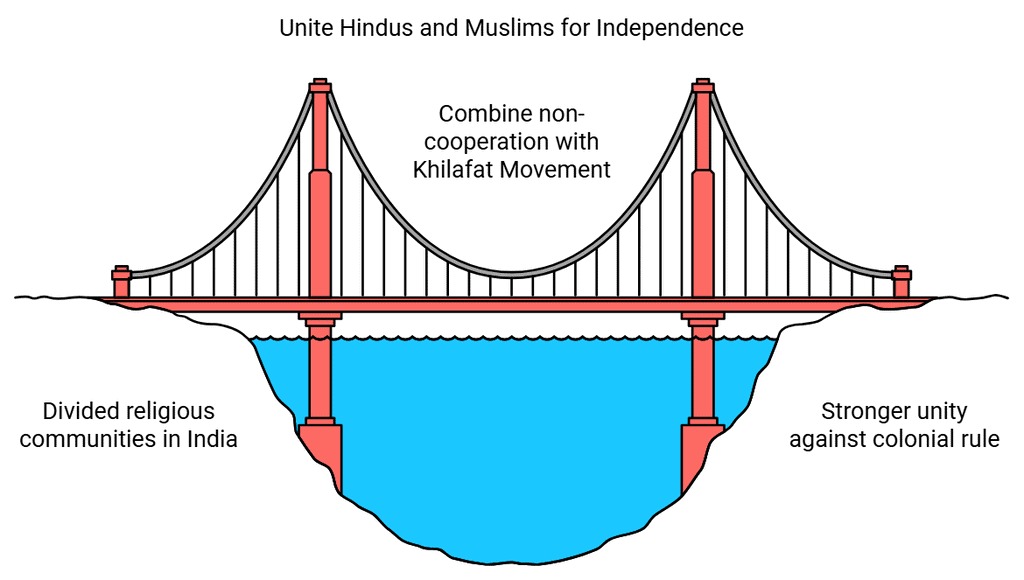
- Gandhi joined forces with the Khilafat Movement, which aimed to restore the Caliphate in Turkey.
- Gandhi's aim was to combine non-cooperation with the Khilafat movement so that India’s two major religious communities, Hindus and Muslims, could work together to end colonial rule.
- Both the movements gained massive support, with students, lawyers, workers, and peasants participating in large numbers.
- Non-cooperation was designed to be peacefully impactful: it involved refusal, giving up certain things, and practicing self-discipline.
- As a result, the foundations of the British Raj were shaken for the first time since the 1857 Revolt.
Chauri Chaura Incident
- In February 1922, violence erupted in Chauri Chaura, in the United Provinces (now, Uttar Pradesh and Uttaranchal), where a group of peasants attached a police station
- This led to Gandhi calling off the Non-cooperation Movement.
- He emphasized non-violence and suspended the movement to prevent further bloodshed.

Fun Fact
The Non-cooperation Movement saw students leaving schools and colleges, and lawyers giving up their practices to support the cause.
Challenges and Conclusion
- The Non-cooperation Movement was called off in 1922 after the violent incident at Chauri Chaura.
- Gandhi was arrested and sentenced to six years in prison but was released in 1924.
A People's Leader
- Gandhi transformed Indian nationalism into a mass movement, involving peasants, workers, and artisans from his BHU speech in 1916 to the conclusion of the non-cooperation movement in 1922.
- Many had started referring to Gandhi as their "Mahatma".
- Gandhi seemed to the Indian peasants like a savior who would free them from heavy taxes and harsh officials and restore their dignity and control over their lives.
- His simple lifestyle, symbolized by the dhoti and charkha, resonated with the common people.
- Gaining popularity among the wealthy: Among the rich Indian businessmen and industrialists, some had openly started supporting Gandhi while others did it tactfully while hiding from the British authorities.
- After his release from imprisonment in 1924, Gandhi diverted his attention to the promotion of Indian-made cloth khadi and the abolition of untouchability.
- Getting rid of social evils: Gandhi believed that to enjoy freedom, Indians needed to eliminate social issues like child marriage and untouchability.
Fun Fact
The mass nationalism movement that Gandhi started is also referred to as Gandhian nationalism.
Key Insight
Gandhi's non-cooperation campaign broadened the base of Indian nationalism, engaging peasants, workers, and other marginalized groups in the struggle for independence.
[Question: 1687984]
The Salt Satyagraha: A Case Study
Context and Strategy
- After his release from prison, Gandhi had focused solely on social reform work. By 1928, however, he started considering re-joining politics.
- Annual session of Congress in 1929: Jawaharlal Nehru was elected as President and the proclamation of commitment to “Purna Swaraj” was made
- On January 26, 1930, "Independence Day" was celebrated with the national flag raised at various locations and patriotic songs sung. Gandhiji provided detailed instructions on how the day should be observed.
- Soon after that day, Gandhi initiated the Salt Satyagraha to protest the British monopoly on salt production and sales.

Impact and Response
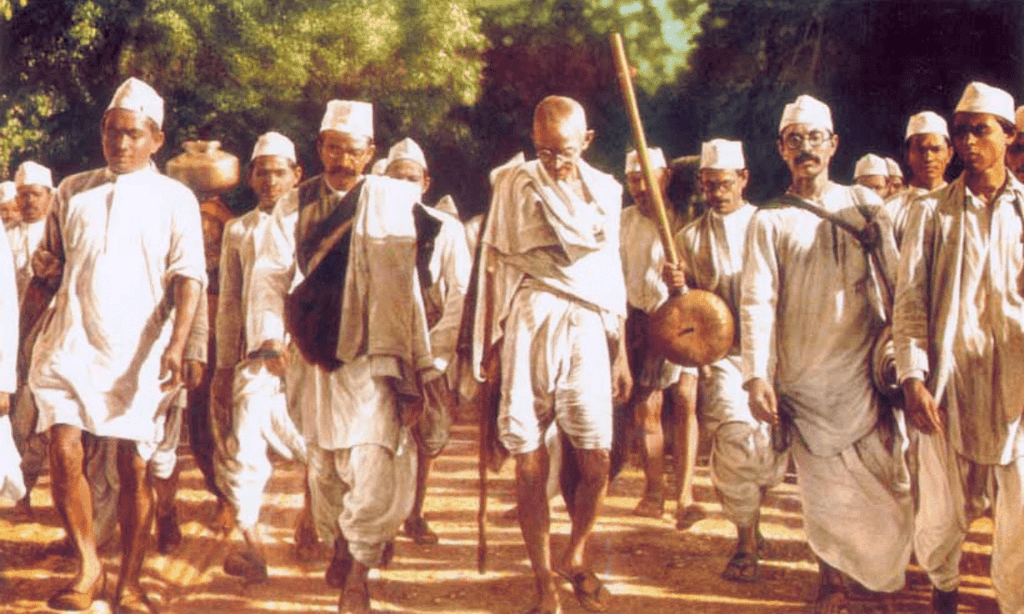
- The Dandi March, also known as the Salt March, began on March 12, 1930, and ended on April 6, 1930, with Gandhi making salt at Dandi. At the same time, similar salt marches were taking place in other parts of the country.
- The march to Dandi was a symbolic act to challenge British authority, as salt was a basic necessity for all Indians.
- The Salt March drew massive support and international attention, highlighting the unjust policies of the British Raj.
- The British response was severe, with mass arrests, including Gandhi himself.
Why the Salt Satyagraha?
- Salt was a vital commodity, and the British monopoly on its production and sale was deeply resented.
- By targeting the salt tax, Gandhi united people across different regions and social strata.
Progress of the March
- Gandhi's march from Sabarmati to Dandi attracted widespread attention.
- The police reports and international media coverage documented the growing support for the movement.
- There are reports of Gandhi being unwell but still gathering strength to march further, as well as documentation of his powerful speeches along the way.
 Importance of Salt (Dandi) March
Importance of Salt (Dandi) March
Fun Fact
Gandhi and his followers walked 240 miles during the Dandi March, gathering supporters and attention along the way.
Dialogues and Agreements
- The Gandhi-Irwin Pact was signed in 1931, leading to the suspension of the civil disobedience movement and the release of political prisoners.
- Gandhi attended the Second Round Table Conference in London in 1931, but it ended inconclusively, ending in Gandhi resuming the civil disobedience movement.
- in 1935, a new Government of India Act resulted in eight out of 11 provinces in India having a Congress “Prime Minister”, working under the supervision of a British Governor.
- In 1939, both Mahatma Gandhi and Jawaharlal Nehru offered to support the British in the Second World War, if the British agreed to grant India independence. The British refused the proposal, resulting in a various satyagrahas by the Congress in the following years.
- in 1940, Muslim League demanded autonomy for Muslim-majority areas.
[Question: 1687987]
Quit India
Background
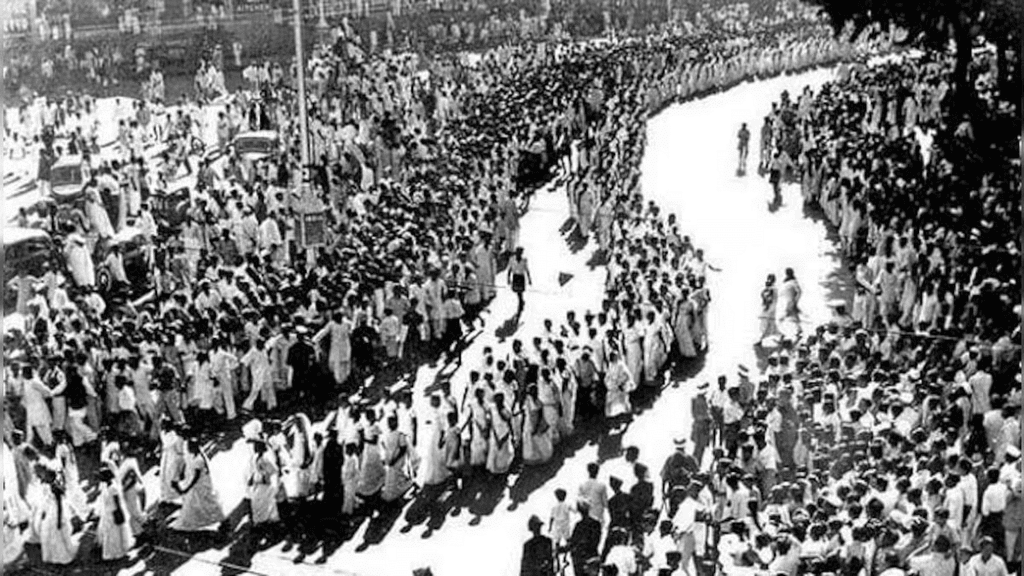
- Following the failure of the Cripps Mission in 1942, Gandhi launched the Quit India Movement, calling for an end to British rule.
- The movement was marked by widespread protests, strikes, and acts of sabotage.

Government Response and Outcome
- The British responded with repression, arresting thousands of activists, including Gandhi and other Congress leaders.
- Despite the crackdown, the Quit India Movement significantly intensified the demand for independence, setting the stage for India's eventual freedom.
Independent Governments
- In districts like Satara and Medinipur, parallel governments were established by local leaders, showcasing the widespread support for the movement.
Rise of the Muslim League
- While Congress leaders were in jail, Jinnah and his Muslim League colleagues were carefully working to broaden their influence.
- On being released from jail in 1944, Gandhi conducted several meetings with Jinnah in an effort to bridge the divide between the Congress and the League.
- However, in the 1946 election results for provinces, the divide between the religions was clear.
- Direct Action Day: Jinnah called for a "Direct Action Day" on 16 August 1946 to push for the League’s demand for Pakistan. As a result, violent riots erupted in many parts of the country. Both Hindus and Muslims suffered.
Division Announced
- Mountbatten, on coming into power in February 1947, called for one final round of talks, but when these also failed to produce results, he announced that British India would be both freed and divided.
- The formal transfer of power was set for August 15.
Fun Fact
The slogan "Do or Die" became popular during the Quit India Movement, inspiring many to join the struggle.
The Last Heroic Days
Efforts for Communal Harmony
- Gandhi worked tirelessly to restore peace between Hindus and Muslims during the partition of India.
- He undertook a fast to bring about reconciliation and ensure the safety of minorities.
- A resolution was passed on "the rights of minorities" with efforts by Gandhi and Nehru
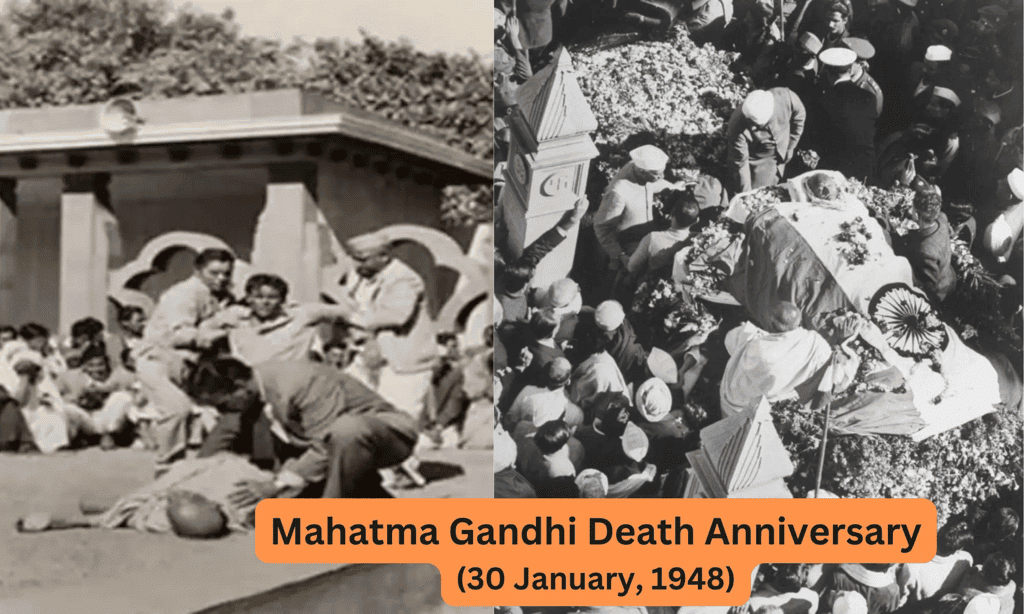
Assassination and Legacy
- Gandhi was assassinated on January 30, 1948, by Nathuram Godse.
- His death was mourned globally, and his principles of non-violence and social justice continued to inspire movements worldwide.
Fun Fact
Gandhi's last words were "Hey Ram," which reflected his deep spiritual beliefs.
[Question: 1687989]
6. Knowing Gandhi
Public Voice and Private Scripts
- Gandhi's writings and speeches provide insights into his public and private thoughts.
- His letters reveal his interactions with associates and adversaries, reflecting his ideals and strategies.
Framing a Picture
- Gandhi's autobiography, "The Story of My Experiments with Truth," offers a personal account of his life and principles.
- Autobiographies offer a personal view of historical events, shaped by the author's perspective and memory.
- Gandhi's autobiography and the writings of his contemporaries help frame a comprehensive picture of his life and impact.

Through Police Eyes
- Government records and police reports offer an official view of Gandhi's activities and their impact.
- These records reveal the British authorities' concerns about the nationalist movement.
Newspapers
- Newspapers from the period covered Gandhi's movements and public reactions.
- They provide contemporary accounts of his campaigns and their reception by different sections of society.
Timeline
- 1915: Gandhi returns to India from South Africa.
- 1917: Champaran Satyagraha.
- 1918: Ahmedabad Mill Strike and Kheda Satyagraha.
- 1919: Rowlatt Act protests and Jallianwala Bagh massacre.
- 1920-1922: Non-cooperation Movement.
- 1930: Salt Satyagraha.
- 1942: Quit India Movement.
- 1947: Indian independence.
- 1948: Gandhi's assassination.
[Question: 1687992]
Conclusion
Mahatma Gandhi's leadership was vital in India's independence movement. His dedication to non-violence, social justice, and communal harmony continues to inspire movements for peace and justice around the world, making him a timeless figure in history.













