Science and Technology: January 2025 UPSC Current Affairs | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
India Joins UN Panel on Big Data

Why in News?
India's recent induction into the United Nations Statistical Council (UNSC) has resulted in its membership in the United Nations Committee of Experts on Big Data and Data Science for Official Statistics (UN-CEBD). This development underscores India's increasing influence in the realm of global statistical frameworks.
Key Takeaways
- India is now a member of the UN-CEBD, enhancing its role in global statistics.
- The UN-CEBD was established to utilize big data and data science for improving official statistical systems.
Additional Details
- About UN-CEBD: This committee is a specialized body under the United Nations, formed in 2014. Its purpose is to harness big data and data science to strengthen global statistical systems.
- Members: The committee consists of 31 member states, including India, and 16 international organizations.
- Objectives:
- Investigate the role of big data in tracking progress toward Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Tackle challenges related to the use of non-traditional data sources for official statistics.
- Governance:
- Advisory Board: This board manages the UN-CEBD and meets approximately four times a year to review its work and offer strategic guidance.
- UN Bureau: This body oversees daily operations and administrative tasks.
- Key Functions:
- Strategic Coordination: Provides vision and direction for a global program using big data in official statistics, particularly for the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- Promotion of Big Data Use: Encourages the practical application of big data and addresses associated challenges while leveraging existing frameworks.
- Capacity Building: Aims to enhance capabilities through training and technical assistance for member nations.
- Building Public Trust: Works to establish public confidence in the use of big data for official statistics.
What is Big Data?
Big data encompasses large and complex datasets that traditional data management systems struggle to efficiently store, process, or analyze. It enables improvements in processes, enhances decision-making, and fosters better product or service development.
India's Big Data Initiatives
- National Data & Analytics Platform (NDAP)
- Big Data Management Policy
- National Data Warehouse on Official Statistics
Drivers of Big Data:
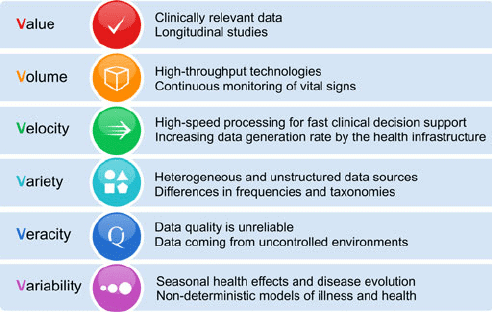
Applications of Big Data:
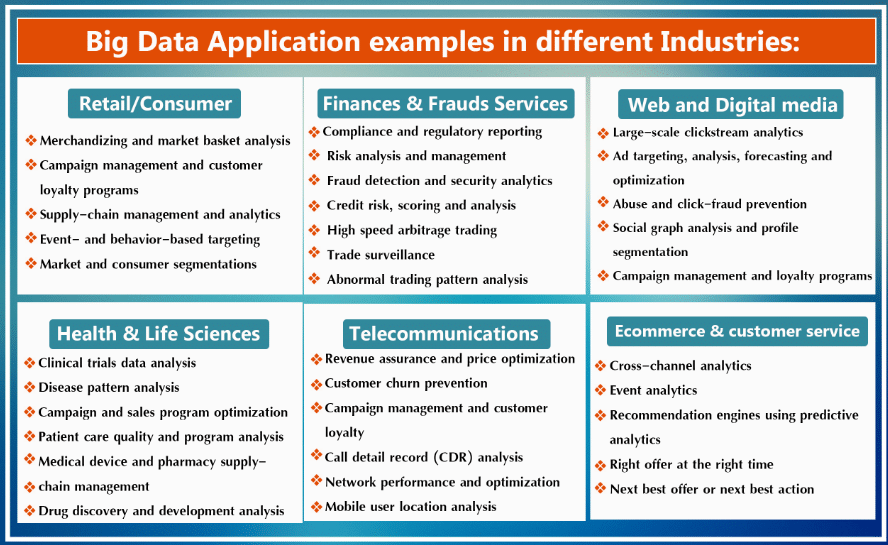
In summary, India's involvement in the UN-CEBD marks a significant step toward leveraging big data for enhancing its statistical systems and contributing to global data initiatives.
Genome India Project: Decoding India’s Genetic Blueprint

Why in News?
The Genome India Project has recently gained attention as Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the completion of the sequencing of the genomes of 10,000 Indians. This is viewed as a major milestone in India's biotechnology sector, with the sequencing data now accessible to researchers through the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC).
Key Takeaways
- The project aims to create a comprehensive catalogue of genetic variations within the Indian population.
- Access to the genomic data will facilitate advancements in personalized medicine and targeted therapies.
- The initiative seeks to identify genetic risk factors for chronic diseases prevalent in India.
Additional Details
- Genome Sequencing: This is the process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism's genome, crucial for understanding genetic information. The most common method used today is next-generation sequencing (NGS).
- Significance of the Project: The Genome India Project allows researchers to study genetic variants specific to Indian populations, which can lead to customized drug therapies and better understanding of diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and cancer.
- Data Security: The project includes a framework for data management ensuring privacy through anonymization and controlled access for research institutes.
In summary, the Genome India Project is a transformative initiative that will significantly enhance the understanding of genetic diversity in India, paving the way for advancements in tailored healthcare solutions for the Indian population.
67th Foundation Day of DRDO

Why in News?
Recently, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) celebrated its Foundation Day on 1st January and paid tributes to former President Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam, known as the Missile Man of India. The event highlighted the significant strides DRDO has made in bolstering India’s defense capabilities.
Key Takeaways
- DRDO was established in 1958, merging several defense organizations.
- Currently operates 41 laboratories and 5 Young Scientist Laboratories.
- The guiding principle is "Balasya Mulam Vigyanam" (Strength lies in science).
- DRDO aims for self-reliance in defense technologies and systems.
Additional Details
- About DRDO: Established in 1958 by merging the Technical Development Establishment (TDEs) of the Indian Army, the Directorate of Technical Development and Production (DTDP), and the Defence Science Organisation (DSO).
- Technology Clusters: DRDO has seven technology domain-based clusters focusing on various defense technologies such as aeronautics, missiles, naval systems, and electronics.
- Key Achievements in 2024: Multiple advanced systems were handed over, including air defense systems and missile systems.
In summary, DRDO has played a pivotal role in enhancing India's defense capabilities and achieving self-reliance in critical technologies, particularly through initiatives like the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP) led by Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam.
Thorium-based Nuclear Energy Production
Why in News?
India's largest power generator, National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) Limited, has recently signed a strategic agreement with US-based Clean Core Thorium Energy (CCTE) to explore the development and deployment of advanced nuclear energy for enriched life (ANEEL), utilizing thorium-based fuel. The ANEEL program involves pressurized heavy water reactors (PHWRs) and is part of India's long-term strategy to leverage its abundant thorium reserves in its three-stage nuclear power program.
Key Takeaways
- NTPC and CCTE are collaborating on thorium-based nuclear energy development.
- ANEEL is a patented nuclear fuel incorporating High Assay Low Enriched Uranium (HALEU).
- The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) aims to integrate thorium into India's nuclear power framework.
Additional Details
- About ANEEL: ANEEL is a patented nuclear fuel that combines High Assay Low Enriched Uranium (HALEU), enriched between 5% and 20%, which is essential for many advanced reactor designs. Currently, HALEU is produced primarily in Russia and China, with limited production in the US.
- ANEEL fuel is compatible with existing PHWRs, which are integral to India's nuclear power infrastructure, consisting of 22 operational reactors with a total capacity of 6780 MWe.
- ANEEL provides an easier and quicker alternative for deploying thorium by leveraging imported HALEU, in contrast to India's traditional method of creating thorium blankets around uranium or plutonium reactors.
- Benefits: The ANEEL fuel boasts a burn-up efficiency of 60,000 MW-days per tonne, significantly reducing operational costs and waste volume in comparison to conventional natural uranium.
- Thorium and spent ANEEL fuel are non-weaponizable, alleviating proliferation concerns for international uranium suppliers.
- Economic and Environmental Impact: The use of ANEEL fuel aligns with India's clean energy goals and supports global commitments to enhance nuclear capacity.
- India's nuclear strategy, based on its three-stage program, aims to utilize abundant thorium reserves for sustainable energy generation. The collaboration with CCTE signifies a promising future for efficient, low-waste nuclear power.
- Despite challenges, thorium presents significant potential in addressing India's energy requirements.
Mains Question
Q: Discuss the significance of thorium-based nuclear reactors in India’s energy strategy. How does the 3-stage nuclear power program align with this objective?
India as Global Hub For Data Centres

Why in News?
India's data centre sector is experiencing remarkable growth, with expectations to double its capacity by FY27. This expansion is largely fueled by factors such as digitalization, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI), the deployment of 5G, and the introduction of data localization laws. However, the sector faces challenges including infrastructure deficits, the necessity for sustainable energy solutions, and competition from international players like China.
Key Takeaways
- India's data centre capacity is projected to increase significantly, presenting vast growth opportunities.
- Challenges such as infrastructure constraints and regional disparities need addressing for sustainable growth.
- Key drivers for growth include digitalization, AI, 5G, and regulatory mandates.
Additional Details
- What are Data Centres: Data centres are specialized facilities designed to store, manage, and process substantial amounts of electronic data. They house critical Information Technology (IT) components, including servers, storage devices, and networking equipment, alongside systems for cooling, power supply, and security.
- Components of a Data Centre:
- Servers and Storage Systems: Handle workloads for hosting websites and cloud storage.
- Networking Equipment: Includes routers, switches, and firewalls for communication.
- Power Supply Systems: Ensures uninterrupted power with UPS and generators.
- Cooling Systems: Necessary to prevent overheating of servers through air conditioning or liquid cooling.
- Security Infrastructure: Encompasses both physical and cybersecurity measures to protect against data breaches.
- Current Status of Data Centres in India: India's data centre market is anticipated to grow from USD 4.5 billion in 2023 to USD 11.6 billion by 2032, indicating a CAGR of 10.98%.
- Geographical Distribution: Over 50% of India's data centre capacity is in Mumbai, with emerging hubs in Ahmedabad, Pune, and Vizag.
Wildfires in California
- The US government has declared a state of emergency in Los Angeles due to the rapid spread of wildfires, which have engulfed nearly 3,000 acres of land.
What are Wildfires?
- A wildfire is an uncontrolled fire that occurs in a natural area like a forest, grassland, or prairie.
- Wildfires can be caused by natural events, such as lightning and volcanic eruptions, or by human activities, such as unattended campfires, discarded cigarettes, arson, and slash-and-burn farming.
Factors Causing Wildfires
Anthropogenic Activities:
- Increased development near forested areas, known as the Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI), raises the risk of wildfires due to human activities.
- Careless actions such as illegal campfires, bonfires, or using fireworks during dry conditions contribute to fire risks.
- Additionally, the loss of forests reduces natural fire barriers, further increasing fire risk.
- Dry Winter: Southern California experiences minimal rainfall from October onwards, resulting in extremely dry vegetation that is highly susceptible to burning.
- Santa Ana Winds: These winds are common in California during this season, but this year they are exceptionally strong. When a fire ignites under these dry conditions, the powerful winds cause the flames to grow larger and spread more rapidly.
- Climate Change: Prolonged and more intense dry seasons increase the stress on vegetation due to lack of moisture, which worsens the risk of wildfires.
Impacts of Wildfires
- Toxic Pollutants: Wildfire smoke is laden with harmful pollutants such as PM2.5, NO₂, ozone, and aromatic hydrocarbons. These substances pose serious health risks, particularly respiratory and cardiovascular issues, for vulnerable populations.
- Climate Change Intensification: Wildfires contribute significantly to global warming by releasing large quantities of CO₂ and methane into the atmosphere.
- Social & Economic Losses: Wildfires lead to the destruction of property, infrastructure, and businesses. Communities located in wildfire-prone areas are often forced to evacuate, resulting in the loss of homes and livelihoods.
- Soil and Land Degradation: Wildfires disrupt soil ecosystems by destroying soil organisms and depleting organic matter. This results in increased soil erosion and the loss of fertile land.
Way Forward
- Enhanced Monitoring and Early Warning Systems: There is a need to expand the use of satellite technology and GIS (Geographic Information Systems) tools to improve the early detection and real-time monitoring of wildfires. For instance, the Forest Survey of India has developed VAN AGNI, a portal that provides alerts and real-time data on forest fires.
- Global Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Strengthening international cooperation is crucial for sharing data, research, and best practices in wildfire prevention and response. Forming partnerships between governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and the private sector can facilitate coordinated efforts in fire management.
- Addressing Climate Change: Implementing policies aimed at combating climate change and reducing global temperatures is essential, as these factors contribute to prolonged fire seasons. Additionally, focusing on carbon sequestration strategies, such as forest conservation and reforestation, can help mitigate the long-term impacts of wildfires.
Sovereign AI

Why in News?
Denmark has become the latest country to actively pursue sovereign AI, in a bid to boost domestic research and competitiveness. Following this example and leveraging the momentum of Digital India, India’s leadership will be instrumental in driving the nation’s Sovereign AI ambition.
What is Sovereign AI?
- Sovereign AI refers to a nation’s autonomous ability to develop, deploy, and regulate Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies that align with its unique data, values, and governance priorities.
- It ensures national control over AI systems, protecting economic and national security interests while fostering innovation.
Key Features of Sovereign AI include:
- Self-reliance: Develops AI systems tailored to national requirements, ensuring minimal dependency on external technologies.
- National Security: Protects critical data and infrastructure from external threats or misuse.
- Cultural Alignment: Embeds a nation’s values, language, and societal norms into AI frameworks.
- Global Competitiveness: Enhances economic growth and innovation through domestic AI capabilities.
About the Proposed AI Strategy for India (GovAI Private AI = Sovereign AI):
- India’s proposed AI strategy focuses on leveraging Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) like Aadhaar and UPI to develop GovAI (Government AI) for efficient and predictive public services.
- It emphasizes data sovereignty, transforming anonymized DPI data into AI training material while ensuring national control.
- The strategy promotes public-private collaboration to build domain-specific Small Language Models (SLMs) that evolve into advanced Large Language Models (LLMs).
- Skill development through Regional Centres of Excellence (RCoE) aims to create a robust AI talent pool.
- This strategy aligns with India’s vision of becoming a global leader in trusted and inclusive AI, enhancing economic growth and national security.
India’s Initiatives for Sovereign AI:
- India’s initiative for Sovereign AI builds on its Digital India framework, leveraging platforms like Aadhaar, UPI, and DigiLocker to create GovAI (Government AI) for efficient public services.
- It utilizes DPI platforms such as Aadhaar, UPI, DigiLocker, and CoWIN.
Domain-Specific AI Models that India seeks to build:
- Builds Small Language Models (SLMs) for specific public service areas like education, healthcare, agriculture, and social welfare.
- SLMs evolve into Large Language Models (LLMs) for advanced, intersectional governance insights.
- The India Datasets Programme transforms anonymized data into resources for AI training while ensuring data sovereignty.
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Science and Technology: January 2025 UPSC Current Affairs - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the significance of India joining the UN panel on Big Data? |  |
| 2. What is the Genome India Project and its objectives? |  |
| 3. What are the key achievements celebrated on the 67th Foundation Day of DRDO? |  |
| 4. How does thorium-based nuclear energy production benefit India? |  |
| 5. Why is India being considered a global hub for data centres? |  |
















