The atomic number of carbon is 6, and it forms covalent bonds by sharing electrons to achieve noble gas configuration. In a demonstration, the teacher explained how methane (CH₄) is formed by the sharing of electrons between one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms, resulting in a tetravalent structure.
(a) Identify the number of valence electrons in a carbon atom. (1 mark)
(b) Write the electron dot structure for methane and explain the type of bond present in it. (2 marks)
(c) Why are covalent compounds generally poor conductors of electricity? (1 mark)
OR
(c) How does carbon attain a stable electronic configuration? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) Carbon has 4 valence electrons.
(b) Electron dot structure of methane (CH₄): Carbon shares one electron with each of the four hydrogen atoms, forming single covalent bonds.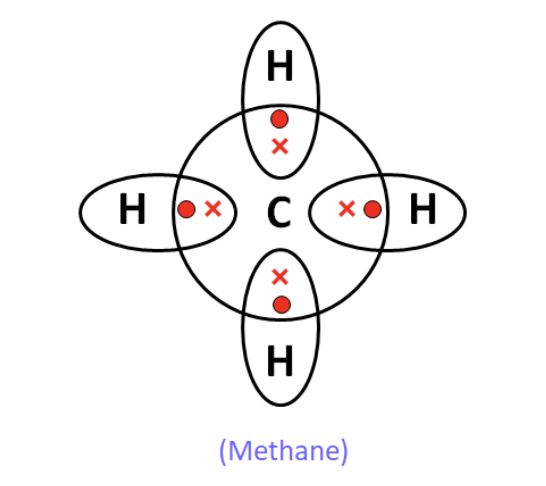
(c) Covalent compounds do not produce free ions, making them poor conductors of electricity.
OR
(c) Carbon attains stable configuration by sharing electrons with other atoms to achieve octet configuration.
Q2: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
The teacher explained structural isomers to students in class. She gave butane (C₄H₁₀) as an example, which has two possible structures: n-butane and isobutane.
(a) Identify the term used for compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures. (1 mark)
(b) Draw the possible structural isomers of butane. (2 marks)
(c) How do structural isomers differ in their physical properties? (1 mark)
OR
(c) Give one more example of a compound that exhibits structural isomerism. (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) Structural isomers compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures are known as structural isomers.
(b) Structures: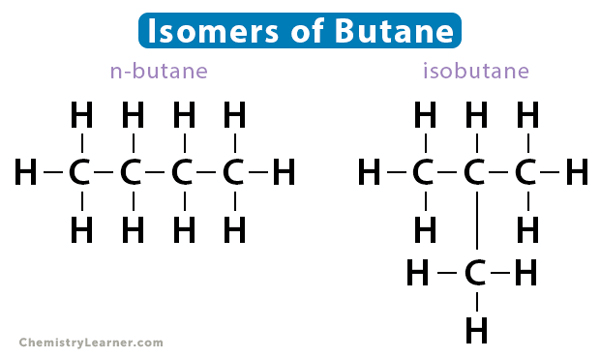
(c) Structural isomers have different boiling points and melting points due to variations in molecular structure.
OR
(c) Pentane (C₅H₁₂) also exhibits structural isomerism.
Q3: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
A chemistry teacher explained the concept of homologous series. She gave examples of alkanes, alkenes, and alcohols and showed that successive members of the series differ by a CH₂ unit and exhibit gradation in physical properties.
(a) Identify the functional group present in alcohols. (1 mark)
(b) Explain the term homologous series with an example. (2 marks)
(c) Why do members of a homologous series show similar chemical properties? (1 mark, )
Ans: (a) –OH (Hydroxyl group)
(b) Homologous series: A series of compounds with the same functional group and similar chemical properties, where successive members differ by a CH₂ unit.
Example: Methanol (CH₃OH), Ethanol (C₂H₅OH), Propanol (C₃H₇OH).
(c) Members of a homologous series have the same functional group, giving them similar chemical properties.
Q4: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
In a laboratory experiment, students burned methane (CH₄) in the presence of oxygen and observed that carbon dioxide and water were formed with the release of heat and light.
(a) Identify the type of reaction taking place during the combustion of methane. (1 mark)
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for the combustion of methane. (2 marks)
(c) Why is complete combustion of fuels preferred over incomplete combustion? (1 mark)
OR
(c) What are the products of incomplete combustion of carbon compounds? (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) Combustion reaction
(b) Balanced equation: CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O + Heat
(c) Complete combustion is preferred because it produces maximum energy and no harmful by-products.
OR
(c) Incomplete combustion produces carbon monoxide (CO) and soot (C), which are harmful pollutants.
Q5: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
A teacher demonstrated the cleaning action of soap by dissolving soap solution in water and adding oil droplets. She explained that micelles are formed, where the hydrophilic head of the soap interacts with water and the hydrophobic tail interacts with oil, trapping the oily dirt.
(a) Identify the type of structure formed by soap in water. (1 mark)
(b) Explain how micelles help in cleaning oily dirt. (2 marks)
(c) Why do detergents work better than soaps in hard water? (1 mark)
OR
(c) Name the two parts of a soap molecule and their roles. (1 mark)
Ans:
(a) Micelle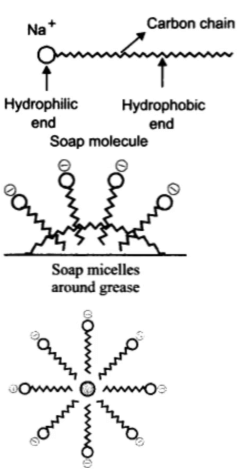 (b) Micelles: The hydrophobic tail traps the oily dirt inside the cluster, while the hydrophilic head interacts with water, forming an emulsion and pulling out the dirt.
(b) Micelles: The hydrophobic tail traps the oily dirt inside the cluster, while the hydrophilic head interacts with water, forming an emulsion and pulling out the dirt.
(c) Detergents do not form insoluble precipitates with calcium and magnesium ions in hard water, making them more effective.
OR
(c) Soap molecules have a hydrophilic head (interacts with water) and a hydrophobic tail (interacts with oil).


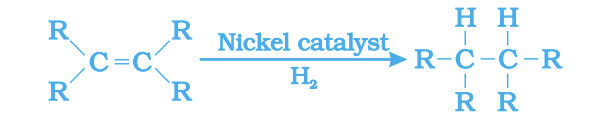 For oils: Unsaturated oil + H₂ → Saturated fat (in presence of Ni)
For oils: Unsaturated oil + H₂ → Saturated fat (in presence of Ni)














