Case Based Questions: The Human Eye and the Colourful World | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Q1: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
The triangular glass prism is a transparent object made of glass having two triangular ends and three rectangular sides. The opposite faces of a triangular glass prism are not parallel to one another. When a ray of light passes through a prism, it bends towards the base of prism. But when white light consisting of seven colours falls on a glass prism, each colour in it is refracted by a different angle, with the result that seven colours are spread out to form a spectrum. The red colour is deviated the least and the violet colour is deviated the maximum.i. Angle of deviation in a prism is the angle between (1 mark)
(a) incident and reflected ray
(b) reflected and emergent ray
(c) incident and emergent ray
(d) incident and refracted ray
ii. Which of the following phenomenon of light are involved in the formation of a rainbow? (1 mark)
(a) Reflection, refraction and dispersion
(b) Refraction, dispersion and total internal reflection
(c) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
(d) Dispersion, scattering and total internal reflection
iii. Which of the following coloured light has the least speed in glass prism? (1 mark)
(a) Violet
(b) Yellow
(c) Red
(d) Green
iv. The colour of light which undergoes least bending on passing through the glass prism is: (1 mark)
(a) green
(b) violet
(c) red
(d) blue
Or
iv. Based on the different orientations of a prism ABC given below, in which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky? (1 mark)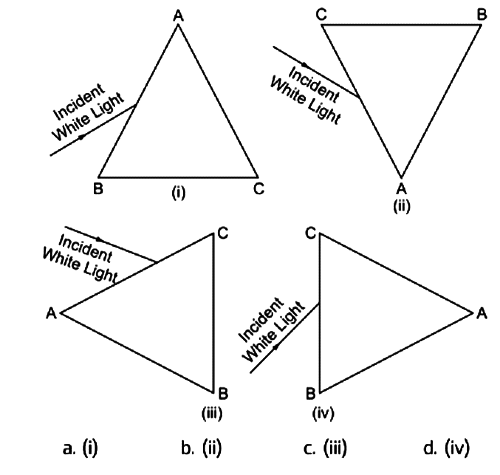
Ans:
i. (c) incident and emergent ray
ii. (c) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
iii. (a) Violet
iv. (c) red
Or
iv. (b) (ii)
Q2: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
We know that when light goes from one medium to another medium having different optical densities, then refraction of light rays (or bending of light rays) takes place. Now, in the atmosphere, we have air everywhere. But all the air in the atmosphere is not at the same temperature. Some of the air layers of the atmosphere are cold whereas other air layers of the atmosphere are comparatively warm (or hotter). Now the cooler air layers of the atmosphere behave as optically denser medium for light rays whereas the warmer air layers (or hotter air layers) of the atmosphere behave as optically rarer medium. for the light rays. So, in the same atmosphere we have air layers having different optical densities. And when light rays pass through the atmosphere having air layers of different optical densities, then refraction of light takes place. The refraction of light caused by the Earth's atmosphere (having air layers of varying optical densities) is called atmospheric refraction.
i. With respect to atmospheric refraction which of the following point distinguish between cold air and hot air? (1 mark)
(a) Cold air is denser than hot air
(b) Hot air is lighter than cold air
(c) Cold air has higher refractive index than hot air.
(d) All of the above
ii. What is the reason behind twinkling of Stars? (1 mark)
(a) Dispersion of star light
(b) Reflection of star light
(c) Refraction of star light
(d) All of the above
iii. Why Sun appears flattened during sunrise and sunset? (1 mark)
(a) Because Sun is closer to Earth
(b) Because Earth is rotating
(c) Because Earth is revolving
(d) Because of atmospheric refraction
iv. How much time from sunrise to sunset is lengthened because of atmospheric refraction? (1 mark)
(a) 4 hours
(b) 2 minutes
(c) 4 minutes
(d) 2 hours
Or
iv. When light rays from Stars enter into Earth's atmosphere, it travels from: (1 mark)
(a) denser to rarer medium
(b) rarer to denser medium
(c) rarer medium to vacuum
(d) denser medium to vacuum
Ans:
i. (d) All of the above Cold air is denser and heavier than hot air. Also, cold air has higher refractive index than hot air. Hence, all are true.
ii. (c) refraction of star light
iii. (d) The Sun appears flattened because of atmospheric refraction.
iv. (c) The time from sunrise to sunset is lengthened by 4 minutes.
Or
iv.(b) When light rays from Stars enter into Earth's atmosphere, it travel from rarer to denser medium.
Q3: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
Different organs of human eye are labelled as A to F.
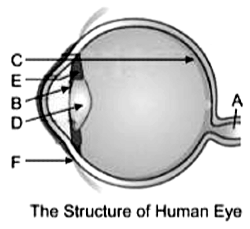 i. Name the parts A, B, C, D and E. (1 mark)
i. Name the parts A, B, C, D and E. (1 mark)
ii. What is the nature of image formed on the retina of the eye? (1 mark)
iii. When light rays enter the eye, most of the refraction occurs at the: (1 mark)
(a) part D
(b) part B
(c) outer surface of part F
(d) part E
iv. Define power of accommodation. (1 mark)
Or
iv. What is aqueous humour and vitreous humour? (1 mark)
Ans:
i. A-Optic nerve; B-Iris; C-Retina; D-Crystalline lens; E-Ciliary muscles
ii. Real and inverted
iii. (c) outer surface of part F
iv. The ability of eye lens to adjust its focal length is called power of accommodation.
Or
iv. The space between cornea and eye lens is filled with a watery liquid called aqueous humour, whereas vitreous humour is a transparent jelly-like substance filled between eye lens and retina.
Q4: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
When light goes from one medium to another medium having different optical densities, then refraction of light rays takes place. All the air in the atmosphere is not at the same temperature. Some of the air layers of the atmosphere are cold (optically denser) whereas other layers of the atmosphere are comparatively warm (optically rarer). So, in the atmosphere we have air layers having different optical densities. Atmospheric refraction is the deviation of light from a straight line as it passes through the atmosphere due to the variation in air density. Such refraction can raise or lower, or stretch or shorten the images of distant objects and can also make distant objects appear to twinkle or shimmer.
i. What is atmospheric refraction? (1 mark)
ii. What causes atmospheric refraction? (1 mark)
iii. Name the effects produced by atmospheric refraction. (1 mark)
iv. Which has more refractive index-hot air or cold air? (1 mark)
Or
iv. How much time from sunrise to sunset is lengthened because of atmospheric refraction? (1 mark)
Ans:
i. The refraction of light caused by the Earth's atmosphere (having air layers of varying optical densities) is atmospheric refraction.
ii. It is caused due to the varying optical densities of different layers of Earth's atmosphere.
iii. Twinkling of Stars, the Stars seem higher than they actually are and advanced sunrise and delayed sunset are some phenomenon produced by atmospheric refraction.
iv. The refractive index of hot air is less than cold air because cold air is denser than hot air.
Or
iv. The sunrise appears 2 minutes early and sunset appears 2 minutes later due to atmospheric refraction. So, total time lengthened is 4 minutes.
Q5: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
A prism is a transparent refracting medium bounded by two plane surfaces inclined to each other at a certain angle. The refraction of light through a prism follows the laws of refraction. In the prism, refraction takes place on its refracting surface, meaning when the light enters the prism and when the light leaves the prism. The refraction through a prism is shown here.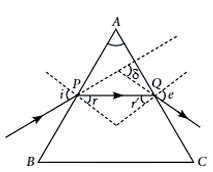 Here, ∠A is the angle of the prism, ∠i is the angle of incidence of face AB, and ∠e is the angle of emergence at the other face AC.The incident ray suffers a deviation or bending through an angle δ due to the refraction through the prism. This angle is called the angle of deviation, as shown in the figure.∠i + ∠e = ∠δ + ∠A
Here, ∠A is the angle of the prism, ∠i is the angle of incidence of face AB, and ∠e is the angle of emergence at the other face AC.The incident ray suffers a deviation or bending through an angle δ due to the refraction through the prism. This angle is called the angle of deviation, as shown in the figure.∠i + ∠e = ∠δ + ∠Ai. The angle between the two refracting surfaces of a prism is called (1 mark)
(a) angle of prism
(b) angle of incidence
(c) angle of deviation
(d) angle of emergence
ii. The angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called (1 mark)
(a) angle of emergence
(b) angle of deviation
(c) angle of incidence
(d) none of these
iii. When a ray is refracted through a prism, then (1 mark)
(a) ∠i = ∠δ
(b) ∠i = ∠e + ∠δ
(c) ∠δ = ∠e
(d) ∠i > ∠r
iv. The angle of deviation depends on (1 mark)
(a) refractive index of prism
(b) angle of incidence
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Or
iv. The rectangular surfaces of a prism are known as (1 mark)
(a) reflecting surfaces
(b) dispersing surfaces
(c) refracting surfaces
(d) none of these
Ans:
i. (a) The angle between the two refracting surfaces of a prism is called the angle of prism.
ii. (b): The angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called the angle of deviation.
iii. (d): As the ray of light enters from a rarer medium (air) to a denser medium (glass), the angle of incidence is more than the angle of refraction.
iv. (c) The greater the refractive index, the greater the angle of deviation, and it also depends on the refractive index of the prism.
Or
iv. (c) The refraction of light takes place through rectangular surfaces.
Q6: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
When white light is incident on one refracting surface of the prism, the light splits up into constituent colours—violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red. The process of splitting of white light into its seven constituent colours is called dispersion. When the dispersed white light is made to fall on a screen, we get the band of seven colours called the spectrum of white light.Red colour bends the least on passing through the prism, and violet colour bends through the maximum angle on passing through the prism.
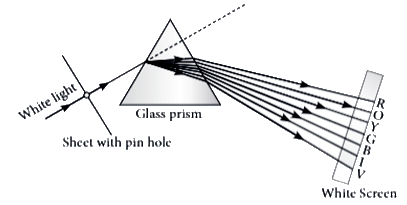
i. The splitting of white light can be done by (1 mark)
(a) lens
(b) prism
(c) mirror
(d) none of these
ii. Which property of light is used by a prism to form a spectrum?(1 mark)
(a) Reflection
(b) Refraction
(c) Dispersion
(d) Scattering
iii. Which of the following dispersion is correct? (1 mark) iv. When a red light passes through a prism, it (1 mark)
iv. When a red light passes through a prism, it (1 mark)
(a) will not split
(b) will split into seven colours
(c) will split into white colour
(d) will split into many different colours
Or
iv. The spectrum produced by the white light by a prism is called (1 mark)
(a) pure spectrum
(b) impure spectrum
(c) monochromatic spectrum
(d) none of these
Ans:
i. (b)
ii. (b)
iii. (a) The deviation is maximum for violet and minimum for red, so option (a) is correct.
iv. (a) The red light has a single wavelength, and when it enters a prism, it will not split into other different colours.
Or
iv. (b) The boundaries of colours in the spectrum produced by the prism are not sharp, so the spectrum is impure.
Q7: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
Light of all colours travels at the same speed in a vacuum for all wavelengths. But in any transparent medium (glass or water), the light of different colours travels at different speeds for different wavelengths. That means the refractive index of a particular medium is different for different wavelengths. As there is a difference in their speeds, the light of different colours bends at different angles. The speed of violet colour is maximum, and the speed of red colour is minimum in glass, so the red light deviates least and violet colour deviates most. Hence, the higher the wavelength of a colour of light, the smaller the refractive index and the less the bending of light.λᵣ > λᵥ and rₙ < vᵣ. Also, frequency, v = c / λ.
i. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of light of different colours of white light in air? (1 mark)
(a) Red light moves fastest.
(b) Blue light moves faster than green light.
(c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed.
(d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light.
ii. Which of the following is the correct order of wavelength? (1 mark)
(a) Red > Green > Yellow
(b) Red > Violet > Green
(c) Yellow > Green > Violet
(d) Red > Yellow > Orange
iii. Which of the following is the correct order of the speed of light in glass? (1 mark)
(a) Red > Green > Blue
(b) Blue > Green > Red
(c) Violet > Red > Green
(d) Green > Red > Blue
iv. Which colour has the maximum frequency?(1 mark)
(a) Red
(b) Violet
(c) Blue
(d) Green
Or
iv. Which of the following is the correct order of the angle of deviation? (1 mark)
(a) Red > Green > Blue
(b) Blue > Yellow > Orange
(c) Orange > Red > Green
(d) Blue > Green > Violet
Ans:
i. (c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed in air.
ii. (c) The increasing order of wavelength of visible spectrum is
Violet < Indigo < Blue < Green < Yellow < Orange < Red
So, the correct order is
Yellow > Green > Violet
iii. (b) The more be the wavelength, more be the speed.
iv. (b) Frequency is inversely proportional to the wavelength. Violet has minimum wavelength among all these colours, so violet has maximum frequency.
Or
iv. (b) The angle of deviation is more for more refractive index.
Q8: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
The spreading of light by the air molecules is called scattering of light. The light having the least wavelength scatters more. The sun appears red at sunrise and sunset, and the appearance of the blue sky is due to the scattering of light. The colour of the scattered light depends on the size of particles. The smaller the molecules in the atmosphere, the more they scatter smaller wavelengths of light. The amount of scattering of light depends on the wavelength of light.When light from the sun enters the earth’s atmosphere, it gets scattered by the dust particles and air molecules present in the atmosphere. The path of sunlight entering a dark room through a fine hole is seen because of the scattering of sunlight by the dust particles present in its path inside the room.
i. To an astronaut in a spaceship, the colour of Earth appears (1 mark)
(a) red
(b) blue
(c) white
(d) black
ii. At the time of sunrise and sunset, the light from the sun has to travel (1 mark)
(a) longest distance of the atmosphere
(b) shortest distance of the atmosphere
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) can’t say
iii. The colour of the sky appears blue, it is due to the (1 mark)
(a) refraction of light through the atmosphere
(b) dispersion of light by air molecules
(c) scattering of light by air molecules
(d) all of these
iv. At the time of sunrise and sunset (1 mark)
(a) Blue colour is scattered and red colour reaches our eye
(b) Red colour is scattered and blue colour reaches our eye
(c) Green and blue are scattered and orange reaches our eye
(d) None of these
Or
iv. The danger signs are made red in colour because (1 mark)
(a) the red light can be seen from the farthest distance
(b) the scattering of red light is least
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Ans:
i. (b) Light is scattered by the air molecules present in atmosphere.
ii. (a) As the distance between us and sun is more at the time of sunrise and sunset.
iii. (c) Due to the more scattering of blue colour by molecules of air.
iv. (a) Red light being of largest wavelength, blue scatters more, red scatters least.
Or
iv. (c) Scattering is least but velocity of red light is more.
Q9: Read the Source below and answer the questions that follow:
Atmospheric refraction is the phenomenon of bending of light on passing through earth’s atmosphere. As we move above the surface of earth, density of air goes on decreasing. Local conditions like temperature etc. also affect the optical density of earth’s atmosphere. On account of atmospheric refraction, stars seen appear higher than they actually are; advanced sunrise; delayed sunset, oval appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset; stars twinkle, planets do not.
i. Due to atmospheric refraction, apparent length of the day (1 mark)
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) remains the same
(d) all of these
ii. Apparent position of the star appears raised due to (1 mark)
(a) atmospheric refraction
(b) scattering of light
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
iii. The sun appears oval shaped or flattened due to (1 mark)
(a) dispersion
(b) scattering
(c) atmospheric refraction
(d) cannot say
iv. Twinkling of stars and non-twinkling of planets is accounted for by (1 mark)
(a) scattering of light
(b) dispersion of light
(c) atmospheric refraction
(d) none of these
Or
iv. In absence of atmosphere, the colour of sky appears (1 mark)
(a) blue
(b) black
(c) red
(d) yellow
Ans:
i. Due to atmospheric refraction, apparent length of the day increases by 4 minutes.
ii. (a) Apparent position of the star appears raised due to atmospheric refraction.
iii. (c)
iv. (c) Twinkling of stars and non-twinkling of planets is on account of atmospheric refraction.
Or
iv. (b) Due to no scattering of light.
Q10: Read the Source below and answer the questions that follow:
The phenomenon of dispersion occurs when white light splits into its constituent colors while passing through a prism. This is due to different refractive indices for different wavelengths of light. The order of colors observed in the spectrum is Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red (VIBGYOR). The formation of a rainbow is a natural example of dispersion, caused by refraction, dispersion, and total internal reflection of sunlight in water droplets. The scattering of light is responsible for various atmospheric effects, such as the blue color of the sky and the reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset. The Tyndall effect explains why the sky appears blue due to the preferential scattering of shorter wavelengths by air molecules.
i. The splitting of white light into its constituent colors is called: (1 mark)
(a) Refraction
(b) Dispersion
(c) Scattering
(d) Reflection
ii. The rainbow is formed due to: (1 mark)
(a) Reflection and dispersion
(b) Refraction and dispersion
(c) Dispersion and total internal reflection
(d) Both (b) and (c)
iii. The sky appears blue due to: (1 mark)
(a) Dispersion of light
(b) Refraction of light
(c) Scattering of shorter wavelengths
(d) Reflection of sunlight
iv. The sun appears reddish during sunrise and sunset because: (1 mark)
(a) Red light has the longest wavelength and is scattered least
(b) The sun emits more red light in the morning and evening
(c) Blue and violet light are absorbed by the sun
(d) The atmosphere blocks all colors except red
Or
iv. The color of the sky in the absence of atmosphere would be: (1 mark)
(a) Blue
(b) Black
(c) Red
(d) Yellow
Ans:
i. (b) The splitting of white light into its constituent colors is called dispersion.
ii. (d) The rainbow is formed due to refraction, dispersion, and total internal reflection.
iii. (c) The sky appears blue due to the scattering of shorter wavelengths by air molecules.
iv. (a) The sun appears reddish during sunrise and sunset because red light has the longest wavelength and is scattered least.
Or
iv. (b) The sky appears black in the absence of atmosphere due to no scattering of light.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Case Based Questions: The Human Eye and the Colourful World - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the main parts of the human eye and their functions? |  |
| 2. How does the human eye perceive color? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the lens in the human eye? |  |
| 4. What are common vision problems associated with the human eye? |  |
| 5. How does light travel through the eye to create an image? |  |

















