Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 31st January 2025) Part - 1 | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
Breast Cancer’s Economic Impact in India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Recent studies have highlighted a disturbing increase in the incidence of breast cancer cases in India, projecting an addition of 50,000 new cases each year. The anticipated economic burden of these cases is estimated to surge to approximately $19.55 billion annually by 2030, underscoring the urgent requirement for strategic healthcare interventions and policy reforms.
Key Takeaways
- Breast cancer incidence in India is rising at a rate of 5.6% per year.
- The age-standardized incidence rate for females increased by 39.1% from 1990 to 2016.
- Younger women in India are particularly affected compared to their counterparts in Western countries.
Additional Details
- Economic Burden: The financial impact of breast cancer is projected to rise from $8 billion in 2021 to $19.55 billion by 2030, based on the autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model.
- Patient Financial Strain: Many patients experience significant financial difficulties. A survey of 500 patients indicated that rural and economically disadvantaged families are the most affected, with only 9% having health insurance coverage.
- Contributing Factors: Factors influencing breast cancer rates include genetic predisposition, obesity, poor lifestyle choices, and environmental influences. Co-morbidities such as hypertension and diabetes complicate treatment and raise costs.
- Survival Rates: Survival rates for breast cancer patients in India are lower than those in Western nations, primarily due to late-stage diagnoses, delays in treatment initiation, and fragmented healthcare services.
- Policy Recommendations: Experts suggest policy interventions to alleviate economic burdens, advocating for routine screenings for high-risk populations and increased health insurance coverage for preventive care.
- Healthcare System Improvements: The study emphasizes the need for increased healthcare budgets to manage the growing breast cancer burden, advanced treatment options in rural areas, and the introduction of AI-based detection methods.
- Community Health Initiatives: Promoting healthier lifestyles through balanced nutrition and regular exercise is crucial for reducing breast cancer incidence. Initiatives should also focus on early detection and diagnosis to enhance patient outcomes.
The rising incidence of breast cancer in India presents a significant health challenge with profound economic implications. Strategic interventions and community awareness programs are essential to address this growing concern effectively.
Nitrogen Pollution and Management
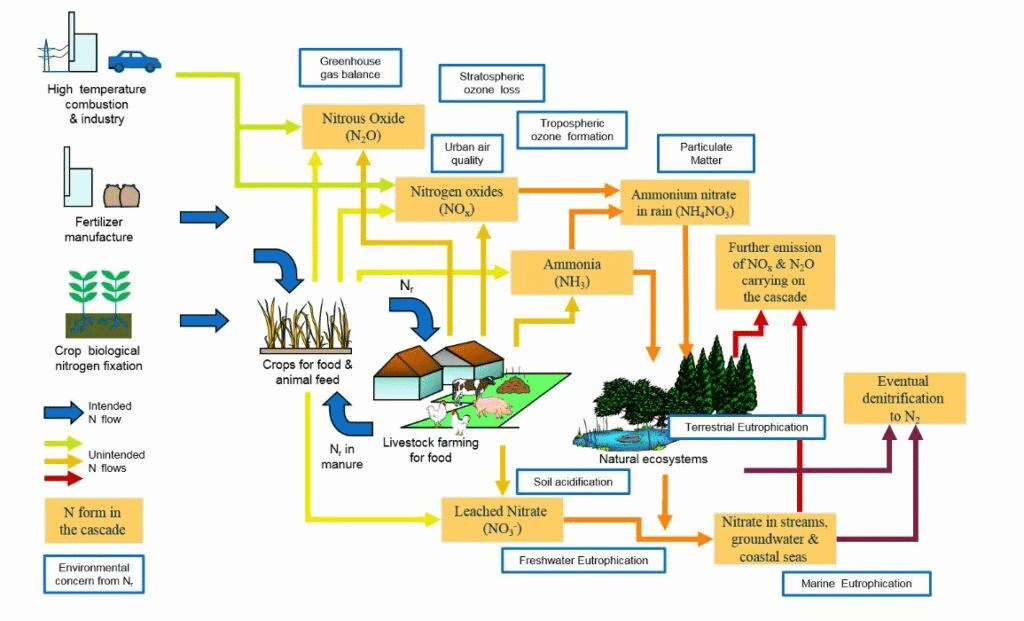 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Recent reports indicate a significant increase in reactive nitrogen deposited on the Earth's surface, primarily due to anthropogenic activities. This increase has doubled compared to pre-industrial levels, with projections forecasting further rises due to climate change. The Food and Agriculture Organization has underscored the urgent need to enhance nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) to lessen environmental repercussions.
Key Takeaways
- Humans contribute approximately 150 teragrammes (Tg) of reactive nitrogen each year, mainly from agriculture and industry.
- Livestock accounts for about one-third of total nitrogen emissions.
- Global nitrogen flows have surpassed safe environmental thresholds, necessitating tailored regional nitrogen management policies.
- Nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) has improved from 40% in the 1980s to 56% in 2022, with regional and crop variations.
- Nitrogen pollution is most critical in North America, Western Europe, and parts of Asia due to extensive fertilizer use.
- Without intervention, nitrogen contributions may surge to 600 Tg annually by 2100, escalating risks to air, water, and soil quality.
Additional Details
- Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE): This metric reflects the ratio of nitrogen recovered in outputs relative to the inputs used. For instance, soybeans exhibit high NUE, while fruits and vegetables display lower efficiency.
- The report recommends that the fertilizer industry reduce greenhouse gas emissions and encourages biological nitrogen fixation through the use of leguminous crops.
- National governments are advised to adopt best practices for manure management and promote organic nitrogen fertilizers.
- Policies must prioritize sustainable nitrogen management within agrifood systems, including spatial planning to redistribute livestock and embracing circular bioeconomy approaches.
- Global commitments to curtail nitrogen pollution are vital for achieving biodiversity and climate goals.
In conclusion, immediate actions are needed to enhance nitrogen use efficiency and mitigate the environmental impacts of nitrogen pollution. Addressing these challenges is essential for the sustainability of ecosystems and the protection of human health.
US Withdrawal from OECD Global Tax Deal
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- On January 23, 2025, shortly after assuming office, US President Donald Trump issued an executive order to withdraw the United States from the OECD’s global tax deal. This agreement, which aimed to tackle tax avoidance by multinational corporations, has been temporarily shelved.
Key Takeaways
- The OECD Global Tax Deal addresses tax avoidance by multinational corporations.
- Two main pillars: Pillar 1 reallocates profits based on revenue generation; Pillar 2 sets a global minimum corporate tax rate of 15%.
- The US executive order criticizes the deal for impinging on US sovereignty and economic competitiveness.
- Experts warn that the US withdrawal will have significant implications for the global tax framework.
Additional Details
- OECD Global Tax Deal: The deal encompasses two pillars aimed at ensuring fair tax practices globally. Pillar 1 focuses on redistributing profits to the locations where business activities occur, while Pillar 2 establishes a baseline corporate tax rate.
- US Executive Order Details: The memorandum from President Trump highlights concerns that the global tax deal undermines U.S. sovereignty and restricts the nation’s ability to implement tax policies that benefit American businesses. As a result, the U.S. will not adhere to the terms of the agreement.
- Impact on Global Tax Landscape: With approximately 50 jurisdictions beginning to adopt the Global Anti-Base Erosion Model (GloBE) rules, the US withdrawal creates uncertainty and may lead these countries to reconsider their strategies.
- India’s Position: India has taken a cautious stance regarding the GloBE rules and has not made any legislative changes in response to the OECD deal. The elimination of the 2% equalization levy in the Union Budget 2024 indicates minimal expected impact on India’s tax collection due to the US withdrawal.
- Role of the OECD: The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) comprises 37 democracies, serving as a platform for developing policy standards that support sustainable economic growth and facilitate international collaboration.
In conclusion, the US's withdrawal from the OECD Global Tax Deal raises questions about future international tax cooperation and may compel other countries to reassess their tax policies in light of the changing global landscape.
33 Industrial Clusters Join WEF’s Transition Initiative
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- On January 23, 2025, thirteen new industrial clusters from diverse countries have become part of the World Economic Forum’s (WEF) Transitioning Industrial Clusters initiative. This expansion increases the total to 33 clusters across 16 nations, significantly enhancing global efforts aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions while fostering economic growth.
Key Takeaways
- The initiative aims to lower greenhouse gas emissions while promoting job creation and economic development.
- The participating clusters are concentrated hubs representing various industries and institutions.
- Collectively, the clusters can potentially reduce carbon dioxide-equivalent emissions by 832 million tonnes annually.
Additional Details
- Environmental Impact: The reduction in emissions is comparable to the total emissions produced by Saudi Arabia, highlighting the significance of regional collaboration for substantial environmental benefits.
- Economic Contributions: These industrial clusters contribute approximately $492 billion to the global GDP and support around 4.3 million jobs, indicating their crucial role in sustainable economic growth.
- New Additions: Notable new clusters include the Cartagena Industrial Cluster (Colombia) focused on clean hydrogen production and the Gopalpur Industrial Park (India) attracting investments in green energy.
- The report titled “Unleashing the Full Potential of Industrial Clusters – Infrastructure Solutions for Clean Energies” was developed in collaboration with Accenture and EPRI, outlining strategies for enhancing clean energy production.
- Experts emphasize collaboration among businesses and public institutions as essential for accelerating the deployment of net-zero infrastructure and securing funding for clean energy transitions.
The WEF aims to foster sustainable economies through partnerships and aligning regulatory strategies. By prioritizing economic development, job creation, and CO2 reductions, the initiative strives to transition industrial clusters towards achieving net-zero economies.
Sebi’s New When-Listed Trading Platform Explained
Why in News?
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (Sebi) is preparing to introduce a “when-listed” trading platform aimed at regulating the trading of shares during the period between their allotment in an initial public offering (IPO) and their formal listing on stock exchanges. This initiative seeks to address the widespread grey market activities associated with unlisted shares.
Key Takeaways
- The “when-listed” platform will enable investors to trade shares right after allotment, prior to official listing.
- This initiative is designed to provide a regulated trading environment, diminishing reliance on the unregulated grey market.
- The current three-day waiting period post-allotment encourages informal trading, which Sebi aims to eliminate.
Additional Details
- Grey Market: This refers to unofficial trading activities that occur before shares are listed on exchanges. Investors engage in buying and selling based on demand and speculative pricing, which can create volatility and misalign investor expectations.
- The current IPO timeline involves allotment on T+1 day and listing on T+3 days, creating a window for grey market trading.
- In the grey market, brokers establish a price band for the IPO and often add a premium, leading to inflated prices compared to the official listing. For example, an IPO priced at Rs 90-100 might see grey market premiums pushing prices to Rs 110-130.
The introduction of the “when-listed” trading facility is expected to enhance transparency and security by allowing investors to trade their allotted shares in a formalized market. This shift aims to stabilize market conditions and lessen the volatility stemming from speculative trading.
Market experts have voiced concerns regarding the risks posed by the grey market, emphasizing the need for a formal trading platform to legitimize trading activities and protect investor interests. While this new platform is a commendable step, there is a call for Sebi to further address grey market activities starting from the IPO announcement phase to ensure retail investors are safeguarded.
Rise in Guillain-Barré Syndrome Cases in Maharashtra

Why in News?
- As of January 24, 2025, Pune has reported a notable increase in the number of Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) cases, with 59 individuals diagnosed, 12 of whom require ventilator support. The Maharashtra health department is currently investigating this sudden surge. Health officials have indicated that while GBS can develop following infections, it is not associated with widespread outbreaks.
Key Takeaways
- 59 cases of Guillain-Barré Syndrome reported in Pune.
- 12 patients are on ventilator support.
- The health department is investigating the sudden rise.
Additional Details
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS): GBS is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system erroneously attacks the peripheral nerves, leading to symptoms such as weakness, numbness, and potentially paralysis. The precise cause remains elusive, but it is often preceded by infections.
- Types of GBS: The most prevalent form is Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP), commonly seen in North America and Europe. Other variations include Miller Fisher Syndrome (MFS), which involves eye-related paralysis, and Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy (AMAN), primarily found in regions like China and Japan.
- Symptoms: Initial symptoms often include tingling and weakness that typically start in the legs and feet, progressing to the upper body. Other potential symptoms involve difficulties with vision, swallowing, facial movements, and severe pain.
- Causes and Triggers: While the exact cause of GBS is unknown, approximately two-thirds of patients report having had preceding infections, such as respiratory or gastrointestinal illnesses. Notably, infections like COVID-19 and the Zika virus have been associated with GBS. The syndrome can affect individuals of any age but is more commonly seen in adults.
- Treatment Options: Although there is no definitive cure for GBS, treatment aims to alleviate symptoms and accelerate recovery. Therapies such as intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and plasmapheresis are used to reduce the severity of the syndrome. Many patients experience full recovery, although the process may take months to years.
- Public Health Response: The recent spike in GBS cases in Pune has led health authorities to closely monitor and investigate the situation. Public health initiatives are being implemented to raise awareness about the syndrome and its potential triggers, ensuring timely diagnosis and treatment for affected individuals.
This alarming rise in Guillain-Barré Syndrome cases highlights the importance of vigilant public health monitoring and response strategies to ensure the safety and health of the population.
US Immigration Policy and Indian Deportations in 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- On January 25, 2025, US Secretary of State Marco Rubio engaged in discussions with Indian External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar regarding the pressing issue of irregular immigration. This dialogue highlighted the significant concern of undocumented Indian immigrants in the United States, with over 20,000 individuals facing deportation as of late 2024. This article delves into the deportation process, appeals, associated costs, and the growing trend of deportations affecting Indian nationals.
Key Takeaways
- The deportation process is initiated due to immigration law violations.
- There are significant costs associated with the deportation of undocumented immigrants.
- India has become a leading country from which citizens are deported, with a notable increase in recent years.
Additional Details
- Deportation Process: Deportation involves the removal of non-citizens from the US for reasons such as criminal activity or visa violations. Non-citizens may be detained prior to deportation, and expedited removal can occur under the US Immigration and Nationality Act for those entering without proper documentation.
- Appeals Against Deportation: Individuals facing deportation can appeal if they fear persecution or wish to seek asylum. A credible fear can lead to formal removal proceedings, allowing for a detailed examination of their case.
- Costs Associated with Deportation: The financial burden can be significant, with options for voluntary departure at personal expense. Deportations are managed by the US Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), which utilizes commercial and charter flights for the process.
- Trends in Deportation: The number of Indian nationals deported has increased in recent years, with 1,616 deported in 2019, rising to 2,312 in 2020, and then experiencing fluctuations down to 1,529 in 2024.
- Reasons for Illegal Migration: Many undocumented Indians seek improved opportunities, primarily originating from Gujarat and Punjab, often traveling through perilous routes like the “donkey route,” which involves navigating several countries before reaching the US.
The rising trend of deportations and the challenges faced by undocumented Indian immigrants are pivotal issues that could potentially affect diplomatic relations between India and the US. Both nations are looking to collaborate on these matters while striving to maintain legal migration pathways and strengthen economic ties as trade dynamics evolve.
India Faces Water Storage Decline
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Recent reports indicate a significant decline in water storage across major reservoirs in India. The Central Water Commission (CWC) has highlighted that water levels have decreased for the twelfth consecutive week. This decline is primarily due to deficient post-monsoon and winter rainfall affecting a substantial part of the country, raising concerns about future water availability for various sectors.
Key Takeaways
- Water storage in 155 major reservoirs has fallen to 66% of total capacity.
- Total current water storage is 119.505 billion cubic meters (BCM) out of a possible 180.852 BCM.
- 83% of India has experienced deficient rainfall from January 1 to January 24.
Additional Details
- Current Water Storage Statistics: The current storage level is higher than last year's and the average of the past decade; however, the ongoing rainfall deficiency poses a serious threat to future water supply.
- Deficient Rainfall Overview: The India Meteorological Department (IMD) reports that over 60% of the country has received scanty or no rainfall, with winter rainfall in January being 62% deficient compared to normal levels.
- Regional Water Storage Analysis:
- Northern Region: 11 reservoirs at 38% capacity; Punjab’s Thein dam at 18% and Himachal Pradesh at 31%.
- Eastern Region: 25 reservoirs at 63.64% capacity; Bihar at 25% and Nagaland at 46%.
- Western Region: 50 reservoirs at 78% capacity; Goa at 93%, Maharashtra at 79%, and Gujarat at 73%.
- Central Region: 26 reservoirs at 69% capacity; Uttar Pradesh below 60% and Madhya Pradesh at 73%.
- Southern Region: 43 reservoirs at 66% capacity; Tamil Nadu at 86%, Andhra Pradesh at 77%, and Telangana at 74%.
- The IMD has forecast below-normal rainfall until February 5, indicating that water storage levels may continue to decline, exacerbating the water crisis.
The ongoing decline in water storage across India underscores the urgent need for effective water management strategies and adequate rainfall to sustain agricultural, industrial, and domestic water needs in the upcoming months.
Silicon Carbide Extraction from Simulated Lunar Soil
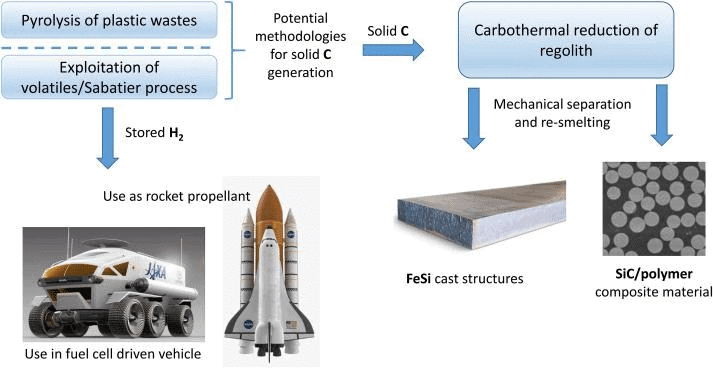 Why in News?
Why in News?
- On January 27, 2025, researchers at IIT Madras achieved a significant breakthrough by successfully extracting silicon carbide from simulated lunar soil. This advancement is crucial for future lunar habitat construction efforts.
Key Takeaways
- Extraction of silicon carbide from lunar regolith has potential applications in building moon habitats.
- Simulated lunar soil is used for research due to the limited availability of actual lunar soil samples.
Additional Details
- Lunar Regolith: The surface layer of loose material on the moon, which is challenging to obtain in its natural form. Only a small quantity of real lunar soil has been returned to Earth, necessitating the use of simulated soil for research.
- Extraction Process: Researchers combined highland regolith simulant with methane at high temperatures to produce silicon carbide. The methane can be sourced from carbon dioxide exhaled by astronauts, which is processed at the International Space Station (ISS) using the Sabatier process.
- Properties of Silicon Carbide: Known for its exceptional hardness, silicon carbide (SiC) is a synthetic crystalline compound with high thermal conductivity, strength at elevated temperatures, and low thermal expansion. It is primarily utilized in abrasives and high-temperature applications.
- Applications of Silicon Carbide: SiC has diverse applications including use in industrial furnaces, wear-resistant components for pumps, rocket engines, and as a substrate for light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Its hardness makes it an effective abrasive, ranking just below diamond and cubic boron nitride.
This successful extraction of silicon carbide not only opens up possibilities for lunar construction but also enhances our understanding of utilizing lunar resources effectively.
|
201 videos|1014 docs|2272 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 31st January 2025) Part - 1 - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What is the economic impact of breast cancer in India? |  |
| 2. What are the implications of the US withdrawal from the OECD Global Tax Deal for India? |  |
| 3. What are industrial clusters in India and their role in the WEF’s Transition Initiative? |  |
| 4. How does Sebi's new when-listed trading platform benefit investors? |  |
| 5. What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome, and why is there a rise in cases in Maharashtra? |  |
















